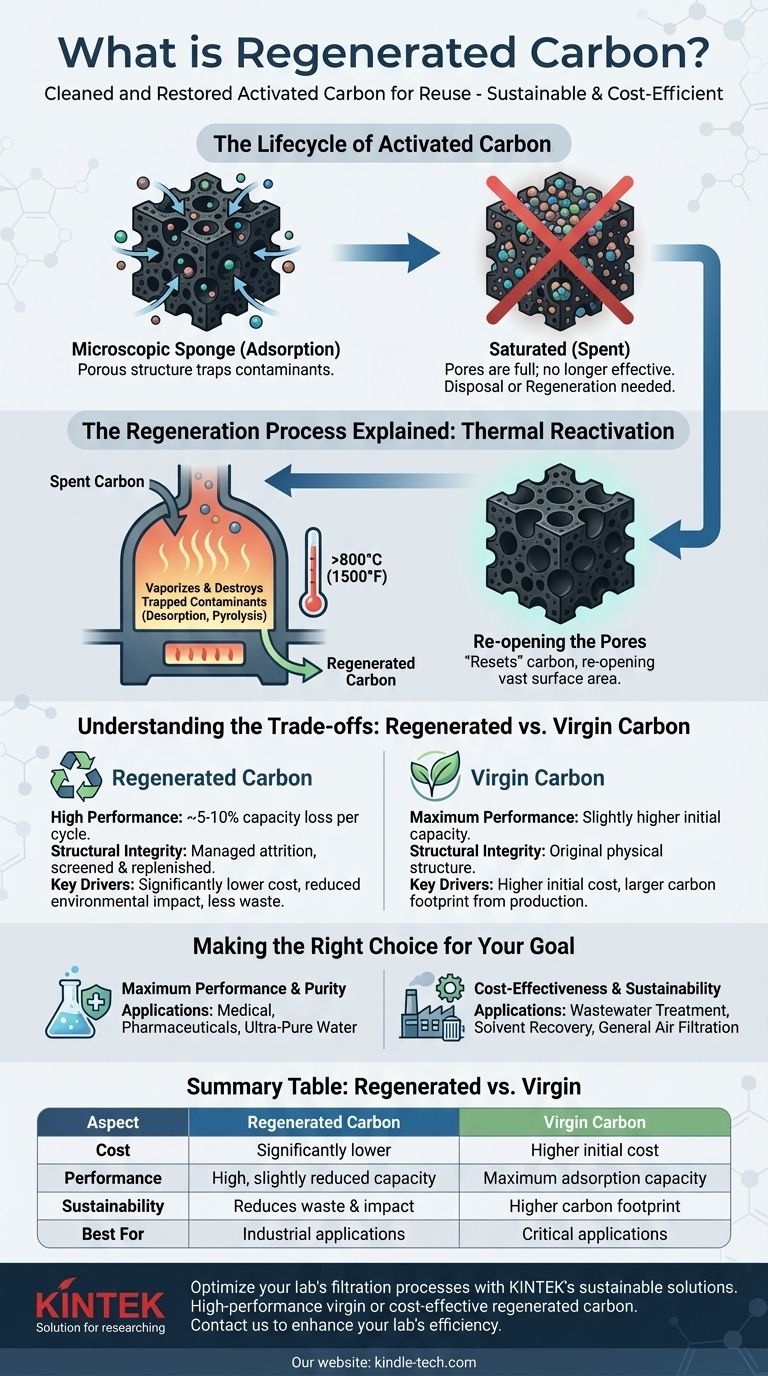
In essence, regenerated carbon is used activated carbon that has been professionally cleaned and restored for reuse. The process, known as regeneration or reactivation, removes the contaminants the carbon has adsorbed, allowing it to once again function as an effective filtration and purification medium.
The core concept is sustainability and cost-efficiency. Instead of discarding "spent" activated carbon, regeneration turns a waste product back into a valuable asset, significantly reducing costs and environmental impact without destroying the carbon's fundamental structure.

The Lifecycle of Activated Carbon
How It Works: A Microscopic Sponge
Activated carbon works through a process called adsorption. Its structure is incredibly porous, creating a vast internal surface area.
These pores act like a molecular trap, physically binding contaminants from liquids or gases that pass through them. Over time, these pores become filled.
The Point of Saturation
When the carbon's pores are full, it is considered "spent" or saturated. At this stage, it can no longer effectively remove contaminants.
This leaves two options: dispose of the spent carbon and replace it with new, "virgin" material, or regenerate it.
The Regeneration Process Explained
The Goal: Re-opening the Pores
The entire purpose of regeneration is to remove the adsorbed materials (adsorbate) from the carbon's pores without destroying the carbon itself.
This effectively "resets" the carbon, re-opening its vast surface area to capture new contaminants.
Thermal Reactivation: The Primary Method
The most common method is thermal reactivation. The spent carbon is heated in a controlled, low-oxygen environment to temperatures exceeding 800°C (1500°F).
This intense heat vaporizes and destroys the trapped organic contaminants through processes like desorption and pyrolysis, clearing the pores and restoring the carbon's adsorptive capacity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Regenerated vs. Virgin Carbon
Performance and Capacity
Regeneration is highly effective but not perfect. Each cycle typically results in a minor loss of adsorptive capacity, often in the range of 5-10%.
This means that while regenerated carbon performs very well, virgin carbon will almost always have a slightly higher capacity.
Structural Integrity
The high-temperature reactivation process can cause a small amount of physical breakdown, creating fine dust. This material loss, known as attrition, is managed by screening the carbon and replacing the lost volume with fresh material.
The Deciding Factors: Cost and Sustainability
The primary drivers for using regenerated carbon are economic and environmental. It is significantly less expensive than purchasing virgin carbon.
Furthermore, it reduces landfill waste and avoids the considerable energy and carbon footprint associated with producing new activated carbon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing between virgin and regenerated carbon depends entirely on your application's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and purity: Virgin activated carbon is the necessary choice for critical applications like medical use, pharmaceuticals, or creating ultra-pure water.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and sustainability: Regenerated carbon is an excellent and widely used solution for most industrial applications, including wastewater treatment, solvent recovery, and general air filtration.
Ultimately, carbon regeneration is a critical industrial process that balances high performance with economic and environmental responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Regenerated Carbon | Virgin Carbon |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Significantly lower | Higher initial cost |
| Performance | High, but slightly reduced capacity (5-10% loss per cycle) | Maximum adsorption capacity |
| Sustainability | Reduces waste and environmental impact | Higher carbon footprint from production |
| Best For | Industrial applications (wastewater, air filtration) | Critical applications (pharmaceuticals, ultra-pure water) |
Optimize your lab's filtration processes with KINTEK's sustainable solutions. Whether you need high-performance virgin carbon for critical applications or cost-effective regenerated carbon for industrial use, KINTEK provides the right lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and sustainability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Three-Necked Round Bottom Flask
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of rotary kiln? Achieve Precise Industrial Material Transformation
- How much energy is needed for pyrolysis? Achieve a Self-Sustaining Operation
- What is the temperature range of a rotary kiln? A Guide to Custom Thermal Profiles
- What technical requirements must high-temperature industrial kilns meet for the chlorination roasting of quartz sand?
- What is the process of pyrolysis to produce biochar? A Guide to Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- What temperature does a rotary kiln get to? A Guide to Process-Specific Thermal Ranges
- How do you reactivate carbon? Restore Adsorption Capacity & Save Costs
- How does carbon regeneration work? Restore Your Activated Carbon's Performance



















