In essence, every heat treatment process is a carefully controlled cycle consisting of three fundamental stages: heating the metal to a specific temperature, holding it there for a set duration, and then cooling it at a predetermined rate. The precise temperatures, times, and cooling methods used in this cycle are what manipulate the metal's internal crystal structure to achieve desired properties like hardness, softness, or strength.
Heat treatment is not a single action but a planned thermal journey. The goal is to intentionally transform a metal's microscopic structure by controlling this three-stage cycle, thereby dictating its final mechanical properties.
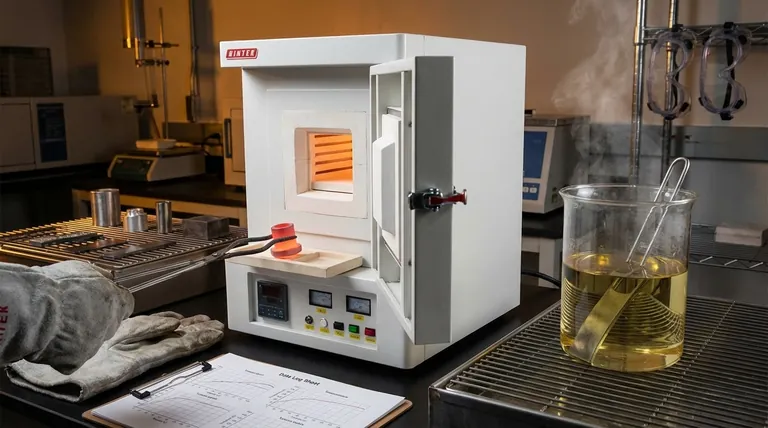

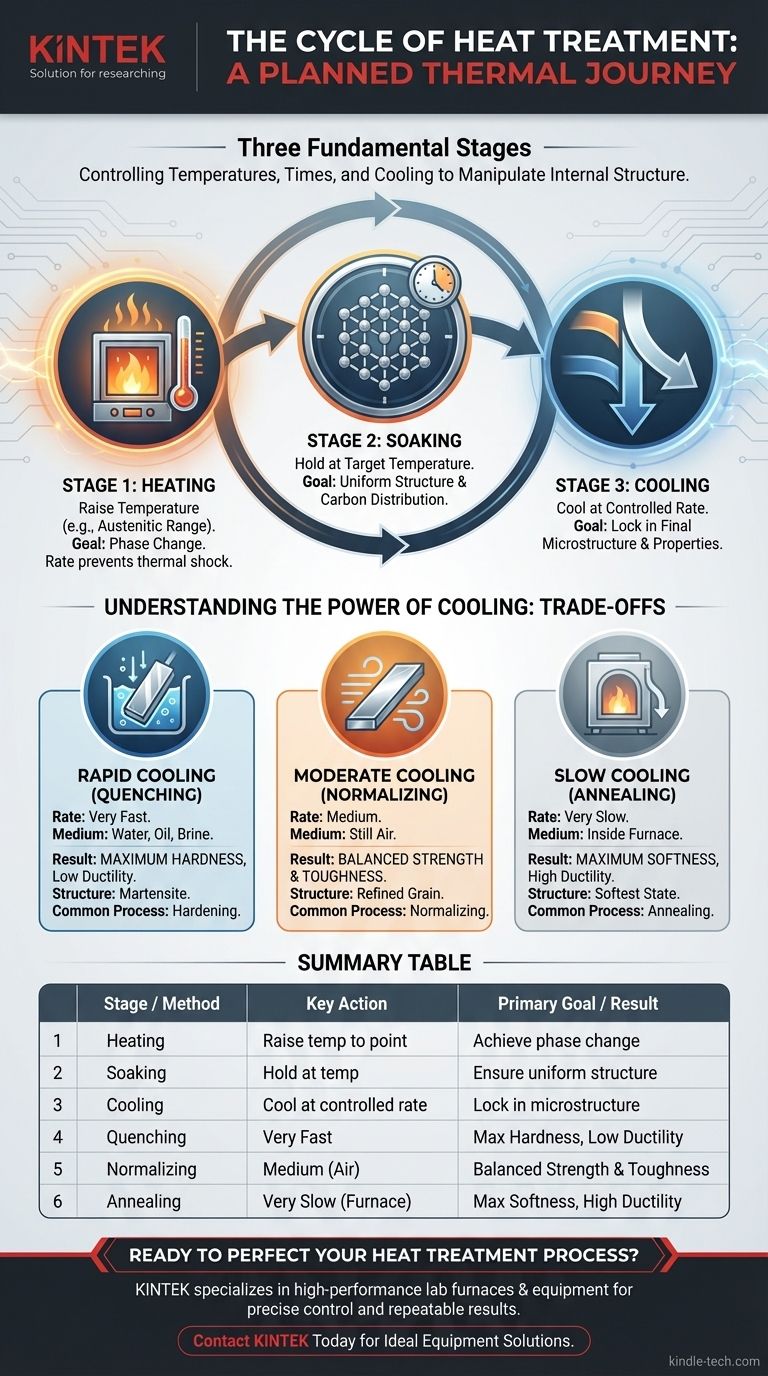
The Three Stages of a Heat Treatment Cycle
Understanding this cycle is key to understanding how we can change a material's behavior. Each stage serves a distinct and critical purpose in the overall transformation of the metal.
Stage 1: Heating to a Target Temperature
The cycle begins by heating the material in a controlled manner, often in a furnace. The goal is to raise its temperature above a critical transformation point.
For steels, this typically means heating into the austenitic range, a high-temperature phase where the iron's crystal structure changes and can dissolve carbon more effectively. The rate of heating is important to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
Stage 2: Soaking (Holding) at Temperature
Once the target temperature is reached, the material is "soaked" or held at that temperature for a specific amount of time. This is not a passive waiting period.
During soaking, the internal structure of the metal becomes uniform. As noted in processes like normalizing, this stage allows elements like carbon to distribute evenly throughout the material and ensures the entire piece has undergone the desired phase transformation.
Stage 3: Cooling at a Controlled Rate
This is arguably the most critical stage, as the rate of cooling locks in the final microstructure and thus determines the metal's properties. Different cooling rates produce vastly different results.
For example, the normalizing process involves cooling the steel in still air. This moderate cooling rate refines the crystal structure, creating a material that is stronger and tougher than in its pre-treated state.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Power of Cooling
The choice of cooling method introduces a fundamental trade-off, usually between hardness and ductility (the ability to deform without breaking).
Rapid Cooling (Quenching)
Quenching involves cooling the metal very quickly by submerging it in a medium like water, oil, or brine. This rapid cooling traps the crystal structure in a hard, brittle state (like martensite in steel).
The result is maximum hardness and wear resistance, but this comes at the cost of significantly reduced ductility and high internal stresses.
Moderate Cooling (Normalizing)
As mentioned, normalizing uses still air as the cooling medium. This is slower than quenching but faster than letting it cool in a furnace.
This method provides a balanced outcome: a refined grain structure with good strength and toughness, relieving the internal stresses that may have built up during manufacturing processes like forging or rolling.
Slow Cooling (Annealing)
Annealing involves cooling the material as slowly as possible, often by simply turning the furnace off and letting the part cool down with it over many hours.
This produces the softest, most ductile state possible for the metal. It is ideal for making a material easier to machine or form, but it results in the lowest strength and hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct heat treatment cycle is entirely dependent on the final application of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Use a hardening cycle that involves rapid quenching in water or oil.
- If your primary focus is refining the structure and improving toughness after fabrication: Use a normalizing cycle with moderate cooling in air.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum softness for easy machining: Use an annealing cycle with very slow cooling inside a furnace.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about understanding how to manipulate this three-stage cycle to dictate the final performance of the metal.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Heating | Raise temperature to a specific point | Achieve a phase change (e.g., austenite in steel) |
| 2. Soaking | Hold at the target temperature | Ensure uniform structure and composition |
| 3. Cooling | Cool at a controlled rate | Lock in the final microstructure and properties |
| Cooling Method | Rate | Resulting Properties | Common Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid (Quenching) | Very Fast | Maximum Hardness, Low Ductility | Hardening |
| Moderate (Air) | Medium | Balanced Strength & Toughness | Normalizing |
| Slow (Furnace) | Very Slow | Maximum Softness, High Ductility | Annealing |
Ready to Perfect Your Heat Treatment Process?
Choosing the right cycle is critical for achieving the precise mechanical properties your components require. The furnace you use is the heart of this controlled thermal journey.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed for exacting heat treatment applications. Whether you are hardening, normalizing, or annealing, our solutions provide the precise temperature control and uniform heating essential for repeatable results.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the ideal equipment for your heat treatment cycles.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the range of sputtering? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films for Any Application
- What are the disadvantages of pyrolysis of plastic to fuel? Key Environmental & Economic Challenges
- What is the function of a forced air drying oven in Ni/CN catalyst recovery? Maximize Reuse Efficiency
- Is brazing a permanent joint? Yes, and here's why it's stronger than you think.
- Why is sintering used as a manufacturing process? Unlock Complex Parts from High-Temp Materials
- What are the three stages of sintering? Master the Microstructural Transformation
- What is sputtering rate? Master the Key to Controlling Thin Film Deposition Speed
- What are the technical requirements for vacuum chambers in desalination? Boost Efficiency with Graphene Technology



















