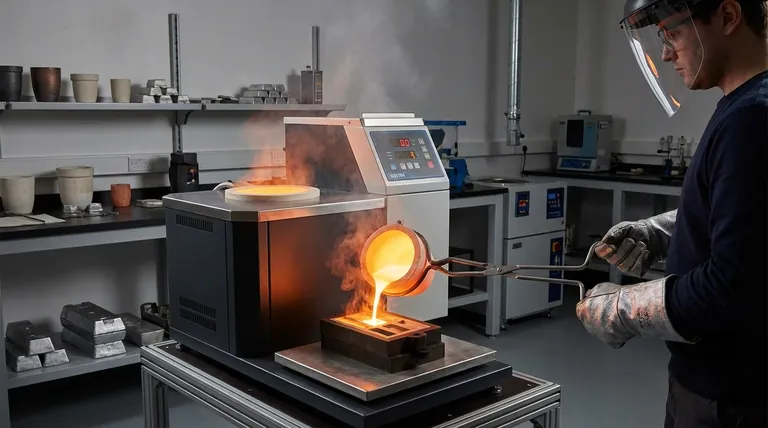
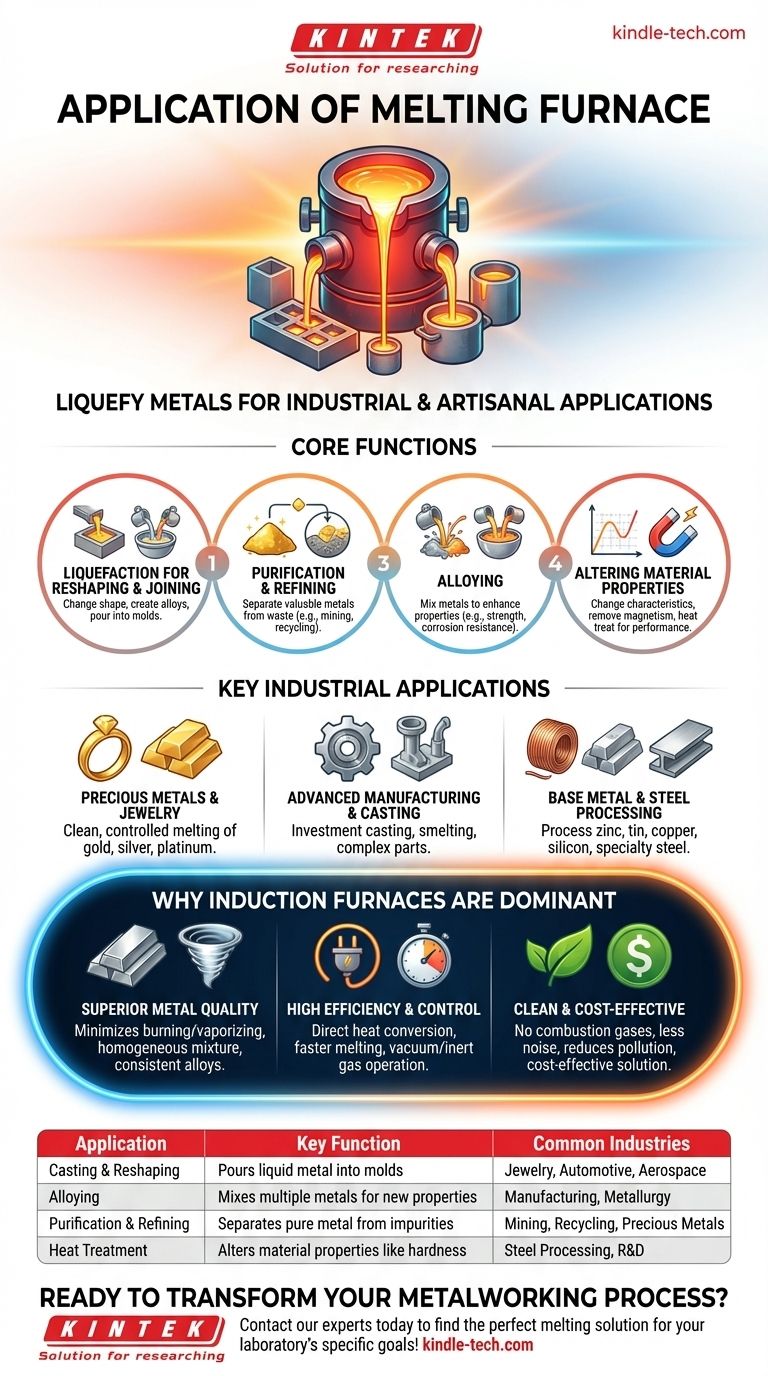
At its core, a melting furnace is used to liquefy metals for a vast range of industrial and artisanal applications. Its fundamental purpose is to apply sufficient heat to transform solid metal into a liquid state, enabling processes like casting, refining, alloying, and reshaping for everything from precious metal jewelry to industrial components.
The primary application of a melting furnace is to achieve complete metal liquefaction. This unlocks the ability to purify materials, create precise alloys, and cast complex shapes, making it an indispensable tool in manufacturing, refining, and metallurgy.

Core Functions of Metal Melting
The act of melting a metal is the first step in several critical transformation processes. The furnace is the tool that makes these transformations possible in a controlled and efficient manner.
Liquefaction for Reshaping and Joining
The most straightforward application is to change the shape of a metal. By melting it, the material can be poured into a mold of nearly any design, a process known as casting.
This is also essential for creating alloys, where multiple metals are melted together and mixed to produce a new material with enhanced properties, such as strength or corrosion resistance.
Purification and Refining
Melting is a crucial step in separating valuable metals from impurities. This is common in recycling and mining, where furnaces are used to melt down materials like gold ash, tin dross, or electronic scrap to isolate and recover the pure metal.
Altering Material Properties
The melting process can fundamentally change a metal's physical characteristics. For example, heating certain types of steel past their Curie temperature and allowing them to cool disrupts their atomic structure, effectively removing any residual magnetism.
It is also the first stage in heat treating, where a metal is heated and cooled under controlled conditions to improve its hardness, ductility, or other performance attributes.
Key Industrial Applications
While the principles are simple, the applications are highly diverse, spanning numerous industries and scales of operation.
Precious Metals and Jewelry
Induction melting furnaces are a cornerstone of the jewelry, mining, and refining industries. They provide the clean, controlled environment needed to melt and purify high-value metals like gold, silver, and platinum without significant material loss or contamination.
Advanced Manufacturing and Casting
Furnaces are central to investment casting, a process that creates complex, high-precision metal parts. A wax model is encased in a ceramic shell, the wax is melted out, and molten metal is then poured into the resulting cavity.
They are also used for smelting, an extractive metallurgy process that uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to extract a base metal from its ore.
Base Metal and Steel Processing
Beyond precious metals, furnaces are used to process zinc, tin, copper, and silicon. Specialized furnaces are also capable of melting small amounts of steel and stainless steel, typically for specialty casting or research purposes.
Why Induction Furnaces Are a Dominant Choice
Modern melting applications increasingly rely on induction heating technology over older arc heating methods. This preference is driven by significant advantages in quality, efficiency, and control.
Superior Metal Quality
Induction heating works without an electric arc, minimizing the risk of burning and vaporizing the metal. This results in less material loss and a higher-quality end product.
Furthermore, the process creates an electrodynamic circulation within the liquid metal. This natural stirring action ensures the mixture is perfectly homogeneous, which is critical for producing consistent alloys.
High Efficiency and Control
Induction furnaces are highly efficient, converting electrical energy directly into heat within the metal itself, which reduces overall heat loss and speeds up melting times.
The small, contained nature of these furnaces allows for melting in a closed chamber, making it possible to operate under a vacuum or with inert gas to prevent oxidation and contamination.
Clean and Cost-Effective Operation
This technology is notably clean, producing no combustion gases and significantly less noise than traditional furnaces. This reduces environmental pollution and improves workplace safety. The combination of speed, efficiency, and automation makes it a highly cost-effective solution for many operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting process depends entirely on the desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is high-purity precious metals: The clean, non-contaminating environment of an induction furnace is the ideal choice to prevent material loss and maintain value.
- If your primary focus is creating specialized, consistent alloys: The natural stirring effect of induction heating ensures a perfectly homogeneous mixture that is difficult to achieve with other methods.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and environmental compliance: The high speed, low energy loss, and clean operation of an induction furnace make it the superior technological option.
Ultimately, the application of a melting furnace is to provide the precise control needed to transform metal into a more valuable and useful form.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Casting & Reshaping | Pours liquid metal into molds | Jewelry, Automotive, Aerospace |
| Alloying | Mixes multiple metals for new properties | Manufacturing, Metallurgy |
| Purification & Refining | Separates pure metal from impurities | Mining, Recycling, Precious Metals |
| Heat Treatment | Alters material properties like hardness | Steel Processing, R&D |
Ready to transform your metalworking process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab melting furnaces, including advanced induction models ideal for precious metals, alloy creation, and R&D. Our furnaces deliver the precise temperature control and clean environment you need for superior results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect melting solution for your laboratory's specific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is the role of a quartz tube in the preparation of Mo2Ga2C powder precursors? Essential Synthesis Benefits
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















