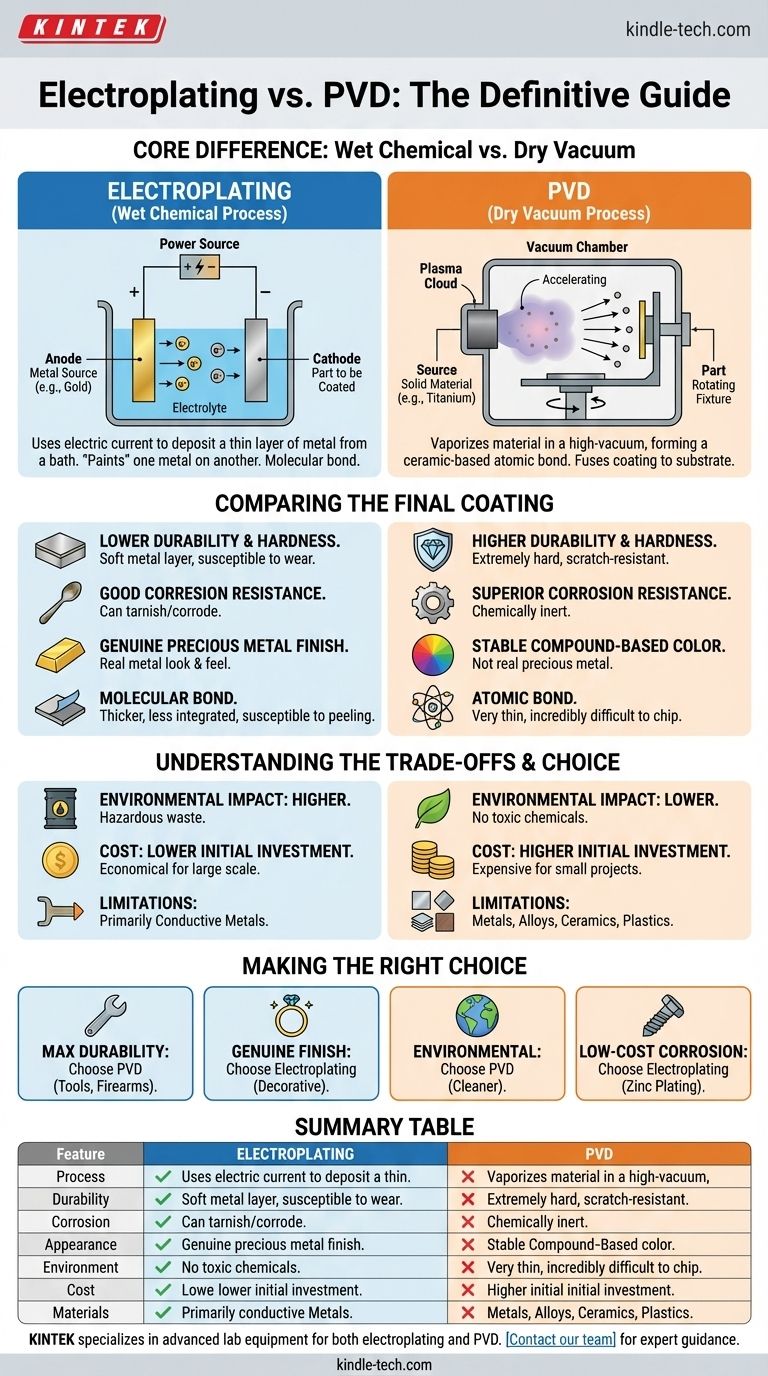
At its core, the difference is simple. Electroplating is a wet chemical process that uses an electric current to deposit a thin layer of metal onto a surface. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a modern vacuum process that molecularly bonds a durable, ceramic-based compound to a surface, creating a finish that is far harder and more resistant to wear.
While both processes apply a thin coating to a substrate, they are fundamentally different. Electroplating is an older, chemical-based method best for achieving a true precious metal finish, whereas PVD is a high-tech vacuum process engineered for superior durability, hardness, and corrosion resistance.

The Fundamental Process: Wet vs. Dry
The most significant distinction lies in how the coating is applied. One is a chemical bath, and the other is a high-tech vacuum chamber.
How Electroplating Works (The Chemical Bath)
Electroplating involves submerging the part to be coated (the cathode) and a solid piece of the plating metal (the anode) into an electrolyte solution.
When an electrical current is passed through the bath, it causes metal ions from the anode to dissolve and then deposit onto the surface of the part. This method essentially "paints" a thin layer of one metal on top of another.
How PVD Works (The Vacuum Chamber)
PVD is a dry process conducted in a high-vacuum environment. A solid source material (like titanium or zirconium) is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules.
An electric field accelerates these particles toward the part being coated, where they condense and form a thin, extremely dense, and highly-adhered film. It's less like painting and more like fusing the coating to the substrate at an atomic level.
Comparing the Final Coating
The differences in process lead to vastly different characteristics in the final product. Understanding these is critical for choosing the right application.
Durability and Hardness
PVD is significantly harder and more durable than electroplating. The PVD process creates a ceramic-based coating, such as titanium nitride, that is exceptionally resistant to scratches and abrasion.
An electroplated coating is simply a thin layer of metal (like gold or chrome), which is much softer and can wear away with friction over time.
Corrosion and Tarnish Resistance
PVD offers superior resistance to corrosion, sweat, and tarnish. The compounds used in PVD are chemically inert and do not react with air, water, or most chemicals.
Electroplated finishes, especially those using metals like silver or nickel, can tarnish or corrode over time, exposing the base metal underneath.
Color and Appearance
Electroplating provides a genuine metal finish. For example, gold electroplating deposits a layer of real gold, giving it that authentic look and feel.
PVD achieves its color through the specific compound used, not a precious metal. A gold-colored PVD finish is typically from titanium nitride. While this color is incredibly stable and won't fade, it is not "real" gold.
Adhesion and Thickness
PVD coatings form an atomic bond with the substrate, making them incredibly difficult to chip or flake. These coatings are typically very thin, often measured in microns.
Electroplating creates a molecular bond. While often applied thicker than PVD, this bond is less integrated, making the coating more susceptible to peeling or wearing through over its lifetime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; the choice depends on your priorities regarding cost, environmental impact, and specific application needs.
Environmental Impact
PVD is a far more environmentally friendly process. It produces no hazardous waste and does not use toxic chemicals.
Electroplating, by contrast, relies on chemical baths that often contain heavy metals and hazardous substances like cyanide. The disposal of this chemical waste is a significant environmental concern and regulatory burden.
Cost Implications
PVD has a high initial investment cost for the vacuum chamber and related equipment. This can make it more expensive for small, one-off projects.
Electroplating is a more mature technology with lower equipment costs, often making it more economical for large-scale production of parts where extreme durability is not the primary concern.
Material Limitations
PVD can be applied to a very wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, ceramics, and some plastics.
Electroplating is generally limited to coating conductive metal substrates, as the process relies on passing an electric current through the part itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision comes down to balancing the requirements for performance, aesthetics, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity: PVD is the definitive choice for items like high-end watches, tools, firearms, and plumbing fixtures.
- If your primary focus is a genuine precious metal finish: Electroplating is the traditional and expected method for decorative items or certain types of jewelry.
- If your primary focus is environmental responsibility: PVD is the far superior and cleaner option.
- If your primary focus is low-cost corrosion protection for industrial parts: Certain types of electroplating, like zinc plating on fasteners, remain the cost-effective industry standard.
Choosing the right coating is about aligning the process with your product's purpose and performance expectations.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electroplating | PVD |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Wet Chemical (Electrolytic Bath) | Dry Vacuum (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
| Durability/Hardness | Lower (Soft Metal Layer) | Higher (Hard Ceramic Coating) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, but can tarnish | Superior, chemically inert |
| Appearance | Genuine Precious Metal Finish | Stable Compound-Based Color |
| Environmental Impact | Higher (Hazardous Waste) | Lower (No Toxic Chemicals) |
| Cost | Lower Initial Investment | Higher Initial Investment |
| Material Compatibility | Primarily Conductive Metals | Metals, Alloys, Ceramics, Plastics |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right coating technology for your laboratory or manufacturing process?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for both electroplating and PVD applications. Our experts can help you choose the optimal solution to enhance durability, improve performance, and meet your specific project requirements.
Contact our team today to discuss your coating needs and discover how KINTEK can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















