The fundamental application of pressure in a hydraulic press is to act as a medium for multiplying force. Based on Pascal's Law, a small force applied to a fluid in a confined space creates pressure that is transmitted equally throughout the fluid. This pressure then acts on a larger surface area, generating a significantly larger output force, enabling tasks that would be impossible with direct mechanical effort alone.
A hydraulic press does not create energy; it transforms it. Its core function is to convert a small, manageable input force into a massive, controlled output force by manipulating pressure within a sealed hydraulic fluid.
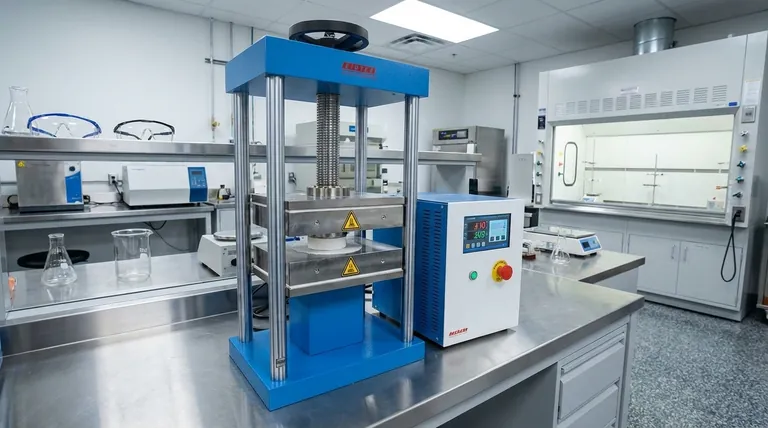

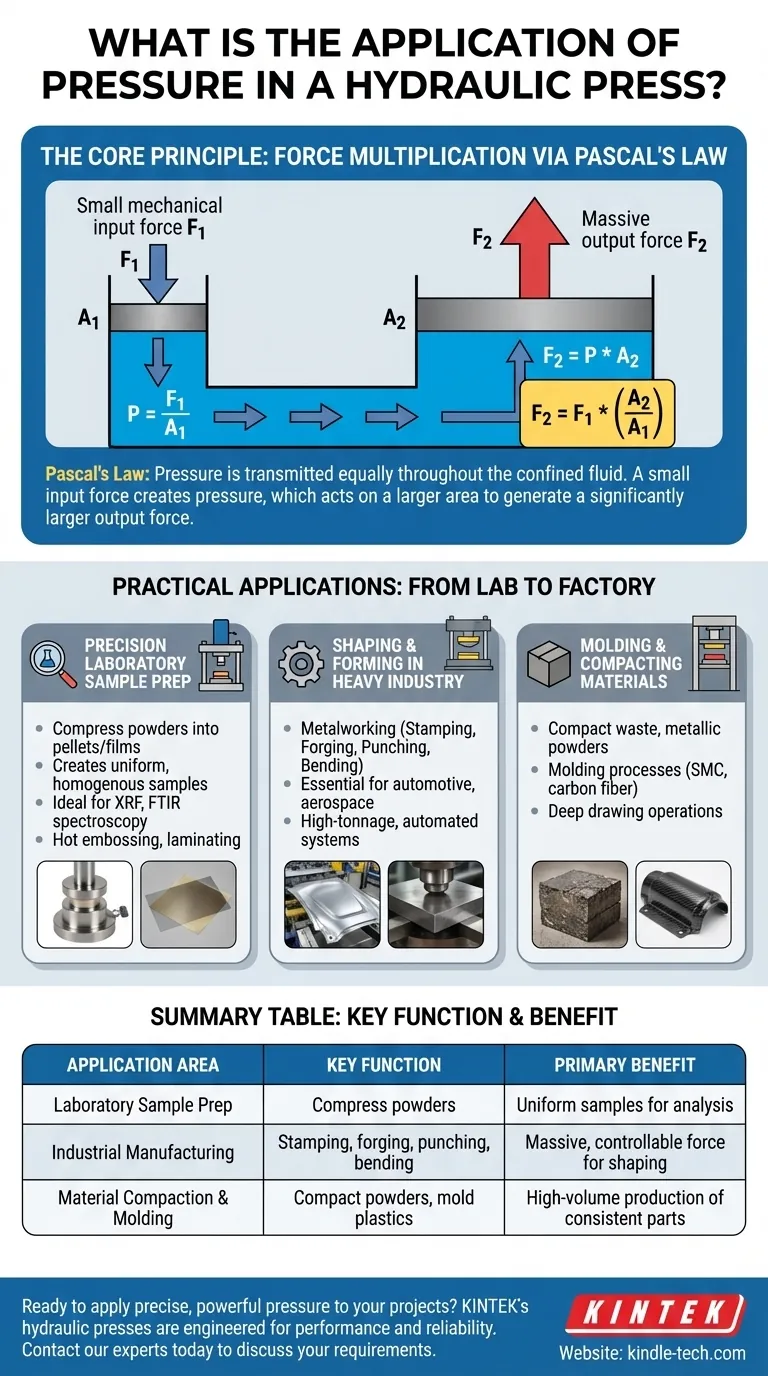
The Core Principle: Force Multiplication via Pascal's Law
The entire function of a hydraulic press is built upon a single, elegant principle of fluid dynamics discovered in the 17th century. Understanding this is key to understanding every application.
What is Pascal's Law?
Pascal's Law states that a pressure change at any point in a confined, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid. Pressure itself is defined as force applied over an area (P = F/A).
In a hydraulic system, this means the pressure in the fluid is constant everywhere.
How a Press Exploits This Law
A hydraulic press uses two connected cylinders of different sizes, each sealed with a piston and filled with fluid. A small mechanical force (F1) is applied to the small piston, which has a small area (A1).
This creates pressure (P) in the fluid (P = F1/A1). This pressure is transmitted undiminished to the larger cylinder, where it pushes on a large piston with a much larger area (A2).
The resulting output force (F2) is therefore immense, as it equals the constant pressure multiplied by the larger area (F2 = P * A2). This creates the force multiplication effect: F2 = F1 * (A2/A1).
The Result: Controllable, Massive Force
Because the output force is directly proportional to the applied pressure, the system is highly controllable.
Modern presses include pressure gauges and adjustable control valves, allowing operators to apply precise, reproducible loads measured in metric or imperial tons for repetitive and sensitive tasks.
Practical Applications: From Lab to Factory
This principle of force multiplication makes the hydraulic press a cornerstone tool in countless fields, from scientific research to heavy industry.
Precision in Laboratory Sample Preparation
In a laboratory setting, a hydraulic press is used to compress powdered material into solid pellets or thin films.
This process creates a perfectly homogenous sample with a uniform density, which is ideal for analytical techniques like X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) or Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy.
Automatic presses can also be used for advanced applications like hot embossing, laminating, or melting polymers into films for research.
Shaping and Forming in Heavy Industry
The immense force generated by hydraulic presses is essential for metalworking.
Industries from automotive to aerospace use them for stamping body panels, forging strong components, punching holes through thick plate, and bending structural steel.
Molding and Compacting Materials
Hydraulic presses are used to compact various materials, from waste products to metallic powders.
They are also critical in the plastics industry for molding processes, including sheet molded composites (SMC), carbon fiber molding, and deep drawing operations where sheet material is formed into a new shape.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While the principle is simple, its application requires an understanding of specific behaviors and system types to achieve the desired outcome.
Uniformity of Pressure
For certain applications, the direction of force matters. In isostatic pressing, the object is submerged in the hydraulic fluid, ensuring pressure is applied uniformly from all directions.
This is critical for creating parts with highly consistent density and minimal internal stress.
Secondary Effects: Heat Generation
Compressing a fluid generates heat. Due to the high pressures involved, the temperature of the hydraulic fluid can rise, sometimes affecting the sample or workpiece.
In sensitive applications, particularly with temperature-sensitive materials, the pressure chamber may require active cooling to maintain stable conditions.
Manual vs. Automatic Control
Manual presses are ideal for simple, one-off jobs or laboratory work where direct feedback is useful.
Automatic hydraulic presses are essential for industrial manufacturing. They offer high-speed, repeatable operations with precise digital control, making them suitable for large-scale production runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of pressure is tailored to the goal. Your choice of equipment and process depends entirely on what you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is analytical precision: You need a press that offers fine control and reproducibility to create uniform samples for spectroscopic analysis.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing: You need a high-tonnage, often automated press designed for specific forming, stamping, or molding operations to maximize throughput and consistency.
- If your primary focus is material testing: You need a versatile press, possibly with attachments for both compression and tension, to accurately measure the physical properties of a material under a controlled load.
Ultimately, understanding how pressure translates to controllable force is the key to leveraging a hydraulic press for any application.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Function | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Sample Prep | Compress powders into pellets/films | Creates uniform, homogenous samples for analysis (XRF, FTIR) |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Stamping, forging, punching, bending | Generates massive, controllable force for shaping metals and composites |
| Material Compaction & Molding | Compact powders, mold plastics (SMC, carbon fiber) | Enables high-volume production of consistent parts |
Ready to apply precise, powerful pressure to your projects?
Whether you are compressing samples for analytical precision in your lab or need robust force for industrial forming, KINTEK's hydraulic presses are engineered for performance and reliability. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right solution for your specific application—from manual control for R&D to automated systems for high-throughput manufacturing.
Let KINTEK provide the force you need. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover the perfect hydraulic press for your laboratory or production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy



















