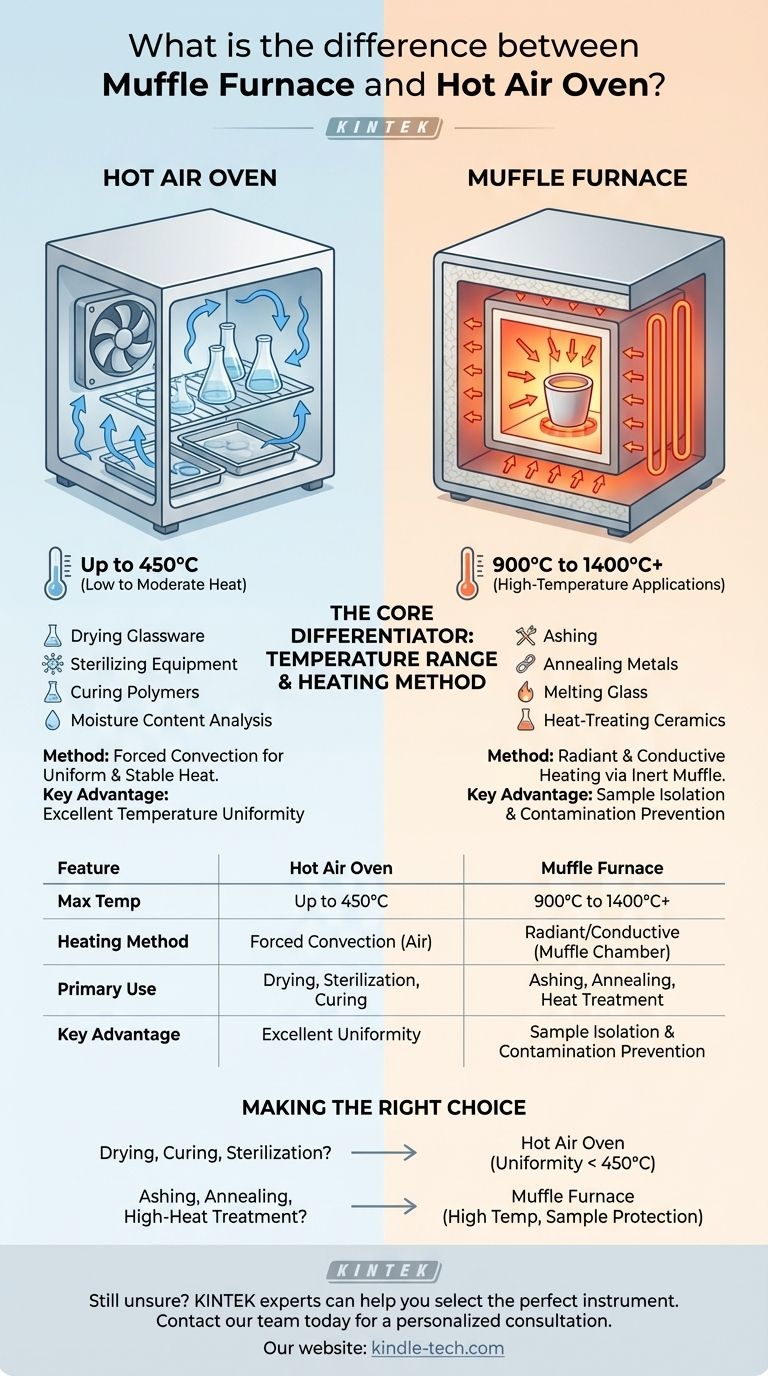
The primary difference between a muffle furnace and a hot air oven lies in their maximum operating temperature, method of heat transfer, and the specific applications they are designed for. A hot air oven provides gentle, uniform heat up to around 450°C, while a muffle furnace is built for intense, high-temperature applications, often exceeding 900°C.
The choice between these two instruments is not about which is superior, but which is the correct tool for the task. A hot air oven is for uniform, low-temperature drying and heating, whereas a muffle furnace is for high-temperature material transformation like ashing or heat treatment.

The Core Differentiator: Temperature Range
The most significant distinction is the temperature each instrument can achieve and sustain. This capability directly dictates their use cases in a lab or industrial setting.
Hot Air Ovens: Low to Moderate Heat
A hot air oven typically operates in a range from slightly above ambient temperature up to 250°C or 450°C.
This range is ideal for processes like drying glassware, sterilizing equipment, curing polymers, or performing sensitive moisture content analysis where precise, stable, and uniform temperature is critical.
Muffle Furnaces: High-Temperature Applications
A muffle furnace is specifically engineered for high-heat processes, with a standard operating range from 900°C to 1400°C, and some models reaching even higher.
This extreme heat is necessary for applications such as determining the ash content of a sample (ashing), annealing metals, melting glass, or heat-treating ceramic materials.
How They Heat: Mechanism and Impact
The method used to generate and transfer heat is fundamentally different, which affects both uniformity and the types of materials that can be processed.
Hot Air Ovens: Forced Convection
Hot air ovens rely on convection. An internal heating element warms the air, and a fan circulates it throughout the chamber.
This method ensures a highly uniform and stable temperature across the entire interior, preventing hot spots and gently heating the entire surface of the sample.
Muffle Furnaces: Radiant and Conductive Heating
A muffle furnace uses radiant and conductive heat. The heating elements are located outside a separate, inert chamber called the "muffle," which is typically made of high-temperature ceramic.
The elements heat the muffle, which then radiates intense, uniform heat onto the sample inside. This design isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any potential contaminants from combustion, which is critical for analytical purity.
Common Applications and Trade-offs
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each design clarifies which instrument to choose for a specific job.
Uniformity vs. Intensity
A hot air oven provides exceptional temperature uniformity, which is essential for curing or drying processes where the entire sample must be treated equally.
A muffle furnace provides sheer thermal intensity, designed to completely combust, melt, or alter the state of a material.
Sample Protection
The key advantage of the muffle furnace is sample isolation. By separating the sample from the heating source, it prevents contamination, making it essential for quantitative analysis like gravimetric ashing.
Energy and Safety
Due to their extreme operating temperatures, muffle furnaces consume significantly more energy and are built with much heavier insulation. They also demand more stringent safety protocols during operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines the correct instrument.
- If your primary focus is drying, curing, or sterilization: A hot air oven is the correct tool, providing the necessary temperature control and uniformity below 450°C.
- If your primary focus is ashing, annealing, or heat-treating metals: A muffle furnace is required to achieve the necessary high temperatures and protect the sample from contamination.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample: The muffle furnace is essential for its ability to completely incinerate organic material at a controlled high temperature.
Choosing the right instrument begins with a clear understanding of your required temperature and process integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 450°C | 900°C to 1400°C+ |
| Heating Method | Forced Convection (Air) | Radiant/Conductive (Muffle Chamber) |
| Primary Use | Drying, Sterilization, Curing | Ashing, Annealing, Heat Treatment |
| Key Advantage | Excellent Temperature Uniformity | Sample Isolation & Contamination Prevention |
Still unsure which heating equipment is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect instrument—whether it's a precise hot air oven for gentle drying or a high-temperature muffle furnace for demanding ashing processes.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and ensure you get the right tool for your specific goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- At what temperature is it safe to open a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Injury and Equipment Damage
- Does ceramic break with heat? The Real Culprit is Thermal Shock
- What are the applications of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Drug Purity and Quality
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction
- Why is sintering important in ceramic processing? Achieve Dense, High-Performance Ceramic Parts



















