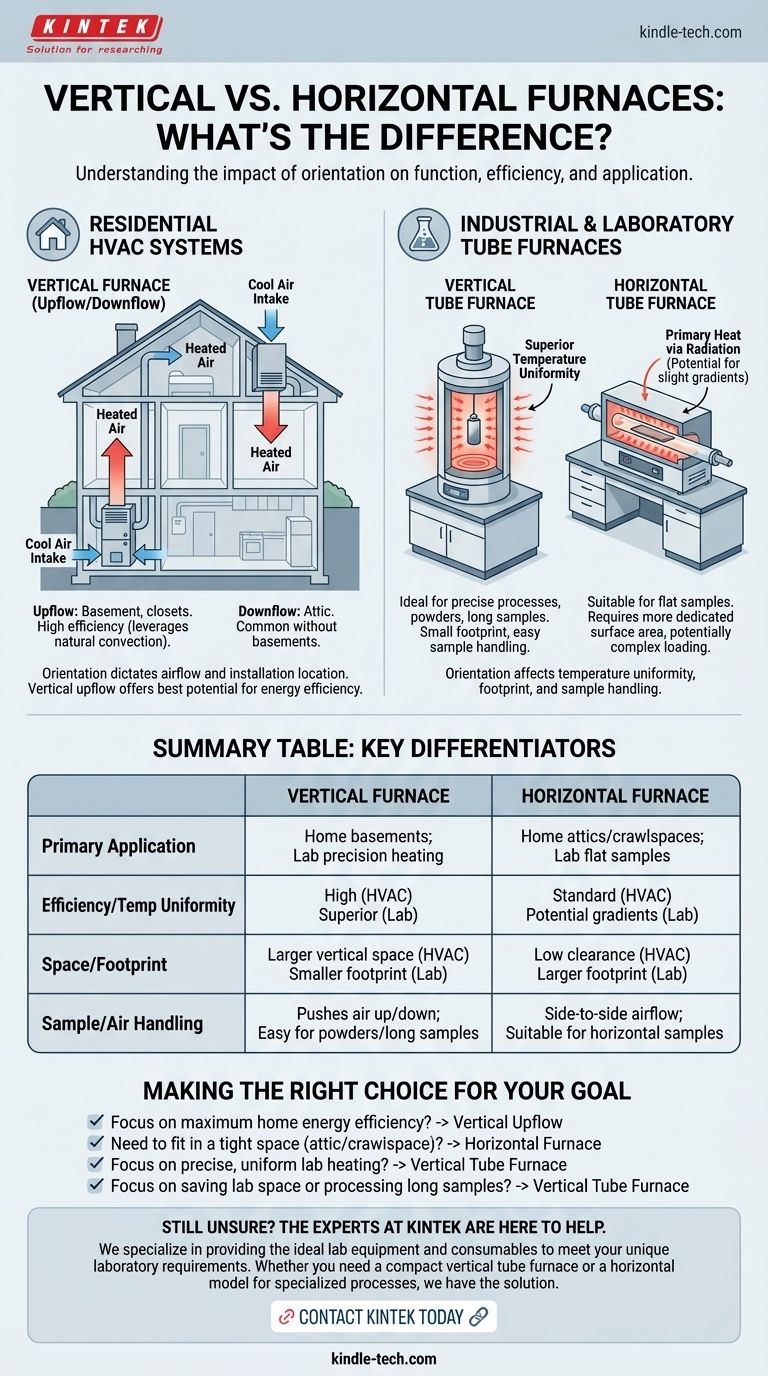
At its core, the difference between a vertical and horizontal furnace is its physical orientation and how that layout impacts its function. For residential heating, this orientation dictates airflow direction and installation location, while for industrial or lab applications, it primarily affects temperature uniformity and physical space requirements.
The choice is not about which furnace type is universally "better," but which is correctly suited for the specific task—distributing heat efficiently through a home versus achieving precise temperature control in a laboratory.

The Critical First Question: What Is Your Application?
Before comparing features, you must first distinguish between the two primary environments where these terms are used. The design principles and goals for each are fundamentally different.
For Residential HVAC Systems
In home heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), the terms refer to how the unit pushes conditioned air. The furnace's orientation determines where it can be installed in a home.
For Industrial and Laboratory Use
In technical settings, the discussion usually centers on tube furnaces. These devices provide high, precise temperatures for processes like material testing or synthesis. Here, orientation directly impacts performance and usability.
Key Differentiators: Residential Furnaces
When heating a home, the furnace's job is to move air effectively through ductwork. The orientation is a practical consideration based on your home's layout.
Vertical (Upflow/Downflow) Furnaces
An upflow furnace takes in cool air from the bottom and pushes heated air out the top. This design works with natural convection (heat rises), making it highly efficient. These are typically installed in basements or closets.
A downflow furnace does the opposite, pulling air from the top and pushing it out the bottom. This is common in homes without basements, where the furnace is located in an attic.
Horizontal Furnaces
A horizontal furnace is designed to be installed on its side. It draws air in from one side and pushes heated air out the other.
This configuration is a space-saving solution for installations in tight areas with low vertical clearance, such as crawlspaces or attics.
The Efficiency Factor
Generally, a vertical upflow furnace offers the best potential for energy efficiency. By pushing hot air upwards, it works with physics rather than against it, reducing the energy needed to circulate air throughout the home.
Key Differentiators: Industrial Tube Furnaces
In a laboratory or industrial setting, the furnace's orientation is a technical choice that affects the precision of your results.
Temperature Uniformity
Vertical tube furnaces provide superior temperature uniformity. As the heating elements surround the vertical tube, heat is transferred through both radiation and natural convection, ensuring a consistent temperature along the sample's entire length.
Horizontal tube furnaces primarily transfer heat via radiation. This can lead to slight temperature variations along the length of the tube, which may require more careful process optimization.
Physical Footprint and Space
Vertical furnaces have a much smaller footprint, making them ideal for crowded labs where floor or bench space is limited.
Horizontal furnaces are longer and require more dedicated surface area, which can be a significant factor in facility planning.
Sample Handling and Access
Loading and unloading samples is often simpler with a vertical furnace. It's particularly well-suited for powders, long samples, or materials that can be suspended.
Horizontal furnaces require samples to be positioned horizontally, which can be more complex but is necessary for processes where the material must remain flat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is without its limitations. The choice involves balancing performance requirements against practical constraints.
The Challenge with Horizontal Furnaces
The primary trade-offs for a horizontal furnace are its larger physical footprint and the potential for slight temperature gradients. While still highly effective, achieving perfect uniformity may require additional calibration.
The Limitations of Vertical Furnaces
In an HVAC context, a vertical furnace simply won't fit in a crawlspace. In a lab setting, a vertical furnace may be unsuitable for specific processes that require a horizontal sample orientation or continuous throughput of materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, align your choice with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency in a home: A vertical upflow furnace is typically the superior choice, as it leverages natural convection.
- If your primary focus is fitting a home furnace in a tight space (attic/crawlspace): A horizontal furnace is specifically designed for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is precise, uniform heating in a lab: A vertical tube furnace offers the best temperature consistency for sensitive processes.
- If your primary focus is saving lab space or processing long samples: A vertical tube furnace provides a smaller footprint and easier sample handling.
Ultimately, understanding your specific application is the key to selecting the furnace that delivers the right performance and efficiency for your needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vertical Furnace | Horizontal Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Application | Home basements; Lab precision heating | Home attics/crawlspaces; Lab processes requiring flat samples |
| Efficiency/Temp Uniformity | High (works with convection); Superior uniformity | Standard; Potential for slight gradients |
| Space/Footprint | Larger vertical space; Smaller lab footprint | Low clearance; Larger lab footprint |
| Sample/Air Handling | Pushes air up/down; Easy for powders/long samples | Side-to-side airflow; Suitable for horizontal samples |
Still unsure which furnace type is right for your specific needs? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables to meet your unique laboratory requirements. Whether you need a compact vertical tube furnace for precise temperature uniformity or a horizontal model for specialized processes, we have the solution.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation that ensures optimal performance and efficiency for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- How does an alumina tube furnace with a controlled atmosphere simulate conditions in CSP environments? Master Accuracy.
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification



















