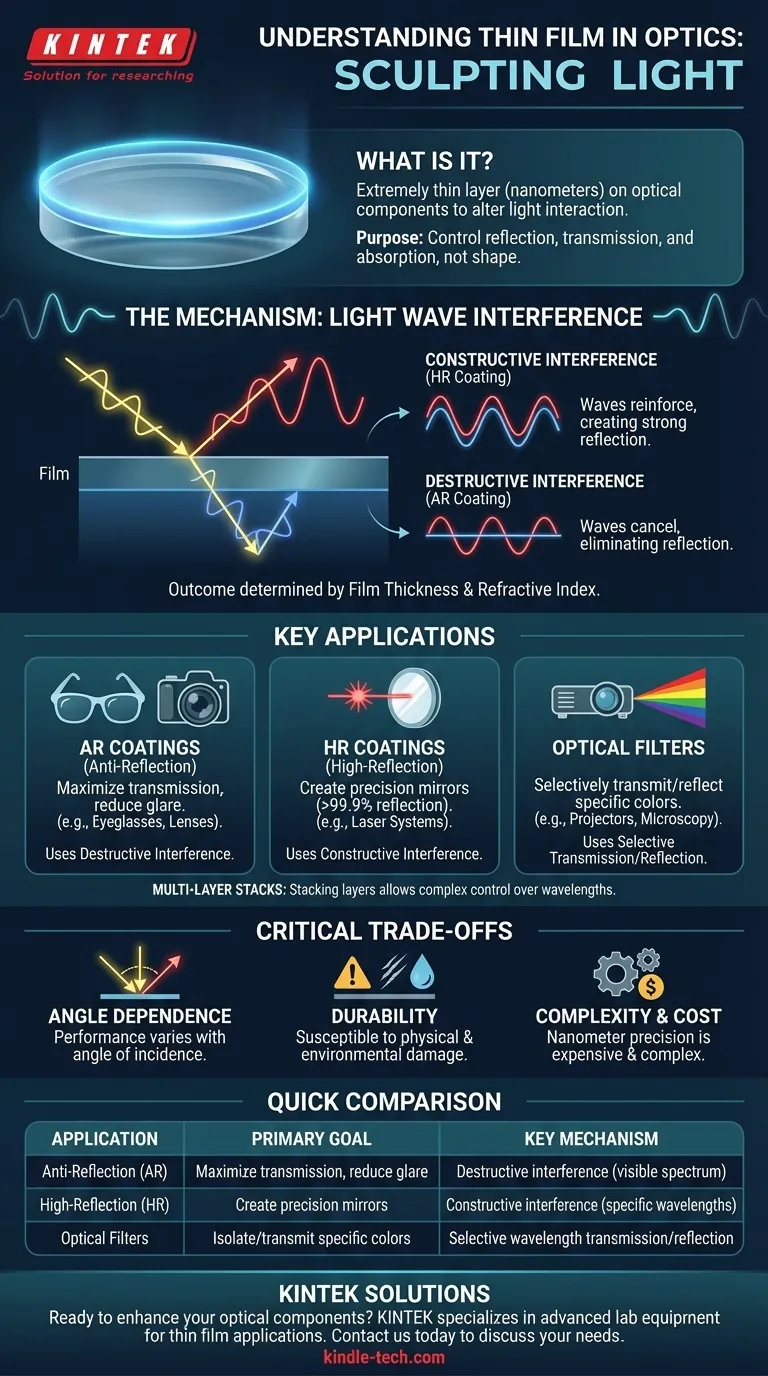
In optics, a thin film is an extremely thin layer of material, often just a few nanometers thick, intentionally deposited onto an optical component like a lens or mirror. Its purpose is not to change the shape of the component, but to precisely alter how light interacts with its surface. By carefully controlling the film's thickness and material, engineers can manipulate which wavelengths of light are reflected, transmitted, or absorbed.
The core principle behind a thin film is not the material itself, but its thickness relative to the wavelength of light. This precision allows for the controlled manipulation of light waves through a phenomenon called interference, giving us the power to "sculpt" light for specific outcomes like eliminating reflections or creating perfect mirrors.

How Thin Films Manipulate Light
The function of a thin film seems almost magical, but it is based on a fundamental property of light: its wave-like nature. When light waves interact, they can either reinforce or cancel each other out.
The Principle of Interference
When a light wave strikes a thin film, a portion of it reflects off the top surface. The rest passes through the film and reflects off the bottom surface (the interface with the underlying material, or substrate).
As this second wave emerges back out of the film, it has traveled a longer path. If this extra distance causes its peaks and troughs to align with the first reflected wave, they reinforce each other (constructive interference), creating a strong reflection.
If the extra distance causes the peaks of one wave to align with the troughs of the other, they cancel each other out (destructive interference), eliminating the reflection.
The Role of Thickness and Material
The outcome of this interference—constructive or destructive—is determined by two key factors: the film's thickness and its refractive index (a property of the material).
By engineering the thickness to be, for example, exactly one-quarter of a specific light wavelength, designers can force destructive interference for that color, making it seem to disappear from the reflection. This is the core mechanism behind most thin film applications.
Single vs. Multi-Layer Films
While a single layer offers significant control, the true power of thin film technology is realized with multi-layer coatings.
By stacking dozens or even hundreds of alternating layers of different materials and thicknesses, engineers can achieve highly complex and precise control over a wide range of wavelengths.
Key Applications in Modern Optics
Thin film coatings are not a niche technology; they are essential to the performance of countless optical devices we use every day.
Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings
Found on eyeglasses, camera lenses, and solar panels, AR coatings are designed for maximum destructive interference. By minimizing reflections, they increase light transmission, which reduces glare and improves image clarity and brightness.
High-Reflection (HR) Coatings
Used to create highly efficient mirrors, HR coatings use constructive interference. Unlike a standard metallic mirror that absorbs some light, a multi-layer dielectric mirror can be designed to reflect over 99.9% of light at a specific wavelength, which is critical for devices like lasers.
Optical Filters
These coatings are designed to selectively transmit or reflect specific colors (wavelengths). A dichroic filter, for example, can reflect blue light while letting red and green light pass through. These are used in digital projectors, fluorescence microscopy, and stage lighting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thin film coatings are not a perfect solution and come with inherent limitations that are critical to understand in any real-world application.
Angle Dependence
The performance of most interference-based films is highly dependent on the light's angle of incidence. A coating designed to block a specific wavelength for light hitting it head-on may transmit that same wavelength if the light comes in at a 45-degree angle.
Durability and Environment
As physical layers, thin films are susceptible to mechanical and environmental damage. They can be scratched, and their performance can degrade over time with exposure to humidity, extreme temperatures, or harsh chemicals. The choice of coating material often involves a trade-off between optical performance and physical robustness.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Depositing a perfectly uniform film with nanometer-level precision is a complex and expensive process. The cost increases significantly with the number of layers and the tightness of the performance tolerances, making advanced coatings a major cost driver in high-end optical systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal thin film strategy is dictated entirely by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing light throughput (e.g., camera lenses, display screens): Your goal is to use an anti-reflection (AR) coating designed to cause destructive interference across the visible spectrum.
- If your primary focus is creating a precision mirror (e.g., laser systems, telescopes): You need a high-reflection (HR) coating, often a multi-layer dielectric stack, that uses constructive interference for the specific wavelengths you need to reflect.
- If your primary focus is isolating specific colors (e.g., scientific instruments, projectors): You require a specialized optical filter coating, such as a band-pass or dichroic filter, engineered to transmit some wavelengths while reflecting others.
By applying these microscopic layers, we gain macroscopic control, turning simple pieces of glass into high-performance optical instruments.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection (AR) Coating | Maximize light transmission, reduce glare | Destructive interference across visible spectrum |
| High-Reflection (HR) Coating | Create precision mirrors (e.g., for lasers) | Constructive interference at specific wavelengths |
| Optical Filters | Isolate or transmit specific colors/bands | Selective wavelength transmission/reflection |
Ready to enhance your optical components with precision thin film coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for optical applications. Whether you need to develop anti-reflection coatings for camera lenses, high-reflection mirrors for laser systems, or custom optical filters for scientific instruments, our expertise and solutions can help you achieve superior performance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's thin film and optical needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
















