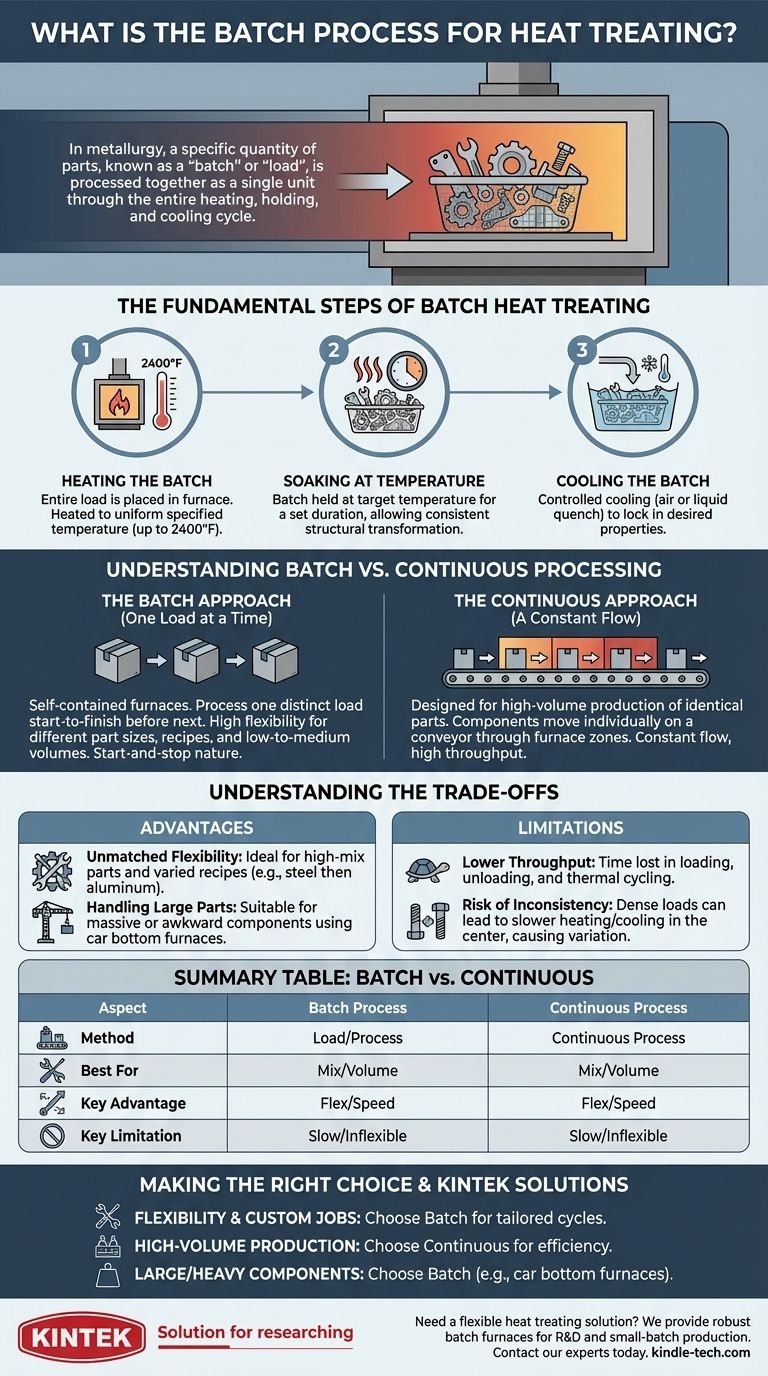
In the world of metallurgy, the batch process for heat treating is a method where a specific quantity of parts—known as a "batch" or "load"—is processed together as a single unit. The entire group of components moves through the complete three-stage cycle of heating, holding at temperature (soaking), and cooling simultaneously within an enclosed furnace.
The defining characteristic of batch heat treating is not the specific temperature or time, but the methodology: processing a discrete group of components as one unit from start to finish. This approach offers excellent flexibility for varied parts but contrasts with the high-volume, continuous flow of other methods.
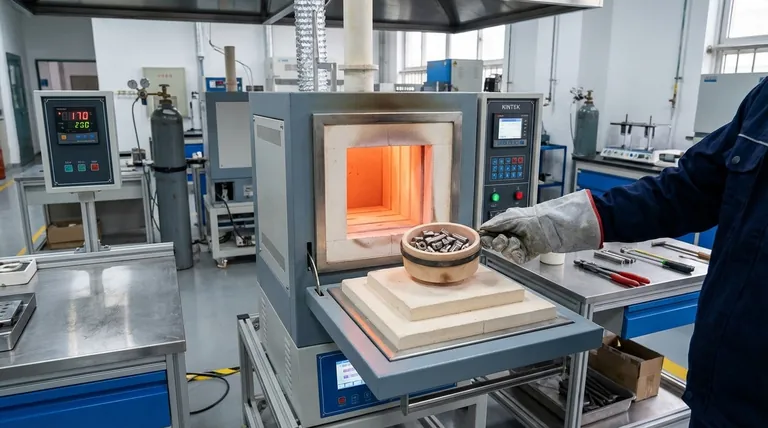

The Fundamental Steps of Batch Heat Treating
The batch method follows the three core principles of any heat treatment process, but applies them to the entire load at once. The goal is to ensure every part in the batch achieves the same structural transformation.
Step 1: Heating the Batch
The process begins by placing the entire load into a furnace. The furnace is then heated to a specified temperature, which can be as high as 2,400°F. A critical challenge here is ensuring uniform heating across all parts, whether they are at the center or the edge of the load.
Step 2: Soaking at Temperature
Once the target temperature is reached, the entire batch is held, or "soaked," for a predetermined period. This duration, ranging from seconds to many hours, allows the material's internal crystalline structure to transform completely and consistently across every part in the load.
Step 3: Cooling the Batch
After soaking, the entire batch is cooled in a controlled manner to lock in the desired properties like hardness or ductility. The load may be cooled slowly in the air, or rapidly quenched by submerging the entire basket of parts in a liquid like water or oil.
Understanding Batch vs. Continuous Processing
The "batch" designation is a direct contrast to "continuous" heat treating. Understanding this distinction is key to knowing when to use each method.
The Batch Approach: One Load at a Time
Batch furnaces are self-contained and process one distinct load from start to finish before the next one can begin. They are often loaded and unloaded manually or with cranes for very large components.
This method is defined by its start-and-stop nature, making it highly adaptable for different part sizes, processing requirements, and production volumes.
The Continuous Approach: A Constant Flow
Continuous processes, by contrast, are designed for high-volume production of identical parts. Components move individually on a conveyor through different zones of a furnace, each set to a specific temperature.
Processes like induction heating, where an electric current heats a small, specific area of a single part before it is immediately quenched, represent a form of single-piece continuous flow, valued for its speed and precision in mass production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the batch process involves clear advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific applications.
Advantage: Unmatched Flexibility
Batch processing is ideal for "job shops" or production environments with a high mix of different parts. Because each cycle is independent, operators can run a batch of steel bolts with one recipe, followed by a batch of aluminum brackets with a completely different temperature and time profile.
Advantage: Handling Large and Awkward Parts
Extremely large or heavy components, like massive gears or structural beams, are often impossible to move on a conveyor. Large-scale "car bottom" furnaces, where parts are loaded onto a movable floor section, are a type of batch furnace designed specifically for these scenarios.
Limitation: Lower Throughput
The primary drawback of the batch process is its lower throughput compared to continuous methods. The time spent loading, unloading, heating the furnace from a cooler state, and cooling it down creates cycle gaps that are inefficient for high-volume, standardized production.
Limitation: Risk of Inconsistency
In densely packed loads, parts in the center of the batch may heat and cool more slowly than those on the exterior. This can create slight variations in metallurgical properties across the batch, requiring careful furnace design and loading strategies to mitigate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process depends entirely on your production needs, part geometry, and desired volume.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and custom jobs: The batch process is ideal, allowing you to tailor each cycle for different materials, part sizes, and desired properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of identical parts: A continuous process will provide far greater throughput, consistency, and cost-efficiency at scale.
- If your primary focus is processing very large or heavy components: Batch furnaces, particularly car bottom or box designs, are often the only practical solution.
Ultimately, understanding the batch process is about recognizing its role as a versatile and foundational method for achieving precise material properties in specific, controlled quantities.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Batch Process | Continuous Process |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Processes a complete "load" of parts as one unit | Parts move individually through furnace zones on a conveyor |
| Best For | High-mix, low-to-medium volume; large/awkward parts | High-volume, identical parts |
| Key Advantage | Flexibility for different part types and recipes | High throughput and efficiency |
| Key Limitation | Lower throughput; risk of inconsistency in dense loads | Inflexible; not suitable for large or varied parts |
Need a flexible heat treating solution for your unique laboratory or production needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and reliable batch furnaces and lab equipment tailored for precise thermal processing. Whether you're working with varied part sizes, complex geometries, or specialized alloys, our solutions deliver the controlled heating and cooling required for consistent results.
We help you:
- Achieve precise material properties for R&D or small-batch production.
- Handle large or awkwardly shaped components with ease.
- Maintain flexibility to switch between different heat treatment recipes.
Let's discuss your specific requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect batch heat treating equipment for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















