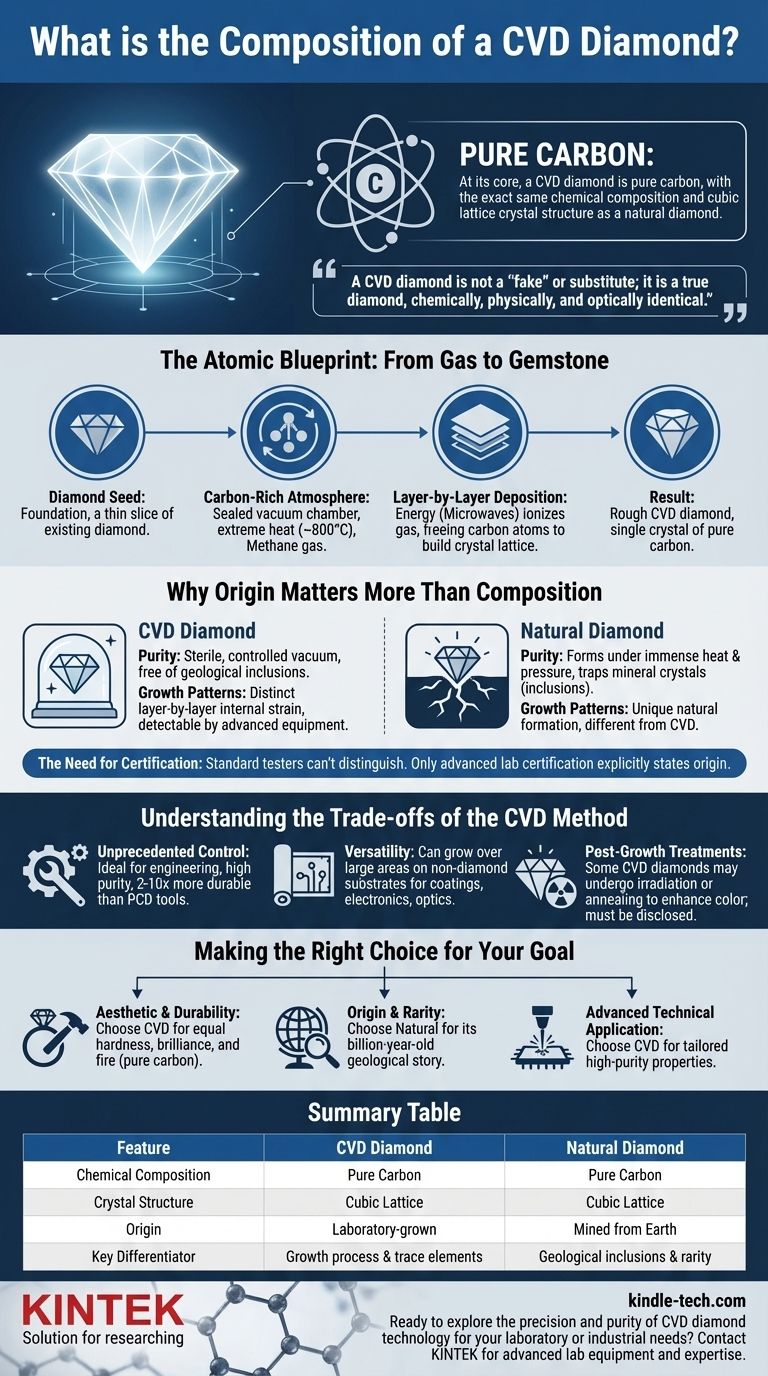
At its core, a CVD diamond is pure carbon. It possesses the exact same chemical composition and crystal structure as a diamond mined from the Earth. The distinction between a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamond and a natural one is not a matter of substance, but of origin and process.
A CVD diamond is not a "fake" diamond or a substitute; it is a true diamond, composed of carbon atoms arranged in a cubic lattice. It is grown in a laboratory environment by depositing carbon atoms onto a seed crystal, resulting in a stone that is chemically, physically, and optically identical to its natural counterpart.

The Atomic Blueprint: From Gas to Gemstone
The composition of a CVD diamond is a direct result of its highly controlled manufacturing process, which mimics natural processes on an accelerated timeline.
The Diamond Seed Foundation
The process begins with a "seed," which is a very thin slice of a high-quality existing diamond. This seed acts as the foundational template upon which the new diamond will grow.
A Carbon-Rich Atmosphere
This seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is then heated to extreme temperatures, typically around 800°C, and filled with a carbon-rich gas, such as methane.
Layer-by-Layer Carbon Deposition
Energy, often in the form of microwaves, is introduced into the chamber. This energy ionizes the gas, breaking down the molecular bonds and freeing the carbon atoms. These individual carbon atoms then attach themselves to the diamond seed, building up the crystal lattice layer by layer.
This meticulous process continues for several weeks until the rough diamond has reached the desired size. The result is a single crystal of pure carbon, identical in structure to a mined diamond.
Why Origin Matters More Than Composition
Since CVD diamonds are chemically pure carbon, the key differentiators lie in the microscopic traces left by their unique growth environment, which can only be identified by specialized gemological labs.
Purity and Inclusions
Natural diamonds form under immense heat and pressure deep within the Earth, a chaotic process that often traps tiny mineral crystals and other foreign materials, known as inclusions. CVD diamonds grow in a sterile, controlled vacuum, so they are free of these geological inclusions.
Growth Patterns
The layer-by-layer growth of a CVD diamond can sometimes create internal strain or graining patterns that are distinct from the growth patterns of natural diamonds. These are invisible to the naked eye but can be detected with advanced equipment.
The Need for Certification
Because they share the same physical properties, a standard jeweler's diamond tester cannot distinguish between a natural and a CVD diamond. The only definitive way to verify a diamond's origin is through a gemological certificate from a reputable lab, which will explicitly state if it is laboratory-grown.
Understanding the Trade-offs of the CVD Method
The CVD process was developed to overcome the limitations of other diamond synthesis techniques, offering distinct advantages but also presenting its own set of considerations.
Advantage: Unprecedented Control
The CVD method allows for exceptionally fine control over the diamond's purity and properties. This makes it ideal for engineering and industrial applications where specific characteristics are required, such as creating tools that are 2-10 times more durable than Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) tools.
Advantage: Versatility
Unlike natural diamonds, CVD diamond films can be grown over large areas and deposited onto a wide variety of non-diamond materials (substrates). This versatility is critical for creating high-performance coatings, electronic components, and advanced optics.
Consideration: Post-Growth Treatments
Some CVD diamonds may undergo post-growth treatments, such as irradiation or annealing, to enhance their color. While perfectly stable, these treatments are a human intervention that must be disclosed on a grading report.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding that the composition is identical allows you to focus on the factors that truly matter for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic beauty and durability: A CVD diamond offers the same hardness, brilliance, and fire as a natural diamond, as these properties are dictated by its pure carbon structure.
- If your primary focus is verifiable origin and rarity: A natural diamond's value is intrinsically linked to its billion-year-old geological story and its finite supply.
- If your primary focus is advanced technical application: CVD technology provides the unique ability to create high-purity diamond layers with specific properties tailored for cutting tools, semiconductors, or optics.
Ultimately, the choice is not about a "real" versus a "synthetic" chemical composition, but about the story, process, and application you value most.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic Lattice | Cubic Lattice |
| Origin | Laboratory-grown | Mined from Earth |
| Key Differentiator | Growth process & trace elements | Geological inclusions & rarity |
Ready to explore the precision and purity of CVD diamond technology for your laboratory or industrial needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise to support your research and development with high-performance materials. Whether you're working on cutting-edge electronics, durable coatings, or high-purity optics, our solutions are designed to meet the demands of modern science. Contact us today to learn how we can help you achieve your goals with reliable, cutting-edge technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of Fluidized Bed Chemical Vapor Deposition (FB-CVD)? Scalable CNT Production
- What is the difference between chemical and physical deposition? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Thin Films
- What is considered a thin film? The Essential Guide to Nanoscale Materials
- What is the sputtering process of surface treatment? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Precision
- What is the deposition rate of CVD? A Key Advantage for Efficient Thin-Film Manufacturing
- What is thin film deposition by magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Precision Coating
- What are the units for deposition rate? Mastering Thickness and Mass Metrics for Your Process
- How is CVD coating done? A Step-by-Step Guide to Superior Surface Engineering



















