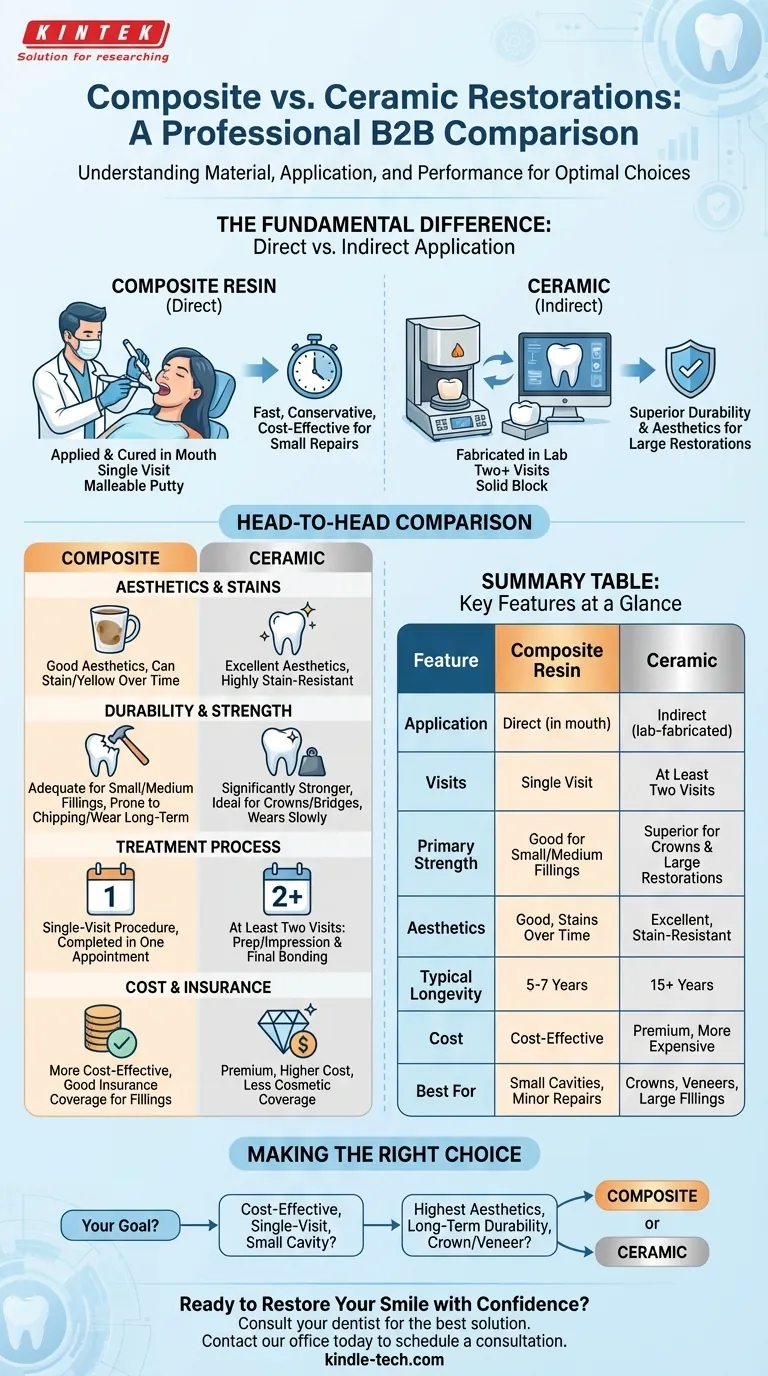
In short, the primary difference lies in the material and the application process. Composite resin is a putty-like plastic mixed with fine ceramic particles that a dentist applies directly to your tooth in a single visit. Ceramic restorations, like porcelain, are solid, custom-fabricated pieces created in a dental lab from an impression of your tooth, requiring at least two visits to place.
The choice between composite and ceramic is not about which material is universally "better," but about which is right for the specific task. Composite offers a fast, conservative, and cost-effective solution for smaller repairs, while ceramic provides superior durability and aesthetics for larger, more demanding restorations.
Material and Application: Direct vs. Indirect
The most fundamental difference between these two materials is how they are placed. This distinction, known as direct vs. indirect restoration, dictates the entire treatment process, cost, and final outcome.
What is Composite Resin? (Direct)
Composite is a blend of a plastic resin matrix and fine, glass-like filler particles. Think of it as a sophisticated, tooth-colored putty.
A dentist applies this malleable material directly onto the tooth in layers, sculpting it to the desired shape. Each layer is hardened, or "cured," in seconds using a special blue light. This is called a direct restoration because it's built entirely in your mouth.
What is Ceramic? (Indirect)
Ceramic restorations, including materials like porcelain or zirconia, are solid blocks of inorganic, non-metallic material. They are exceptionally hard and glass-like.
These restorations are fabricated outside of the mouth, earning them the name indirect restorations. The process involves the dentist preparing the tooth, taking a precise impression or digital scan, and sending it to a dental laboratory. A technician then crafts the final crown, veneer, or inlay, which is later bonded permanently to the tooth.
A Head-to-Head Comparison
Understanding the direct vs. indirect nature of these materials helps explain their key differences in performance, appearance, and cost.
Aesthetics and Stain Resistance
Ceramic is the undisputed winner for high-end aesthetics. Its translucent properties mimic the look of natural tooth enamel more closely than any other material.
Furthermore, ceramic is non-porous and acts like glass. It is highly resistant to staining from coffee, tea, or wine. Composite, being part plastic, can absorb stains over time and may discolor or yellow.
Durability and Strength
For large restorations subjected to heavy biting forces, ceramic is significantly stronger and more durable than composite. It wears down much more slowly, making it the ideal choice for crowns, bridges, and large fillings on molars.
Composite is perfectly adequate for small to medium-sized fillings but can be prone to chipping and wear in high-stress areas over the long term.
The Treatment Process
A composite filling is a single-visit procedure. You can walk out of the dental office with the entire restoration complete in one appointment.
A ceramic restoration requires at least two visits. The first is for tooth preparation and taking impressions. The second, typically a week or two later, is for bonding the final lab-fabricated piece into place.
Cost and Insurance
Composite is the more cost-effective option by a significant margin. The single-visit procedure and lower material cost make it a more accessible choice. Most dental insurance plans provide good coverage for composite fillings.
Ceramic is a premium material that involves custom lab work, making it considerably more expensive. While insurance may cover a portion of a medically necessary ceramic crown, it is less likely to cover it for purely cosmetic reasons.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material requires balancing longevity, cost, and the specific needs of your tooth.
Longevity vs. Repairability
A well-maintained ceramic restoration can last 15 years or more, while a composite restoration typically lasts 5 to 7 years.
However, if a ceramic crown chips or fractures, repairing it is complex and may require a full replacement. A chipped composite filling, on the other hand, can often be easily and seamlessly repaired by a dentist in one visit.
Preserving Healthy Tooth Structure
For a small filling, a composite restoration is often more conservative, meaning the dentist needs to remove less of your healthy tooth structure to place it.
For larger restorations like crowns or veneers, the amount of tooth preparation is often dictated by the structural or cosmetic need, and can be similar for both materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Your final decision should be made in consultation with your dentist, but you can use your goals to guide the conversation.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective, single-visit solution for a small cavity: Composite is the clear and practical choice.
- If your primary focus is the highest aesthetic quality and long-term durability for a crown, veneer, or large molar filling: Ceramic is the superior investment for strength and appearance.
- If your primary focus is repairing a minor cosmetic chip or closing a small gap: Direct composite bonding offers a conservative, immediate, and affordable fix.
- If your primary focus is replacing a large, old metal filling with a strong, tooth-colored alternative: A ceramic inlay or onlay provides superior strength and longevity compared to a large composite.
Understanding these key differences empowers you to collaborate with your dentist on the best solution for your health, budget, and smile.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Composite Resin | Ceramic (Porcelain/Zirconia) |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Direct (applied in mouth) | Indirect (lab-fabricated) |
| Visits Required | Single visit | At least two visits |
| Primary Strength | Good for small/medium fillings | Superior for crowns & large restorations |
| Aesthetics & Stains | Good, but can stain over time | Excellent, highly stain-resistant |
| Typical Longevity | 5-7 years | 15+ years |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Premium, more expensive |
| Best For | Small cavities, minor repairs | Crowns, veneers, large fillings |
Ready to Restore Your Smile with Confidence?
Choosing the right restoration material is key to a long-lasting, healthy, and beautiful smile. Your dentist will recommend the best option based on your specific needs, the location of the tooth, and your cosmetic goals.
Have more questions or ready to discuss your dental restoration options?
Contact our office today to schedule a consultation. We'll help you achieve the optimal result for your oral health and confidence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















