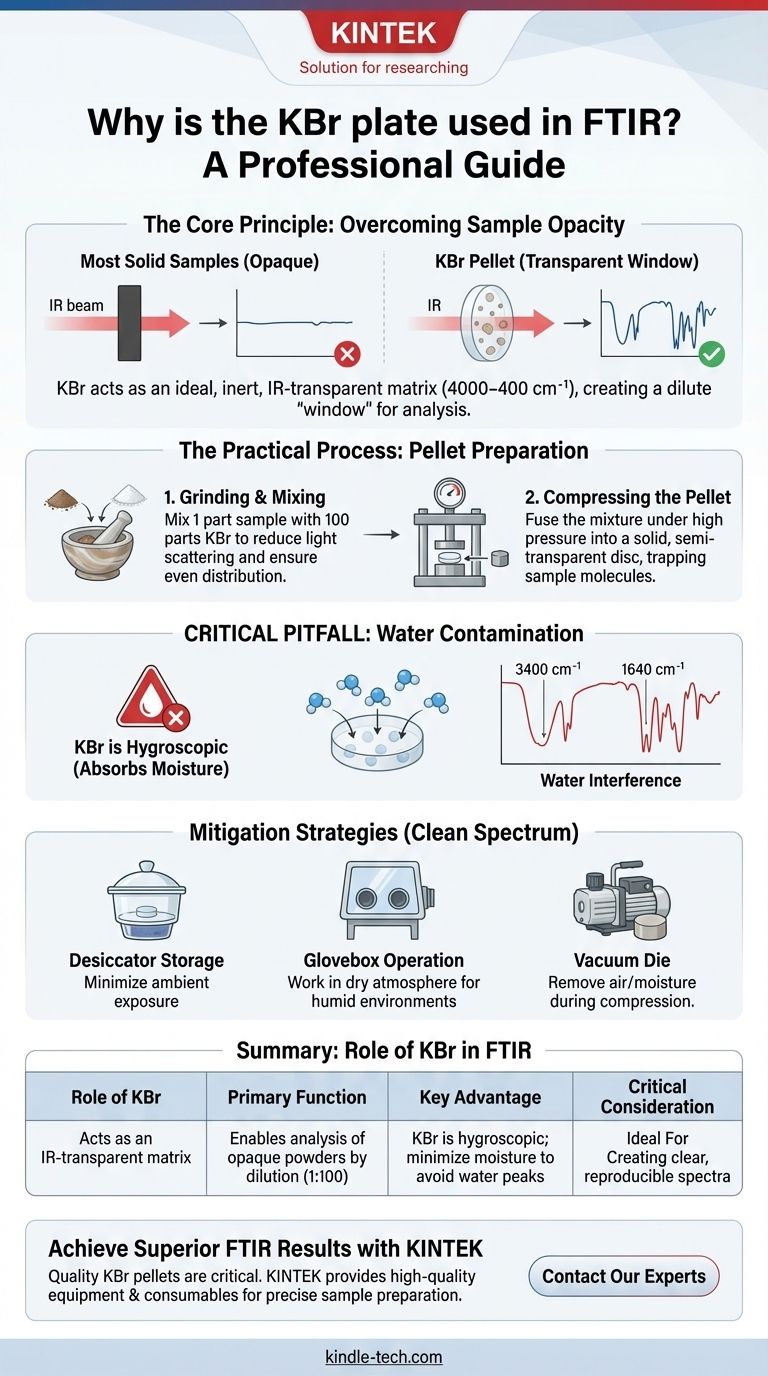
In Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, a potassium bromide (KBr) plate, or pellet, is used because it acts as an ideal solid-state matrix for analyzing samples. Its primary function is to hold a solid sample in the instrument's light path while being almost completely transparent to infrared light. This ensures the resulting spectrum comes purely from the sample, not from the material holding it.
The core challenge in analyzing solid powders with FTIR is that they are often too dense or opaque, blocking the infrared beam. KBr solves this by allowing you to create a dilute, solid, and IR-transparent pellet, effectively turning an opaque powder into a "window" that contains just enough sample for measurement.

The Core Principle: Overcoming Sample Opacity
Why Solid Samples Are Challenging
Most pure, solid samples in their powder form are too dense for FTIR analysis. If you place a thick layer of powder in the instrument, it will either absorb or scatter nearly all of the infrared light.
This prevents a usable amount of light from reaching the detector, resulting in a flat line or an uninterpretable spectrum.
KBr as an Infrared "Window"
Potassium bromide is chosen because it is optically transparent across the vast majority of the mid-infrared range (4000-400 cm⁻¹) where most functional groups absorb light.
It has no significant vibrations of its own in this region, meaning it doesn't produce interfering peaks. This makes it an ideal, inert "window" material that won't obscure the spectral features of the sample being analyzed.
The Critical Role of Dilution
To create a pellet, the sample is mixed with KBr powder at a typical ratio of 1 part sample to 100 parts KBr. The sample is not just sitting on the KBr; it is finely ground and dispersed within the KBr matrix.
This dilution ensures that the infrared beam interacts with the correct concentration of sample molecules—not so much that all the light is blocked, but enough to generate a strong, clear spectrum.
The Practical Process of Pellet Preparation
Grinding and Mixing
First, a few milligrams of the sample are ground together with a much larger amount of dry KBr powder, typically using an agate mortar and pestle.
The goal is to create a fine, homogenous mixture. This reduces light scattering from large particles and ensures the sample is evenly distributed throughout the final pellet.
Compressing the Pellet
The KBr-sample mixture is then transferred into a pellet die and compressed under high pressure using a hydraulic press.
This immense pressure fuses the KBr powder into a solid, semi-transparent disc. The sample molecules are trapped within this solid KBr matrix, held perfectly in place for analysis.
Understanding the Critical Pitfall: Water Contamination
The Hygroscopic Nature of KBr
Potassium bromide is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. The moment a container of KBr is opened, it begins to attract water molecules from the air.
How Water Interferes with Analysis
Water (H₂O) has very strong and broad absorption bands in the infrared spectrum, particularly around 3400 cm⁻¹ and 1640 cm⁻¹.
If your KBr is "wet," these large water peaks can easily obscure important sample peaks in those regions, leading to inaccurate data and misinterpretation.
Mitigation Strategies
To get a clean spectrum, you must minimize water contamination. This can be achieved by storing KBr in a desiccator and working quickly.
For the highest quality results, especially in humid environments, the grinding and pressing should be performed inside a glovebox with a dry atmosphere or by using a specialized vacuum die that removes air and moisture during compression.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your FTIR results are reliable, you must treat pellet preparation as a critical step in your analysis.
- If your primary focus is routine identification of a stable solid: Concentrate on achieving a fine, homogenous mixture and press a clear pellet quickly to minimize ambient water exposure.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Consistency is paramount; use the exact same sample-to-KBr ratio and pressing pressure for every sample and standard to ensure comparability.
- If your primary focus is working in a humid environment or with a moisture-sensitive sample: Using a glovebox or a vacuum die is not optional, but essential to prevent water peaks from corrupting your data.
By treating KBr not just as a holder but as a critical optical component, you will produce clean, accurate, and reproducible FTIR data.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of KBr in FTIR |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as an IR-transparent matrix to hold solid samples. |
| Key Advantage | Enables analysis of opaque powders by dilution (typically 1:100 sample:KBr). |
| Critical Consideration | KBr is hygroscopic; moisture contamination must be minimized to avoid water peaks. |
| Ideal For | Creating clear, reproducible spectra for qualitative and quantitative analysis. |
Achieve superior FTIR results with confidence. The quality of your KBr pellet is critical for accurate data. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables—including reliable pellet dies, presses, and pure KBr salt—that your laboratory needs for precise and reproducible sample preparation. Contact our experts today to find the perfect FTIR solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis



















