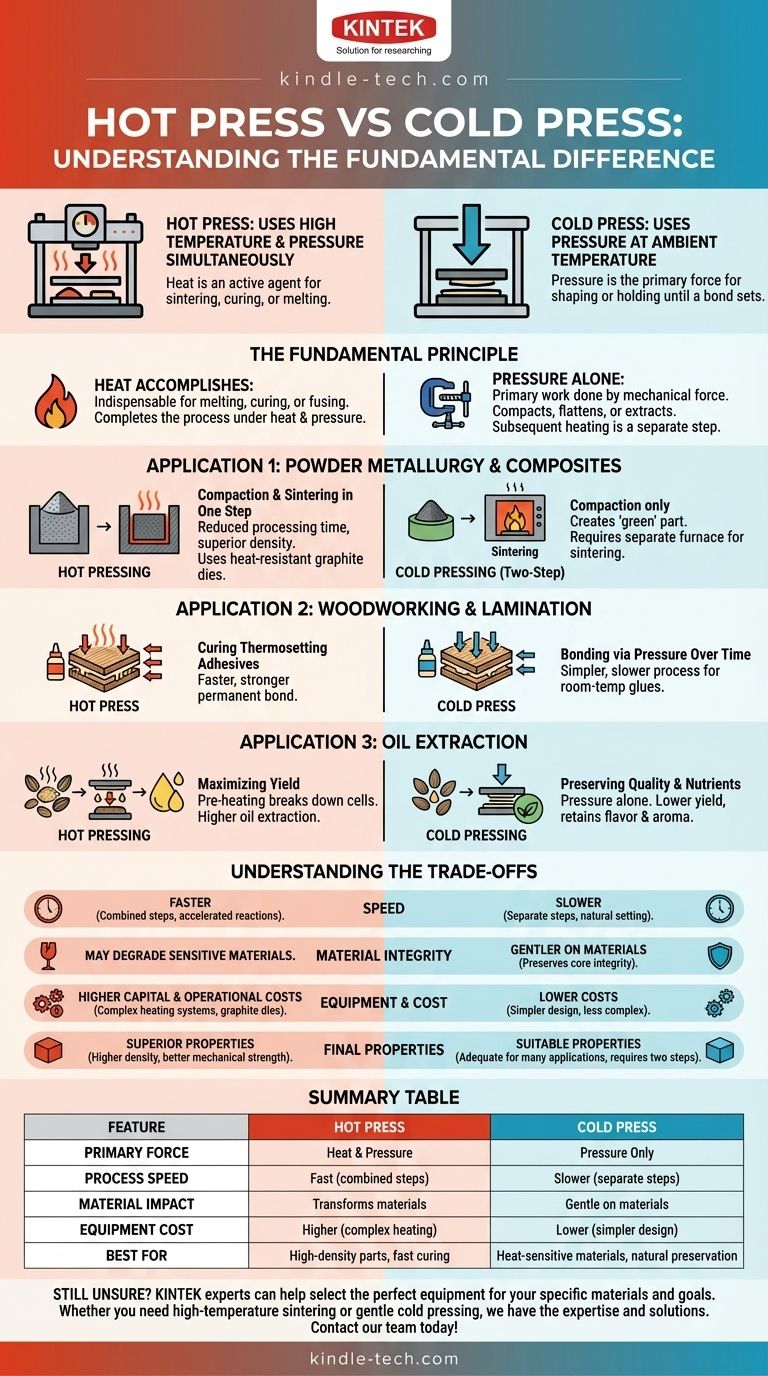
At its core, a hot press uses both high temperature and pressure simultaneously to form or bond materials, while a cold press uses pressure primarily at ambient or room temperature. The specific function of each machine, however, changes dramatically depending on the industry—from metallurgy and woodworking to food processing. Understanding this context is the key to grasping the true difference.
The fundamental distinction is not just the presence of heat, but its purpose. In a hot press, heat is an active agent of transformation, causing materials to sinter, cure, or melt. In a cold press, pressure is the primary force, shaping the material or holding it until a bond sets naturally.

The Fundamental Principle: Heat as an Active Agent
The choice between a hot or cold press is determined by the material's properties and the desired outcome. The core question is whether heat is required to achieve the final state.
### What Heat Accomplishes
In hot pressing, heat is an indispensable part of the process. It might be used to melt solder, cure a thermosetting adhesive, or cause microscopic particles of a metal powder to fuse together. The process is designed to be completed under heat and pressure.
### The Role of Pressure Alone
In cold pressing, the primary work is done by mechanical force. This pressure compacts a powder into a preliminary shape, flattens a wood veneer while glue sets, or squeezes oil from seeds. Any subsequent heating is a completely separate step in a different piece of equipment.
Application 1: Powder Metallurgy and Composites
This is one of the most common technical applications where the distinction is critical. The goal is to turn metal or ceramic powder into a solid, dense object.
### Hot Pressing: Compaction and Sintering in One Step
A hot press combines two processes: compaction (squeezing the powder) and sintering (fusing the particles together with heat). This combined action reduces processing time and often results in a final part with superior density and strength.
Because of the extreme temperatures, the machine's dies are typically made from heat-resistant materials like graphite.
### Cold Pressing: A Two-Step Process
A cold press performs only the first step: compaction. It uses a hardened steel die to press powder into a precisely shaped object called a "green" part.
This "green" part is stable enough to be handled but has not yet achieved its final strength. It must then be moved to a separate furnace for the high-temperature sintering process to fuse the particles.
Application 2: Woodworking and Lamination
In furniture and panel manufacturing, presses are used to bond layers of wood, veneers, or laminates together using adhesives.
### Hot Press: Curing Adhesives for a Faster, Stronger Bond
A hot press is used with thermosetting adhesives, which require heat to cure and create a permanent, rigid bond. The heat dramatically accelerates the curing time, allowing for much faster production cycles in an industrial setting.
### Cold Press: Bonding Through Pressure Over Time
A cold press is used for flattening and bonding components using glues that cure at room temperature. It simply applies uniform pressure across a surface while the adhesive sets naturally. This process is simpler but significantly slower than hot pressing.
Application 3: Oil Extraction
The terms are also used in food production, most notably for extracting oil from seeds and nuts. Here, the trade-off is between quantity and quality.
### Hot Pressing: Maximizing Yield
In hot pressing, the seeds are heated (steamed or fried) before being pressed. This process breaks down the cells more effectively, making it much easier to extract the oil and resulting in a higher yield.
### Cold Pressing: Preserving Quality and Nutrients
Cold pressing involves extracting oil through pressure alone, without pre-heating the seeds. This gentler method produces a lower yield but preserves the oil's natural flavor, aroma, and nutritional content, which can be damaged by heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method requires balancing competing priorities of cost, speed, and final product quality.
### Speed and Efficiency
Hot pressing is almost always faster. By combining steps (like in metallurgy) or accelerating chemical reactions (like curing glue), it significantly shortens production cycles.
### Material Integrity
Cold pressing is gentler on materials. For heat-sensitive products like health-food oils or certain composites, cold pressing is the only way to prevent degradation of the core material.
### Equipment and Cost
Hot pressing systems are more complex and expensive. They require heating elements, advanced temperature controls, and more robust, heat-resistant components like graphite dies, all of which increase capital and operational costs.
### Final Product Properties
In technical applications like metallurgy, hot pressing often produces a superior final product. The simultaneous application of heat and pressure can achieve higher density and better mechanical properties than the two-step cold press and sinter method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application and desired outcome will dictate the correct method.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength in advanced materials: Hot pressing is the superior choice for creating high-performance ceramic or metal parts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simpler metal parts: Cold pressing followed by sintering is often more cost-effective and suitable for mass production.
- If your primary focus is preserving the natural quality of a raw material: Cold pressing is necessary for applications like high-quality oils or processing heat-sensitive composites.
- If your primary focus is speed and strength in industrial bonding: Hot pressing is the standard for curing adhesives quickly in woodworking and laminate production.
Ultimately, the choice depends on whether heat is a necessary ingredient for the transformation you wish to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Press | Cold Press |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Force | Heat & Pressure | Pressure Only |
| Process Speed | Fast (combined steps) | Slower (separate steps) |
| Material Impact | Transforms materials | Gentle on materials |
| Equipment Cost | Higher (complex heating) | Lower (simpler design) |
| Best For | High-density parts, fast curing | Heat-sensitive materials, natural preservation |
Still unsure which press is right for your lab or production needs? The experts at KINTEK can help you select the perfect equipment for your specific materials and goals. Whether you need high-temperature sintering for advanced ceramics or gentle cold pressing for sensitive composites, we have the expertise and equipment to support your success. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment solutions can optimize your processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What technical conditions does a heated hydraulic press provide for PEO batteries? Optimize Solid-State Interfaces
- How does a laboratory hydraulic hot press ensure the quality of PHBV/natural fiber composites? Expert Guide
- What is the role of a laboratory-grade heated hydraulic press in MEA fabrication? Optimize Fuel Cell Performance
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic hot press play in rice husk-based composite boards? Achieve Structural Density



















