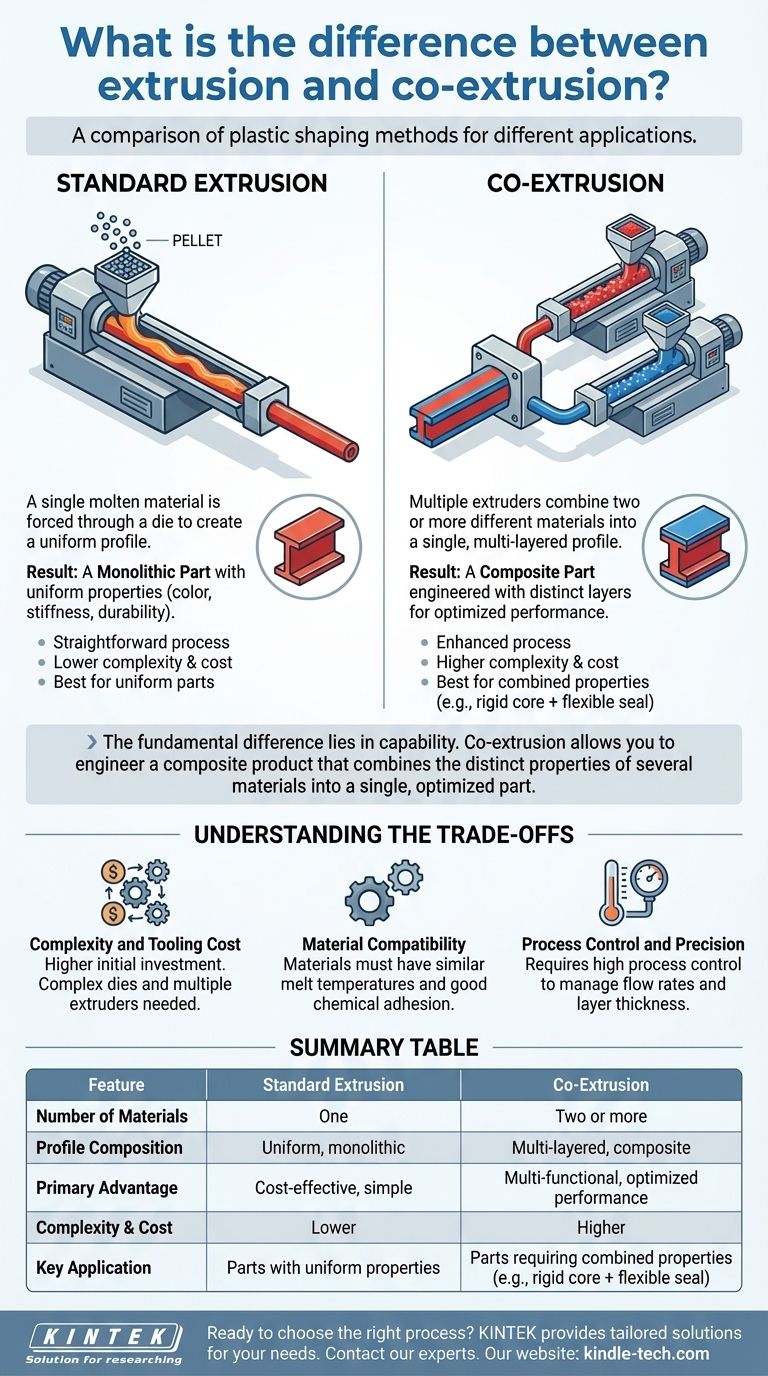
While both are methods for shaping plastic, the essential difference is one of composition. Standard extrusion forces a single molten material through a die to create a uniform profile. In contrast, co-extrusion uses multiple extruders to combine two or more different materials into a single, multi-layered profile before they exit the die.
The fundamental difference lies in capability. While standard extrusion creates a uniform product from one material, co-extrusion allows you to engineer a composite product that combines the distinct properties of several materials—such as rigidity, color, and weather resistance—into a single, optimized part.

The Foundation: How Standard Extrusion Works
Standard extrusion is a straightforward, continuous process for creating parts with a fixed cross-sectional profile. It is a foundational technology in plastics manufacturing.
The Core Process: From Pellet to Profile
Solid plastic pellets are fed from a hopper into a long, heated barrel. Inside the barrel, a rotating screw melts the plastic through friction and heat, simultaneously pushing the molten material forward.
This process is analogous to a sophisticated meat grinder or pasta maker. The molten plastic is forced under pressure through a precisely shaped die, emerging as a continuous profile that is then cooled and cut to length.
The Result: A Monolithic Part
The final product from standard extrusion is monolithic, meaning it is composed of a single, uniform material. Its properties—such as color, stiffness, and durability—are consistent throughout the entire part.
The Evolution: How Co-Extrusion Expands Capability
Co-extrusion is not a different process but an enhancement of standard extrusion. It leverages the same core principles but multiplies the capability by introducing more materials.
The Principle of Multi-Material Flow
Co-extrusion uses two or more extruders, each melting and pressurizing a different material. These separate streams of molten plastic are brought together in a special co-extrusion die.
The die is engineered to combine these streams just before they exit, forming a single, cohesive profile where the materials are bonded together but remain as distinct layers.
Key Applications of Combining Materials
This ability to combine materials unlocks significant performance and cost advantages.
For example, a rigid PVC can be used for a product's structural core while a thin outer layer of flexible PVC provides a soft-touch surface or an integrated seal.
Another common use is applying a thin, expensive, UV-resistant "cap stock" over a thicker core made from cheaper or recycled material. This provides excellent weather resistance without the cost of making the entire part from the premium material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, co-extrusion introduces complexities that are not present in standard extrusion. Choosing the right process requires understanding these trade-offs.
Complexity and Tooling Cost
Co-extrusion requires multiple extruders and a significantly more complex, and therefore expensive, die. The initial investment and setup costs are higher than for a single-material extrusion line.
Material Compatibility is Crucial
The materials being combined must be compatible. They need to have similar melt temperatures to process correctly in the die, and they must have good chemical adhesion to bond securely to one another. Poor bonding can lead to delamination and product failure.
Process Control and Precision
Managing the flow rates and temperatures of multiple materials simultaneously requires a higher degree of process control and operator expertise. Maintaining consistent layer thickness and adhesion is a critical engineering challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between extrusion and co-extrusion is driven entirely by the functional requirements and cost targets of your final product.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective part with uniform properties: Standard extrusion is almost always the correct and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a part with multiple functions: Co-extrusion is essential for combining different material properties, like a rigid frame with a flexible hinge or seal.
- If your primary focus is optimizing cost and durability: Co-extrusion allows you to place expensive, high-performance materials only where they are needed, such as on an exposed surface, while using a lower-cost core.
Ultimately, the choice depends on whether your product's requirements can be met by one material or demand the engineered synergy of several.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Extrusion | Co-Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Materials | One | Two or more |
| Profile Composition | Uniform, monolithic | Multi-layered, composite |
| Primary Advantage | Cost-effective, simple | Multi-functional, optimized performance |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Key Application | Parts with uniform properties | Parts requiring combined properties (e.g., rigid core + flexible seal) |
Ready to choose the right process for your plastic profile?
Whether you need a simple, single-material extrusion or a complex multi-layer co-extrusion, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to bring your project to life. Our team specializes in providing tailored solutions for laboratory and industrial plastic processing needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your material properties, performance goals, and cost targets. Let us help you engineer the perfect part.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of blowing film? A Guide to Biaxial Orientation and Stronger Plastic Films
- What are the advantages of coextrusion? Achieve Multi-Material Efficiency and Superior Performance
- What machine is used to make pellets? The Complete Guide to Pellet Mills & Production Systems
- What are the advantages of waste plastic pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Valuable Fuel and Chemicals
- What is the screw extrusion process? A Guide to Continuous Plastic Profiling



















