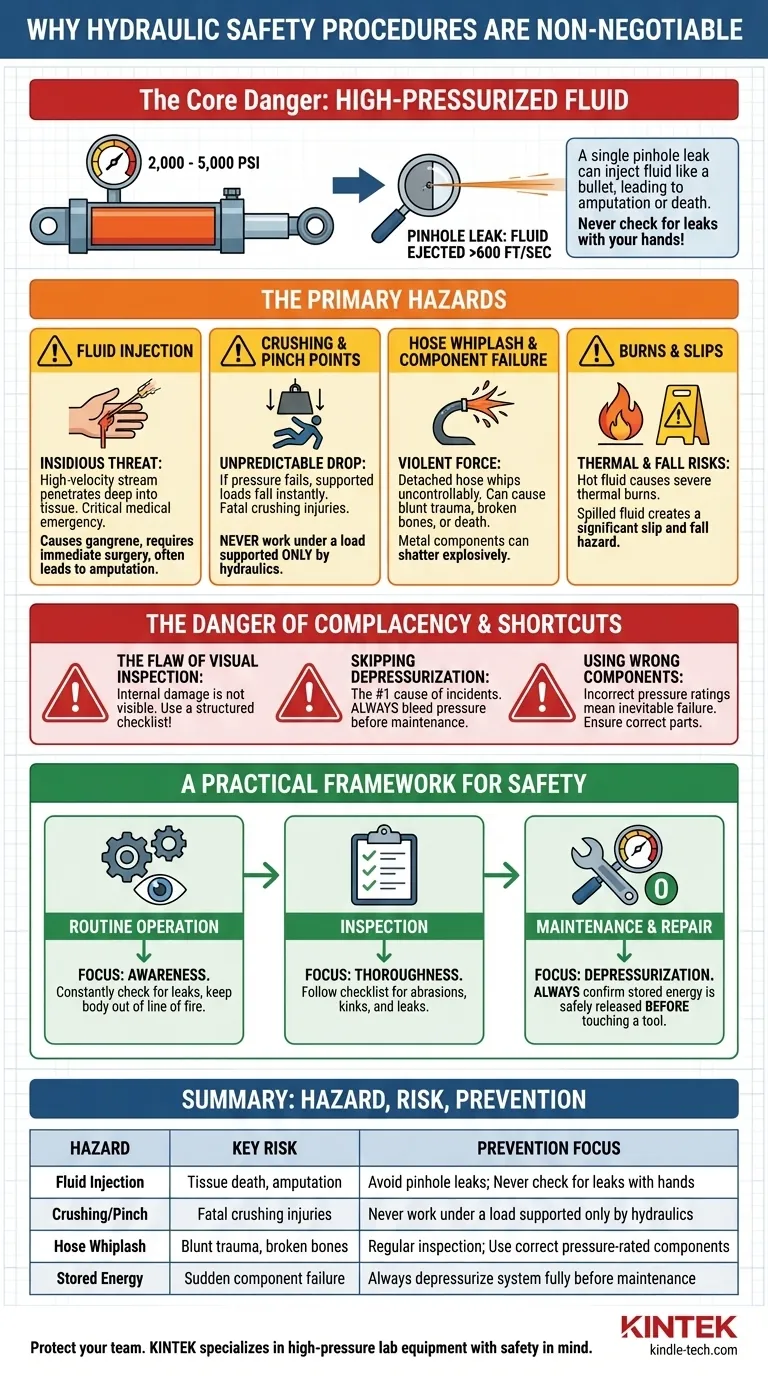
Following hydraulic safety procedures is a non-negotiable requirement because the immense pressure stored within these systems can cause catastrophic equipment failure and life-altering injuries. A single pinhole leak, invisible to the naked eye, can inject hydraulic fluid into the body with the velocity of a bullet, leading to amputation or death. The energy contained is immense, and disrespecting it has severe and immediate consequences.
The core danger of hydraulic tools is not the tool itself, but the highly-pressurized fluid that powers it. Understanding that this fluid can instantly become a projectile, a source of crushing force, or a severe toxin is the fundamental principle behind every safety rule.

The Physics of Hydraulic Danger
To appreciate the necessity of safety procedures, you must first understand the forces at play. Hydraulic systems don't just move fluid; they transmit enormous force by pressurizing it to extreme levels.
Extreme Pressure Concentrated
A typical hydraulic system on heavy equipment can operate at 2,000 to 5,000 pounds per square inch (PSI) or more. For context, a car tire is around 35 PSI. This means every square inch of a hydraulic hose is withstanding the force of a small car.
The Pinhole Leak Phenomenon
When this extreme pressure finds a tiny escape route—a pinhole leak in a hose—the fluid is ejected at speeds exceeding 600 feet per second. This is fast enough to easily penetrate skin, work gloves, and other protective clothing.
Stored Energy in Components
Even when the power source is turned off, pressure can remain trapped within hoses, cylinders, and accumulators. This stored energy means a system that appears inert can still be incredibly dangerous if a component is disconnected improperly.
The Primary Hazards of Hydraulic Systems
Disregarding safety procedures exposes operators and technicians to a specific set of severe, life-threatening risks.
Hydraulic Fluid Injection
This is the most insidious and dangerous hydraulic hazard. The high-velocity stream from a pinhole leak can inject fluid deep into body tissue. This may initially look like a minor cut or bee sting, but it is a critical medical emergency.
The injected fluid quickly causes tissue to die, leading to gangrene. Immediate surgical intervention is required to remove the toxic fluid, and amputation is a common outcome.
Crushing and Pinch Points
Hydraulic systems are used to lift and hold immense loads. If a hose bursts or a fitting fails, that pressure is lost instantly.
Any load supported by the hydraulic system can drop without warning, causing immediate and fatal crushing injuries. This is why you must never work under a load supported only by hydraulics.
Hose Whiplash and Component Failure
A hydraulic hose that detaches or bursts under pressure does not simply leak. The hose itself will whip around with violent, uncontrollable force, capable of causing blunt force trauma, broken bones, or death.
Similarly, a failing metal component can shatter, sending shrapnel flying with explosive force.
Burns and Slips
Hydraulic fluid in operation becomes extremely hot. A leak can cause severe thermal burns on contact. Spilled fluid also creates a significant slip and fall hazard on work surfaces.
The Danger of Complacency and Shortcuts
Most hydraulic incidents are not caused by spontaneous, unpredictable failures. They are the direct result of overlooking procedures due to complacency or a desire to save time.
"It Looks Fine": The Flaw of Visual Inspection
Internal hose damage, microscopic cracks in fittings, or metal fatigue are not visible to the naked eye. Relying on a quick glance instead of following a structured inspection checklist leaves you vulnerable to sudden failure.
Skipping the Depressurization Step
The single most common shortcut before maintenance is failing to properly bleed pressure from the system. Attempting to loosen or disconnect a fitting on a pressurized line is the leading cause of fluid injection and explosive component failure incidents.
Using the Wrong Components
Using a hose, fitting, or seal that is not rated for the system's operating pressure is a critical error. These components will fail, and it is only a matter of when. Procedures exist to ensure the correct parts are used every time.
A Practical Framework for Hydraulic Safety
To translate this understanding into action, adopt a systematic approach to every interaction with hydraulic equipment. Procedures are not obstacles; they are your primary defense.
- If your task is routine operation: Your primary focus must be on awareness. Constantly check for leaks, keep your body out of the line of fire of hoses and fittings, and never rely on hydraulics alone to secure a suspended load.
- If your task is inspection: Your primary focus must be on thoroughness. Follow a checklist to look for hose abrasions, kinks, and leaks, and ensure all safety guards and features are in place.
- If your task is maintenance or repair: Your primary focus must be on depressurization. Always confirm that all stored energy has been safely released from the system before you ever touch a tool.
Ultimately, treating every hydraulic line as if it is a loaded gun is the only reliable mindset to ensure you complete your work without injury.
Summary Table:
| Hydraulic Hazard | Key Risk | Prevention Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Injection | Tissue death, amputation | Avoid pinhole leaks; never check for leaks with hands |
| Crushing/Pinch Points | Fatal crushing injuries | Never work under a load supported only by hydraulics |
| Hose Whiplash | Blunt force trauma, broken bones | Regular inspection; use correct pressure-rated components |
| Stored Energy | Sudden component failure | Always depressurize system fully before maintenance |
Protect your team and equipment from hydraulic hazards. KINTEK specializes in high-pressure lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that rely on hydraulic systems for critical operations. Our products are designed with safety and durability in mind, ensuring reliable performance under extreme conditions. Contact our safety experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's safety protocols and prevent costly accidents.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is a sintering process? A Guide to Fusing Powders into High-Performance Parts
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating



















