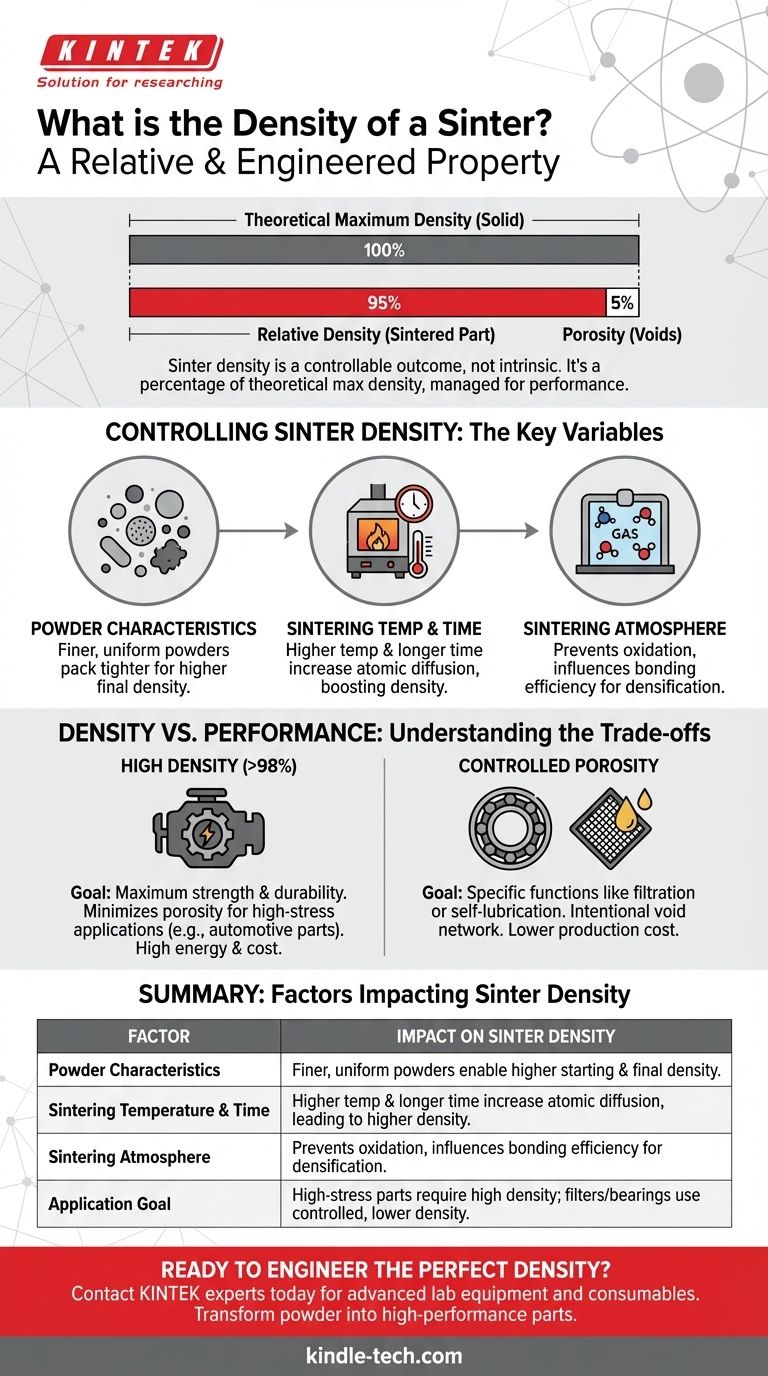
Crucially, a "sinter" does not have a single, fixed density. Instead, the density of a sintered part is a highly variable and engineered property. It is most accurately described as a relative density, which is a percentage of the theoretical maximum density of the solid material used to create it. For example, a sintered steel part might have a density that is 95% of the density of a solid, non-sintered steel bar.
The central concept to grasp is that the density of a sintered component is a controllable outcome of the manufacturing process, not an intrinsic property. This control allows engineers to intentionally manage porosity to balance mechanical performance, special functions, and production cost.

Why Density is a Variable, Not a Constant
A sintered part begins as a collection of fine powders that are compressed and then heated. This process inherently leaves microscopic voids between the original powder particles.
Theoretical vs. Relative Density
Theoretical density is the maximum possible density of the base material if it were a perfectly solid, void-free mass.
Relative density, the key metric for sintered parts, is the actual measured density of the component divided by its theoretical density, expressed as a percentage. A part is never 100% dense, but high-performance applications aim to get as close as possible.
The Role of Porosity
The voids that remain after the sintering process are known as porosity. The amount of porosity directly determines the part's density; higher porosity means lower relative density. The initial goal of sintering is often to achieve a relative density above 75% to eliminate the largest, most critical pores.
How the Sintering Process Controls Density
The final density of a component is not an accident; it is the direct result of carefully controlled variables during manufacturing.
The Impact of Powder Characteristics
The size, shape, and distribution of the initial powder particles play a fundamental role. Finer, more uniform powders can pack together more tightly, resulting in a higher starting density and a denser final product.
The Influence of Sintering Temperature and Time
Higher sintering temperatures and longer hold times give atoms more energy and opportunity to diffuse, closing the gaps between particles. High-temperature sintering is directly linked to higher density, which in turn leads to superior tensile strength and impact energy.
The Effect of Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace (such as a vacuum, nitrogen, or argon) prevents oxidation and can influence the chemical reactions at the particle surfaces, affecting how efficiently they bond together and densify.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Density vs. Performance
The "right" density depends entirely on the part's intended application. There is often a trade-off between achieving maximum density and other factors like cost or desired functionality.
The Goal of Full Densification
For high-stress applications like engine or transmission components, the goal is to achieve the highest possible density (often >98%). This minimizes porosity, which can act as a stress concentration point, and maximizes mechanical properties like strength and fatigue resistance.
The Advantage of Controlled Porosity
In some cases, porosity is a desirable feature. For example, self-lubricating bearings are made with intentionally controlled porosity. These voids are impregnated with oil, which is released during operation to provide continuous lubrication. Similarly, sintered metal filters rely on interconnected pores to function.
The Cost Factor
Achieving very high densities requires more energy, longer furnace cycles, or more complex multi-stage sintering processes. For less critical components, manufacturers may choose a lower target density that provides adequate performance at a significantly lower production cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal density for a sintered part is determined by its final application. By manipulating the sintering process, you can engineer a wide range of material properties from the same base powder.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: Aim for the highest achievable relative density, minimizing porosity to create a part with properties approaching its solid, wrought equivalent.
- If your primary focus is creating a filter or self-lubricating part: Intentionally engineer a specific, lower density to create a network of controlled and interconnected pores.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for a non-critical component: Target a moderate relative density that offers a reliable balance between acceptable mechanical performance and lower manufacturing costs.
Ultimately, controlling the density of a sintered part is how you transform a simple powder into a high-performance, engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Sinter Density |
|---|---|
| Powder Characteristics | Finer, more uniform powders enable higher starting and final density. |
| Sintering Temperature & Time | Higher temperatures and longer times increase atomic diffusion, leading to higher density. |
| Sintering Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and can influence bonding efficiency for densification. |
| Application Goal | High-stress parts require high density (>98%); filters/ bearings use controlled, lower density. |
Ready to engineer the perfect density for your sintered components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to precisely control the sintering process. Whether your goal is maximum strength, controlled porosity for filtration, or cost-effective production, our solutions help you achieve the exact material properties you require.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering needs and help you transform powder into high-performance parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
People Also Ask
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More



















