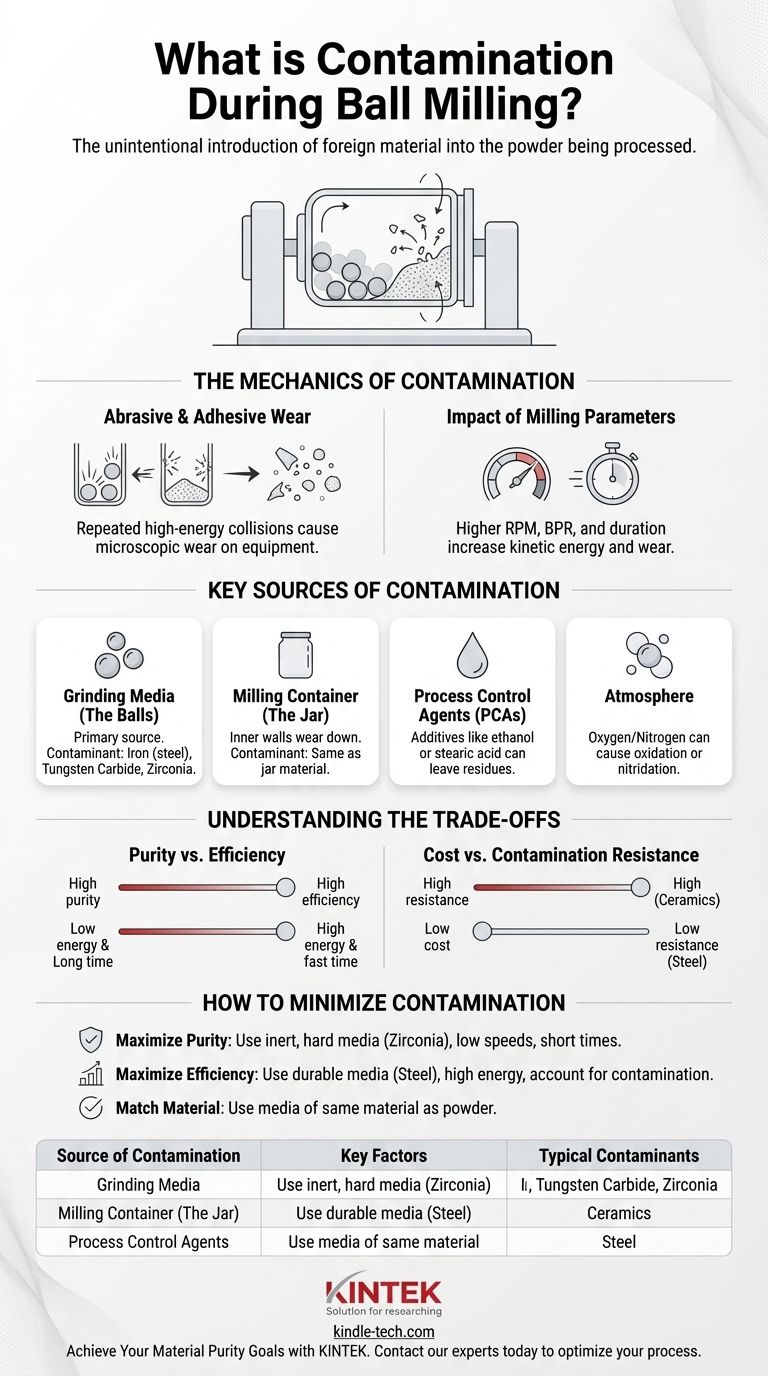
Contamination during ball milling is the unintentional introduction of foreign material into the powder being processed. This occurs because ball milling is a high-energy mechanical process where repeated, forceful collisions cause microscopic wear on the milling equipment itself. Consequently, particles from the milling jar and the grinding balls are abraded and become mixed into your sample.
The central takeaway is that contamination is not a flaw but an inherent consequence of the ball milling process. The goal is not to achieve impossible, zero-percent contamination, but to understand its sources and control the process to keep it within acceptable limits for your specific application.

The Mechanics of Contamination
Abrasive and Adhesive Wear
The core mechanism of contamination is mechanical wear. As the balls collide with each other, the powder, and the jar walls at high velocity, tiny fragments of the jar and ball material are chipped off (abrasion) or transferred (adhesion).
This process is a direct result of the intense mechanical energy a ball mill imparts to the system. Every impact is an opportunity for a microscopic piece of your equipment to become part of your sample.
The Role of Material Hardness
A fundamental principle of wear is that the softer material will abrade more quickly. For effective milling, the grinding media and jar should be significantly harder than the material being milled.
If the powder is harder than the steel balls, for instance, the balls will wear down rapidly, leading to significant iron contamination in the final powder.
The Impact of Milling Parameters
The rate of contamination is directly proportional to the energy of the milling process. Aggressive parameters designed for rapid results will always increase contamination.
Key factors include milling speed (RPM), the ball-to-powder weight ratio (BPR), and the milling duration. Higher speeds, a greater BPR, and longer times all increase the kinetic energy and the number of collisions, accelerating equipment wear.
Key Sources of Contamination
Grinding Media (The Balls)
The grinding balls are often the most significant source of contamination due to their massive surface area and direct, constant impact with the powder.
The material of the balls—be it hardened steel, tungsten carbide, zirconia, or agate—will be the primary contaminant found in your sample. For example, using steel balls will introduce iron.
Milling Container (The Jar)
The inner walls of the milling jar are subject to the same abrasive forces as the balls. The jar's material will also inevitably wear away and mix with your powder.
This is why selecting a jar and balls made of the same material is a common strategy to limit the types of contaminants, even if it cannot eliminate the contamination itself.
Process Control Agents (PCAs)
In some cases, small amounts of liquids (like ethanol) or solids (like stearic acid) are added as PCAs to prevent the powder from cold-welding to the equipment.
While often intentional, these agents can leave residues or react with the powder, acting as another form of process contamination if not fully removed or accounted for.
Atmosphere
If not performed under a vacuum or an inert gas (like argon), the atmosphere inside the jar can contaminate the sample. The high energy can induce reactions with oxygen (oxidation) or nitrogen (nitridation), altering the chemical composition of your material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Purity vs. Efficiency
This is the central conflict in ball milling. High-energy milling (high RPM, high BPR) achieves faster particle size reduction or alloying but guarantees higher rates of contamination.
Conversely, low-energy milling preserves material purity but requires dramatically longer processing times, sometimes making a process impractical.
Cost vs. Contamination Resistance
The materials best at resisting wear are often the most expensive. Hardened steel is a cost-effective and common choice, but it contributes iron contamination.
High-purity, wear-resistant media like silicon nitride or zirconia are excellent for minimizing contamination but come at a significant premium, which may not be justifiable for all applications.
The "Acceptable" Contamination Level
"Zero contamination" is a theoretical ideal, not a practical reality. The critical question is what level of contamination your final application can tolerate.
A small amount of iron from steel media might be perfectly acceptable for producing a structural steel alloy. However, that same level of iron would be a critical failure point in a high-purity ceramic for electronic or biomedical use.
How to Minimize Contamination in Your Process
Choosing a strategy requires you to define your primary goal. The right approach is always a deliberate compromise between purity, speed, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material purity: Use grinding media and a jar made from a material that is exceptionally hard and inert (e.g., zirconia, silicon nitride), and run the mill at lower speeds for shorter durations.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing and efficiency: Use durable, cost-effective media like hardened steel with high-energy parameters, but be prepared to analytically account for the resulting contamination in your final material composition.
- If you are milling a powder that is chemically similar to the media: Consider using media of the same material (e.g., milling silicon powder with silicon nitride media) so that any contamination does not introduce a foreign element.
By treating contamination as a controllable process variable, you can strategically optimize your ball milling outcomes to meet precise material specifications.
Summary Table:
| Source of Contamination | Key Contributing Factors | Typical Contaminants |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding Balls | Material hardness, ball-to-powder ratio, milling speed/duration | Iron (steel), Tungsten Carbide, Zirconia |
| Milling Jar | Material hardness, jar wall abrasion, milling duration | Same as jar material (e.g., Steel, Zirconia) |
| Process Control Agents (PCAs) | Type and amount of PCA used (e.g., ethanol, stearic acid) | Organic residues, reaction byproducts |
| Atmosphere | Presence of oxygen/nitrogen (if not inert/vacuum) | Oxides, nitrides |
Achieve Your Material Purity Goals with KINTEK
Controlling contamination is critical for successful material processing. Whether you need high-purity ceramics for electronics or efficient alloy production, the right lab equipment makes all the difference.
KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality, wear-resistant milling jars and grinding media (like zirconia, tungsten carbide, and agate) designed to minimize contamination. We help laboratories balance purity, efficiency, and cost.
Let us help you optimize your ball milling process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How to increase the efficiency of a ball mill? Optimize Speed, Feed, and Grinding Media for Peak Performance
- What are the steps in ball milling? A Guide to Effective Particle Size Reduction
- What are the principles of a ball mill? Master Impact & Attrition for Perfect Particle Size
- What is the advantage of ball milling method? Achieve Cost-Effective Particle Size Reduction & Material Modification
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? Key Limitations for Your Grinding Process



















