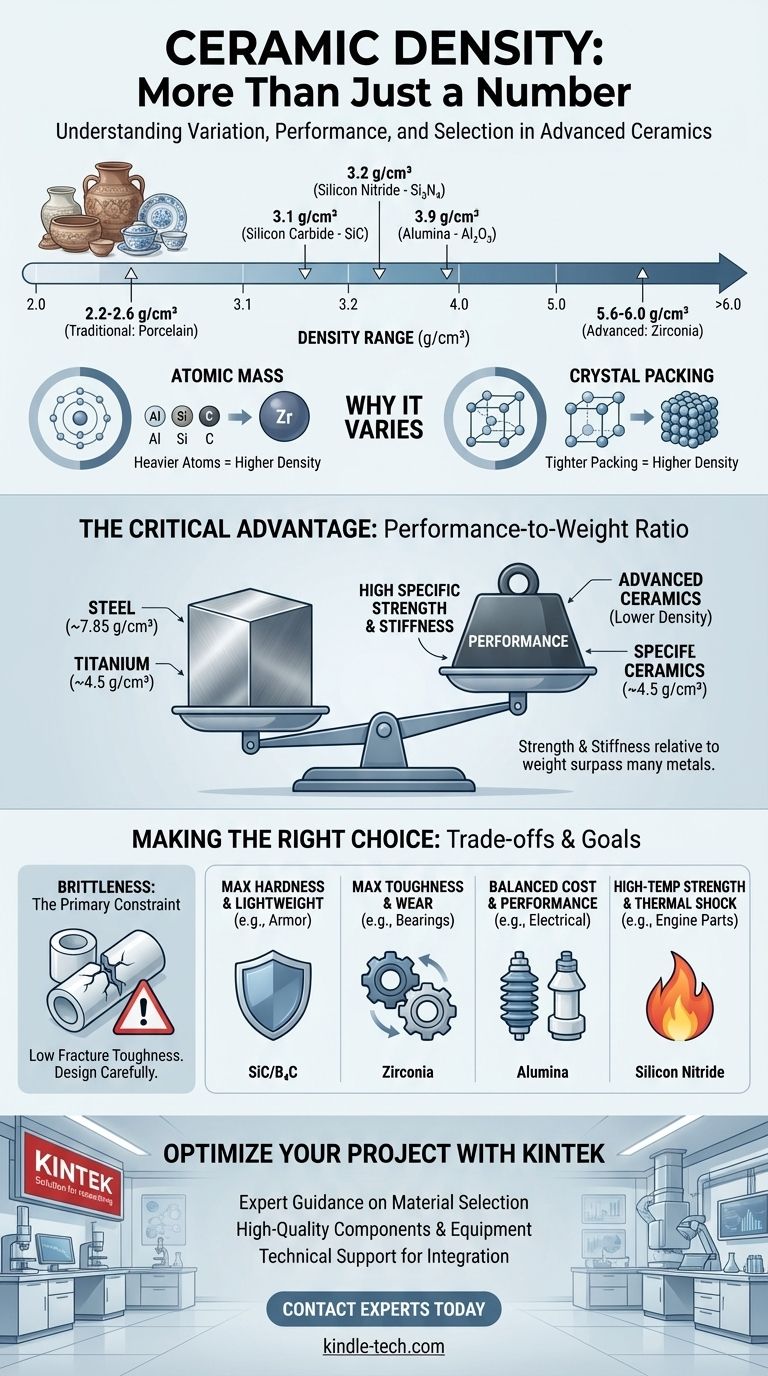
The density of a ceramic material is not a single value but spans a wide range, typically from about 2.0 g/cm³ to over 6.0 g/cm³. This variation depends entirely on the specific chemical composition and crystalline structure of the ceramic. While traditional ceramics like porcelain are at the lower end of this range, advanced technical ceramics like zirconia can be surprisingly dense, almost approaching the density of some metals.
The core takeaway is that "ceramic" is too broad a term for a single density value. The true value of technical ceramics lies not just in their density, but in their exceptionally high strength- and stiffness-to-weight ratios, which often surpass those of metals.

Why Ceramic Density Varies So Widely
The term "ceramic" covers a vast family of materials, from clay-based pottery to highly engineered compounds used in aerospace and medical implants. Their properties, including density, are fundamentally different.
Traditional vs. Advanced Ceramics
Traditional ceramics, like porcelain or earthenware, are primarily made from natural raw materials like clay and silica. Their densities are generally low, often in the 2.2 to 2.6 g/cm³ range.
Advanced ceramics (also called technical or engineering ceramics) are synthesized from highly pure powders for specific high-performance applications. Their densities are determined by their precise chemical makeup.
Key Examples in Advanced Ceramics
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) is one of the most common advanced ceramics. It offers a great balance of properties and has a density of approximately 3.9 g/cm³.
Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide, ZrO₂) is notable for being exceptionally tough (for a ceramic) and also unusually dense. Its density is typically around 5.6 to 6.0 g/cm³, making it denser than many aluminum and titanium alloys.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is an extremely hard, lightweight ceramic. With a density of about 3.1 g/cm³, it is prized for applications requiring high rigidity and wear resistance without a major weight penalty.
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) is another high-performance, low-density ceramic. Its density is around 3.2 g/cm³, and it is known for its outstanding thermal shock resistance and high strength.
What Determines a Ceramic's Density?
Two factors primarily control the density of a ceramic:
- Atomic Mass: The weight of the constituent atoms. Zirconia is dense because the Zirconium atom is much heavier than the Aluminum, Silicon, or Carbon atoms found in other ceramics.
- Crystal Packing: How tightly these atoms are packed together in the material's crystal lattice. Most technical ceramics are processed to achieve maximum theoretical density with minimal porosity.
The Critical Advantage: Performance-to-Weight Ratio
Simply looking at density is misleading. The reason engineers choose ceramics is for what that density delivers in terms of performance.
Specific Strength and Specific Modulus
Specific Strength (strength divided by density) and Specific Modulus (stiffness divided by density) are the true measures of a material's structural efficiency. This is where advanced ceramics excel.
While a high-strength steel might be stronger than Alumina in absolute terms, the Alumina is less than half the weight. For applications where weight is critical, such as in aviation or vehicle armor, a ceramic can provide the required performance with a significant weight saving.
Comparison with Metals
- Steel: ~7.85 g/cm³
- Titanium: ~4.5 g/cm³
- Aluminum: ~2.7 g/cm³
Notice that many advanced ceramics like Alumina and Silicon Carbide have densities comparable to or slightly higher than aluminum, but offer far greater hardness, stiffness, and high-temperature stability. Zirconia is the outlier, with a density closer to that of titanium.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a ceramic based on its favorable density requires an objective understanding of its limitations.
Brittleness: The Primary Constraint
The most significant trade-off for ceramics is their inherent brittleness, or low fracture toughness. Unlike metals, which bend and deform under high stress, ceramics tend to fracture suddenly. This behavior must be the central consideration in any design using ceramic components.
Cost and Manufacturability
Producing high-purity ceramic powders and sintering them into dense, final shapes is an energy-intensive and precise process. This makes advanced ceramics significantly more expensive to manufacture than most metals. Complex geometries can also be difficult and costly to achieve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material requires balancing its properties against your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and low weight: Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Boron Carbide (B₄C) are leading candidates for applications like armor and high-wear components.
- If your primary focus is maximum toughness and wear resistance: Zirconia (ZrO₂) is an excellent choice, but you must account for its relatively high density in your design.
- If your primary focus is a versatile balance of cost and performance: Alumina (Al₂O₃) is the most widely used technical ceramic for a reason, offering good strength, hardness, and electrical insulation.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength and thermal shock resistance: Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) excels in demanding thermal environments like engine components.
Understanding a ceramic's density is the first step to leveraging its unique combination of properties to solve challenging engineering problems.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Material | Typical Density (g/cm³) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | ~3.9 | Excellent balance of strength, hardness, and electrical insulation |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | ~5.6-6.0 | High toughness and wear resistance, similar density to titanium |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | ~3.1 | Extreme hardness, lightweight, excellent thermal conductivity |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | ~3.2 | Outstanding thermal shock resistance, high-temperature strength |
| Traditional Porcelain | ~2.2-2.6 | Lower density, common in pottery and basic insulators |
Optimize Your Project with the Right Ceramic Material
Struggling to choose the ideal ceramic for your specific application? The density and performance characteristics of advanced ceramics can make or break your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in helping laboratories and engineering teams select the perfect lab equipment and ceramic consumables for their unique needs.
We provide:
- Expert guidance on material selection based on your specific requirements (strength, weight, thermal properties)
- High-quality ceramic components and lab equipment tailored to your application
- Technical support for integrating advanced ceramics into your designs
Don't let material selection uncertainty slow your innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how our ceramic solutions can enhance your project's performance and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection



















