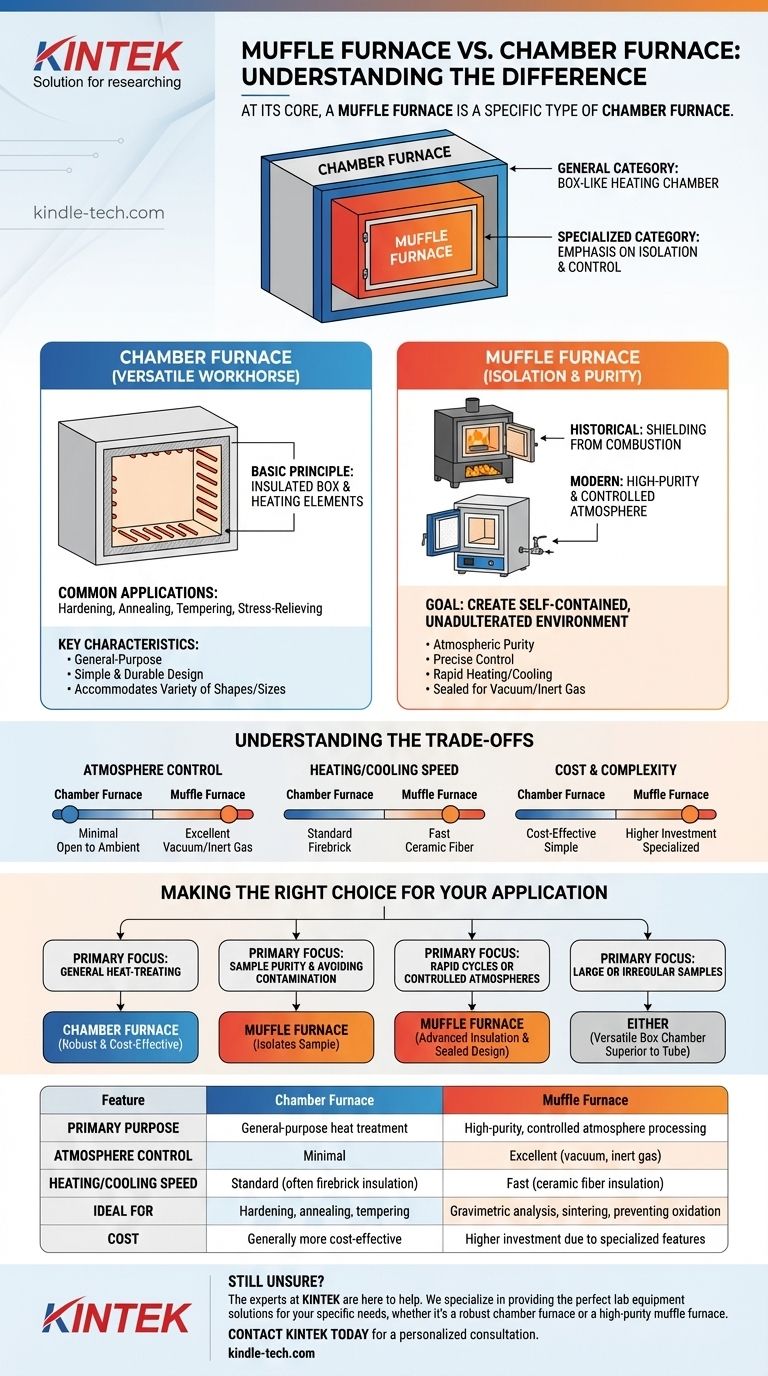
At its core, a muffle furnace is a specific type of chamber furnace, not a fundamentally different category. The key distinction lies in the principle of isolation: a muffle furnace is designed to isolate the material being heated from the heat source and its byproducts, ensuring a pure, controlled environment. A "chamber furnace" is a more general term for any furnace with a box-like heating chamber.
While all muffle furnaces are chamber furnaces, not all chamber furnaces are muffle furnaces. The defining feature of a muffle furnace is its emphasis on isolating the sample, historically from combustion contaminants and today for creating a highly controlled atmospheric environment.

What Defines a Chamber Furnace?
A chamber furnace is the most common furnace configuration, acting as a versatile workhorse for a wide range of thermal processing applications.
The Basic Principle: An Insulated Box
The term "chamber furnace" is primarily descriptive. It refers to a furnace constructed as a rectangular or box-like chamber made of thermally insulating materials.
Heating elements, typically electric, are positioned along the interior walls to radiate heat and raise the temperature of the internal chamber and its contents.
Common Applications and Characteristics
These furnaces are used for general-purpose applications like hardening, annealing, tempering, and stress-relieving materials. Their design prioritizes simplicity, durability, and the ability to heat a variety of sample sizes and shapes.
What Makes a Muffle Furnace Special?
The term "muffle" points to a specific design philosophy centered on purity and isolation. This concept has evolved as furnace technology has advanced from fuel-fired to electric heating.
The Historical Definition: The "Muffle"
In traditional fuel-fired furnaces, the "muffle" was a physical, secondary chamber (often made of ceramic) that contained the sample. This inner box shielded the material from the direct flames and contaminating byproducts of combustion, such as soot and gases.
Think of it like placing food in a covered ceramic dish before putting it in a wood-fired oven. The dish is the muffle, protecting the food from smoke and ash.
The Modern Definition: High-Purity Electric Heating
With the advent of clean electric heating elements, the need to shield a sample from combustion byproducts disappeared. However, the term muffle furnace was retained and evolved.
Today, it signifies a high-performance chamber furnace designed for processes that demand atmospheric purity and precise control. These units feature superior ceramic fiber insulation for rapid heating and cooling, and tightly sealed doors to enable controlled atmospheres, such as vacuum or inert gas backfills.
The Goal is Isolation and Control
The consistent theme is isolation. Whether isolating from historic fuel combustion or the modern ambient atmosphere, a muffle furnace is engineered to create a self-contained, unadulterated processing environment. This makes it essential for sensitive lab work like gravimetric analysis, sintering, or chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a general-purpose chamber furnace and a specialized muffle furnace involves clear performance and cost trade-offs.
Atmosphere Control
A standard chamber furnace offers minimal atmospheric control. A muffle furnace, with its sealed design, is far superior for applications requiring a vacuum or a specific inert gas environment (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation.
Temperature Ramp Rates and Uniformity
Modern muffle furnaces often use lightweight ceramic fiber insulation. This allows for significantly faster heating and cooling rates compared to the heavier firebrick insulation found in some general-purpose chamber furnaces. This design also contributes to excellent temperature uniformity.
Sample Shape and Size
The box-like shape of a muffle furnace makes it ideal for processing batches of samples or materials with irregular shapes that would not fit easily into a tube furnace.
Cost and Complexity
A simple chamber furnace is a basic, cost-effective tool. A muffle furnace is a more specialized instrument with advanced insulation and sealing, making it a more significant investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is general heat-treating: A standard, robust chamber furnace is often the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and avoiding contamination: A muffle furnace is essential, as its core design principle is to isolate the sample.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating/cooling cycles or controlled atmospheres: The advanced insulation and sealed design of a modern muffle furnace are required.
- If your primary focus is processing large or irregularly shaped samples: The versatile box chamber of a muffle or chamber furnace is superior to the constraints of a tube furnace.
Ultimately, your choice depends on whether you simply need to apply heat or if you need to control the precise environment in which that heat is applied.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Chamber Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | General-purpose heat treatment | High-purity, controlled atmosphere processing |
| Atmosphere Control | Minimal | Excellent (vacuum, inert gas) |
| Heating/Cooling Speed | Standard (often firebrick insulation) | Fast (ceramic fiber insulation) |
| Ideal For | Hardening, annealing, tempering | Gravimetric analysis, sintering, preventing oxidation |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective | Higher investment due to specialized features |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the perfect lab equipment solutions for your specific needs. Whether you require a robust general-purpose chamber furnace or a high-purity muffle furnace for sensitive processes, we have the expertise and products to ensure your success.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and let us help you achieve precise and reliable thermal processing results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- What is dry ashing in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Mineral Analysis
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and air oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What is the structure of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components and Design
- What do you use a muffle furnace for? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing



















