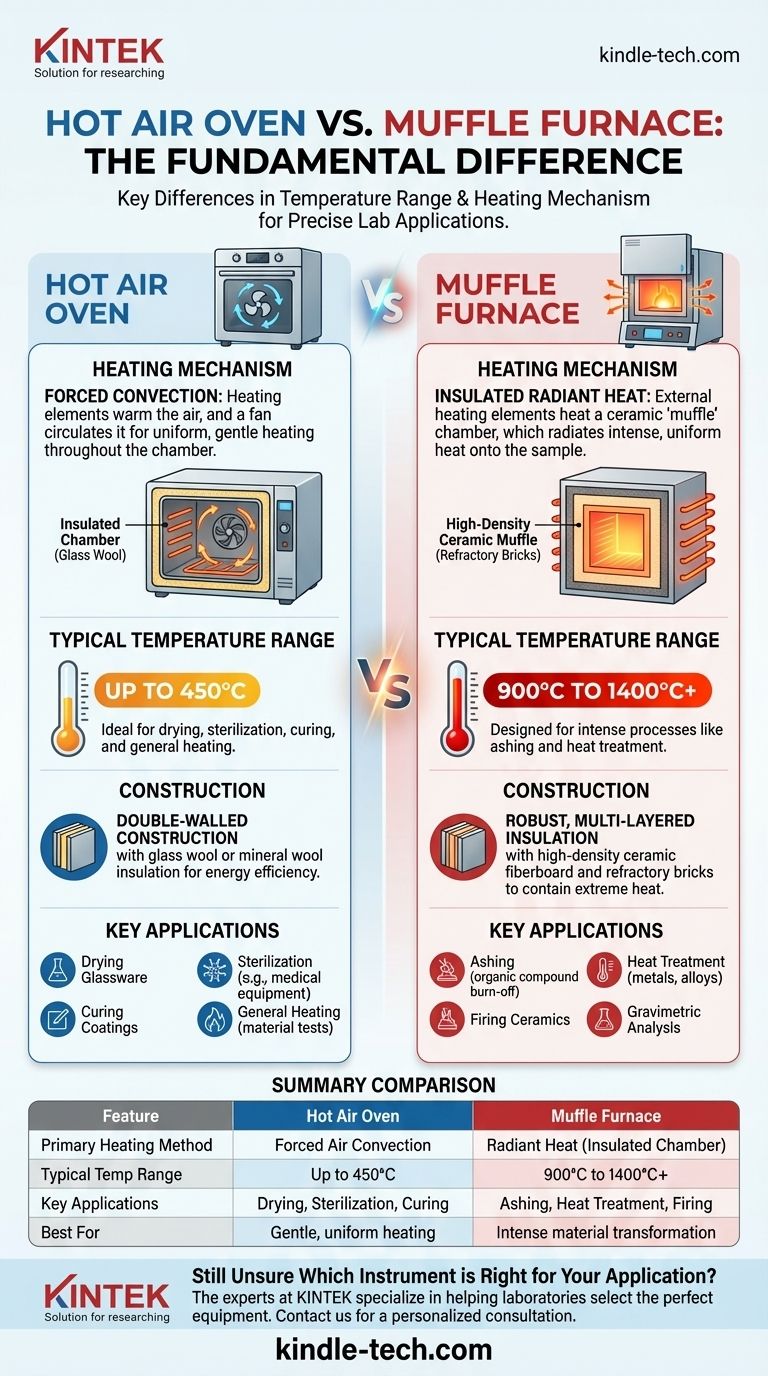
At a fundamental level, the primary difference between a hot air oven and a muffle furnace is their operational temperature range and the underlying heating mechanism. A hot air oven is a lower-temperature device, typically operating up to 450°C, used for drying and sterilization via circulated air. In contrast, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature unit reaching 900°C to 1400°C, designed for intense processes like ashing and heat treatment using radiant heat in a heavily insulated chamber.
The choice is not about which is "better," but which is correct for the task. Hot air ovens use forced air convection for uniform, gentle heating, while muffle furnaces use intense radiant heat to fundamentally transform materials at extreme temperatures.

The Core Difference: Heating Mechanism and Temperature
The distinct applications for these two instruments stem directly from how they generate and apply heat.
The Hot Air Oven: Forced Convection
A hot air oven functions much like a high-precision kitchen convection oven. It uses heating elements to warm the air inside the chamber.
A fan then actively circulates this hot air, ensuring a highly uniform and stable temperature throughout the interior. This method is ideal for processes that require gentle and consistent heating.
The typical maximum temperature for a hot air oven is around 300°C to 450°C.
The Muffle Furnace: Insulated Radiant Heat
A muffle furnace generates far more intense heat by using a completely different principle. Its heating elements are positioned on the outside of the main sample chamber.
This chamber, known as the "muffle," is made of a high-temperature ceramic material. The external elements heat the muffle, which then radiates intense, uniform heat onto the sample inside.
This design isolates the sample from direct exposure to the heating elements, preventing contamination from combustion byproducts. It also allows the furnace to safely reach extreme temperatures, typically from 900°C up to 1400°C or even higher.
How Construction Dictates Function
The vast temperature difference necessitates radically different designs and materials.
Oven Insulation and Design
A hot air oven typically features a double-walled construction. The space between the inner and outer walls is filled with an insulator like glass wool or mineral wool.
This level of insulation is sufficient for its lower operating temperatures, keeping the exterior relatively cool and maintaining energy efficiency.
Furnace Insulation and Design
A muffle furnace requires a much more robust, multi-layered insulation system to contain its extreme heat.
It is built with heavy-gauge steel and lined with high-density ceramic fiberboard and refractory bricks. This ensures the outer casing remains safe to touch and that the heat is focused inside the chamber for maximum efficiency. The door is also significantly thicker and heavier to prevent heat loss.
Understanding the Applications and Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong instrument can ruin a sample, create a safety hazard, or simply fail to produce the desired result.
When to Use a Hot Air Oven
A hot air oven is the standard choice for low-temperature thermal processing. Its uniform, gentle heat is ideal for:
- Drying: Removing moisture from lab glassware, chemical powders, or paper.
- Sterilization: Sterilizing heat-stable medical or laboratory equipment.
- Curing: Hardening coatings, adhesives, and polymers at controlled temperatures.
- General Heating: Performing material tests or aging components at moderately elevated temperatures.
When to Use a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is purpose-built for high-temperature material transformation. Common applications include:
- Ashing: Burning off all organic compounds in a sample to determine the weight of the inorganic residue (ash). This is critical in food, soil, and materials analysis.
- Heat Treatment: Altering the properties of metals and alloys through processes like hardening, annealing, and tempering.
- Firing Ceramics: Turning clay and other ceramic materials into a finished, hardened state.
- Gravimetric Analysis: Separating components of a sample by vaporizing them at high temperatures.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The most common mistake is attempting a high-temperature application in an oven or a low-temperature one in a furnace.
Using a hot air oven for ashing will fail, as it cannot reach the necessary temperatures to fully combust the material.
Conversely, using a massive muffle furnace to simply dry glassware at 105°C is extremely inefficient and a waste of energy and time, as the furnace takes much longer to heat up and cool down.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct instrument, focus entirely on the temperature and process requirements of your specific task.
- If your primary focus is sterilization, drying, or gentle heating below 450°C: A hot air oven is the correct, safe, and energy-efficient tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is determining ash content, heat-treating metals, or any process requiring temperatures above 900°C: A muffle furnace is the only suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is protecting a sample from atmospheric contamination during heating: The isolated chamber of a muffle furnace offers a distinct advantage, as it can be adapted for use with inert gases.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference in their heating principles empowers you to select the precise tool needed for accurate and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Heating Method | Forced Air Convection | Radiant Heat (Insulated Chamber) |
| Typical Temperature Range | Up to 450°C | 900°C to 1400°C+ |
| Key Applications | Drying, Sterilization, Curing | Ashing, Heat Treatment, Firing Ceramics |
| Best For | Gentle, uniform heating at lower temperatures | Intense processes that transform materials at high temperatures |
Still Unsure Which Instrument is Right for Your Application?
Choosing between a hot air oven and a muffle furnace is critical for achieving accurate, repeatable results. The experts at KINTEK specialize in helping laboratories like yours select the perfect equipment for specific thermal processing needs, from sterilization and drying to high-temperature ashing and heat treatment.
We provide reliable, high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to ensure your lab's efficiency and success.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and let us help you make the right choice for your lab's unique requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of a furnace? A Guide to Heating, Comfort, and Material Transformation
- What is a muffle furnace? The Definitive Tool for Contaminant-Free, Precise Heating
- What is the heating element of a muffle furnace? The Engine for High-Temp Precision
- Why is it called a muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Heating
- What is the muffle furnace method? A Guide to Clean, High-Temperature Processing



















