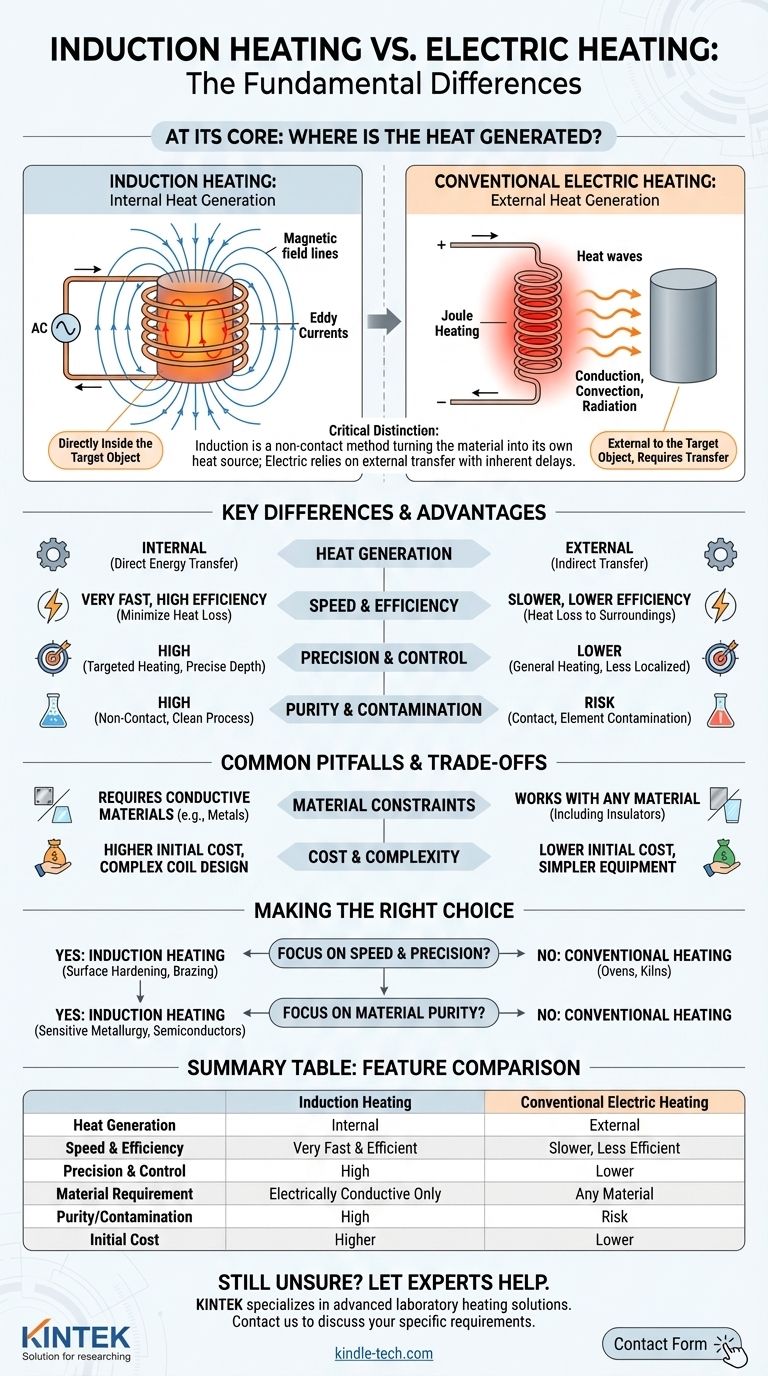
At its core, the difference between induction heating and other forms of electric heating is where the heat is generated. Conventional electric heating uses a resistive element to get hot and then transfers that heat to a target object. Induction heating uses a magnetic field to generate heat directly inside the target object itself, making the object its own heating element.
The critical distinction is that induction heating is a non-contact method that turns a conductive material into its own heat source. This offers a level of speed, precision, and purity that is fundamentally different from traditional electric heating methods that rely on external heat transfer.

How Conventional Electric Heating Works
Conventional or "resistive" heating is the most common form of electric heating we encounter daily, from a kitchen stove to an industrial furnace.
The Principle of Resistance
This method works by passing an electric current through a material with high electrical resistance, often called a heating element.
As electrons struggle to flow through this resistive material, they release energy in the form of heat. This phenomenon is known as Joule heating.
The Role of Heat Transfer
The heat generated in the element must then be transferred to the target workpiece. This happens through conduction (direct contact), convection (air or fluid movement), or radiation (infrared energy). This is an indirect process with inherent delays and energy loss.
How Induction Heating Works
Induction heating is a more advanced process that leverages the principles of electromagnetism to deliver energy with exceptional precision.
The Core Mechanism: A Magnetic Field
An induction system uses a coil through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
Generating Internal Heat: Eddy Currents
When an electrically conductive workpiece is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces circulating electrical currents inside the material. These are known as eddy currents.
The Result: Instant, Direct Heating
The material's own internal resistance fights against the flow of these eddy currents. This internal resistance generates intense, localized heat—the same Joule heating effect, but occurring directly inside the part itself, not in an external element.
Understanding the Key Differences
The distinction between generating heat externally versus internally has significant practical consequences for industrial applications.
Heat Generation: Internal vs. External
This is the central difference. Induction creates heat within the workpiece, while resistive methods create heat outside of it and must transfer it in.
Speed and Efficiency
Induction is significantly faster and more energy-efficient. Energy is delivered directly where it's needed, minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment and equipment. Startup is nearly instantaneous.
Precision and Control
The magnetic field can be precisely controlled by the coil's shape and location. This allows for highly targeted heating of specific areas of a part, to a specific depth, without affecting the rest of the component.
Purity and Contamination
Because induction is a non-contact process, it is exceptionally clean. As the provided research notes, it is ideal for melting high-purity metals or low-carbon steel in a vacuum furnace, as there are no graphite electrodes or flames to introduce carbon or other impurities.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Material Constraints
The primary requirement for induction heating is that the target material must be electrically conductive. It is not an effective method for heating insulators like ceramics, plastics, or glass.
Cost and Complexity
Induction heating systems, including their specialized power supplies and custom-designed copper coils, typically have a higher initial capital cost than simpler resistive heating equipment.
Geometric Dependence
The efficiency of the process is highly dependent on the shape of the workpiece and its proximity to the coil. Achieving uniform heating on complex geometries often requires sophisticated coil design and testing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct technology requires a clear understanding of your application's primary driver.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, precision heating of conductive parts: Induction is the superior choice for its direct energy transfer, repeatability, and control, ideal for tasks like surface hardening or brazing.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating or processing non-conductive materials: Conventional resistive heating offers greater versatility and a lower initial cost for applications like ovens and kilns.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute material purity: The non-contact nature of induction heating makes it the only viable choice for many sensitive metallurgical and semiconductor applications.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental physics of how each method generates heat empowers you to select the tool that perfectly matches the task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Heating | Conventional Electric Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Internal (within the workpiece) | External (via heating element) |
| Speed & Efficiency | Very fast and highly efficient | Slower, with heat loss to surroundings |
| Precision & Control | High (targeted heating possible) | Lower (general heating) |
| Material Requirement | Electrically conductive materials only | Any material |
| Purity/Contamination | High (non-contact process) | Risk from heating elements or atmosphere |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
Still Unsure Which Heating Method is Right for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory heating solutions, from high-precision induction systems for metal processing to versatile electric furnaces for general-purpose use. Our experts can help you select the perfect equipment to achieve the speed, control, and purity your work demands.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let us help you optimize your process. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere

















