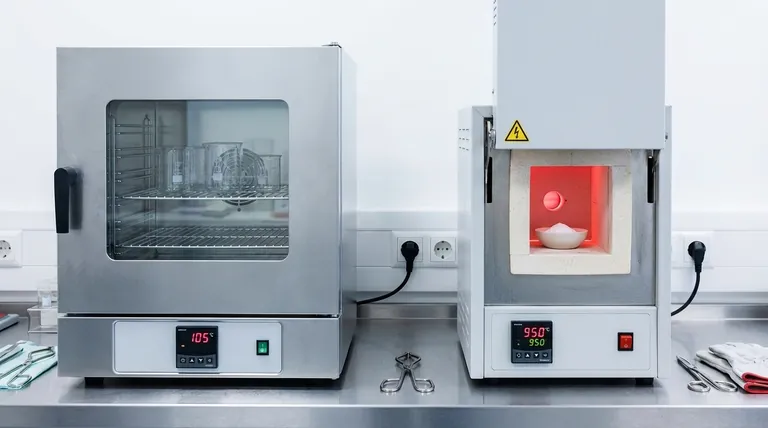
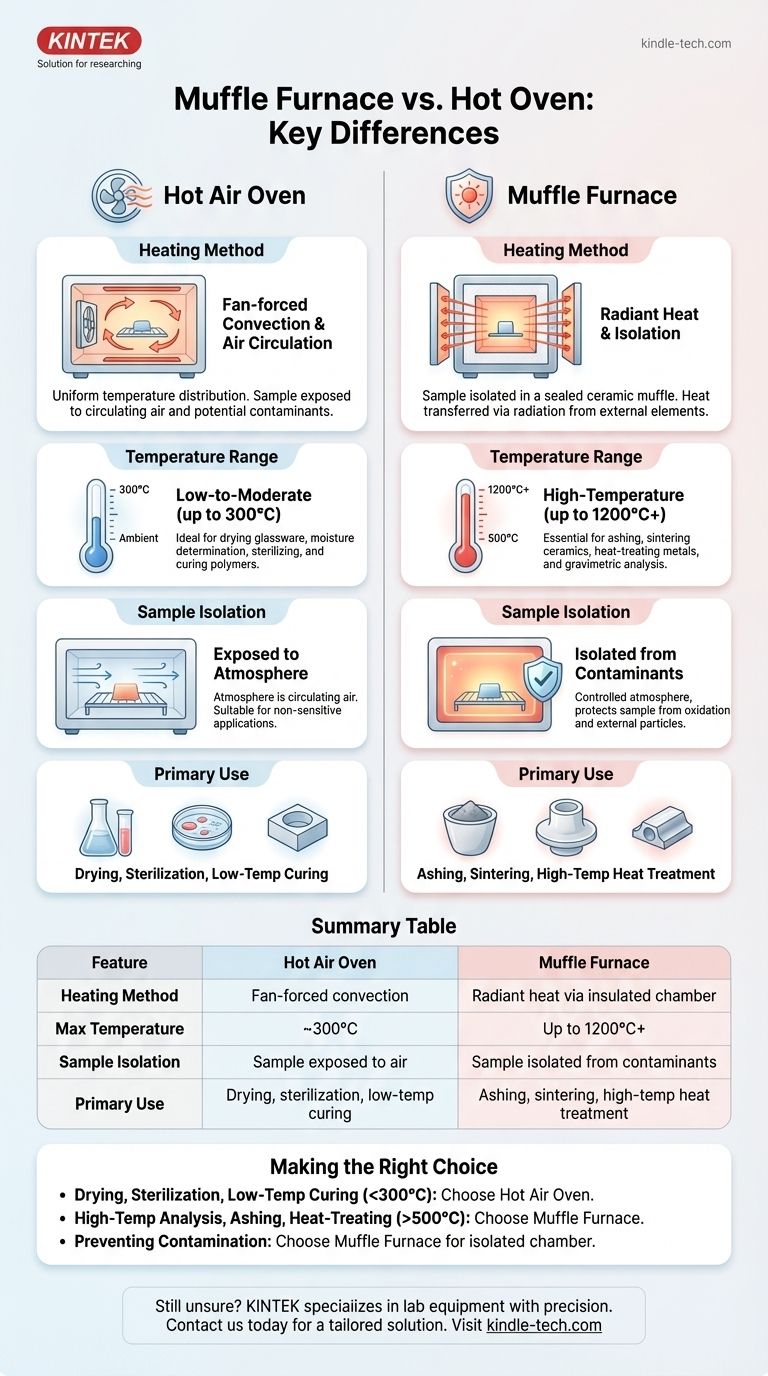
At its core, the difference between a muffle furnace and a hot air oven comes down to three factors: heating method, temperature range, and sample isolation. A hot air oven uses fan-forced convection to heat samples up to around 300°C in a circulating air environment. In contrast, a muffle furnace uses shielded radiant heating elements to reach much higher temperatures (often over 1000°C) while protecting the sample from contamination inside a sealed chamber.
While both are used for thermal processing, a hot air oven is a general-purpose tool for low-temperature heating and drying, whereas a muffle furnace is a specialized instrument for high-temperature applications that require a controlled, contaminant-free atmosphere.

The Fundamental Difference: Heating Method and Atmosphere
The most significant distinction lies in how each device transfers heat to the sample and what surrounds the sample during the process.
Hot Air Ovens: Convection and Air Circulation
A hot air oven operates much like a kitchen convection oven. It uses heating elements to warm the air inside its chamber, and a fan actively circulates this hot air.
This method ensures a relatively uniform temperature distribution throughout the chamber. However, it also means the sample is in direct contact with the circulating air and any potential contaminants it carries.
Muffle Furnaces: Radiant Heat and Isolation
A muffle furnace gets its name from the "muffle"—a high-temperature ceramic chamber that contains the sample. The heating elements are located outside this chamber.
Heat is transferred to the muffle via radiation, and the muffle, in turn, radiates heat to the sample. This design isolates the sample from the heating elements and any gaseous byproducts, preventing contamination. This is critical for sensitive chemical analyses.
Comparing Key Operational Parameters
Understanding the heating method helps explain the vast differences in application and capability between the two instruments.
Temperature Range
Hot air ovens are designed for low-to-moderate temperature applications. Their typical operating range is from slightly above ambient temperature up to 250°C or 300°C.
Muffle furnaces are built for high-temperature work. Standard laboratory models easily reach 1000°C to 1200°C, with specialized units capable of achieving 1800°C or more.
Atmosphere and Contamination Control
In a hot air oven, the atmosphere is simply air. This is suitable for many tasks but is a significant drawback if the sample can react with oxygen or be contaminated by airborne particles.
The sealed chamber of a muffle furnace provides a controlled atmosphere. It protects the sample from oxidation and external contaminants, which is essential for processes like ashing or quantitative analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
Choosing the wrong instrument can ruin an experiment or process. The decision hinges entirely on your temperature and atmospheric requirements.
When to Choose a Hot Air Oven
A hot air oven is the ideal and most cost-effective choice for general laboratory heating.
Common applications include drying glassware, performing moisture determination, sterilizing equipment, and curing polymers or epoxies that require uniform heat below 300°C.
When to Choose a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is indispensable for high-temperature material science and analytical chemistry.
Its primary uses include ashing (burning off organic material to measure inorganic content), sintering ceramics, heat-treating metals (annealing, hardening), and performing gravimetric analysis.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Never attempt to use a standard hot air oven for ashing. The temperatures are insufficient, and the lack of isolation will lead to inaccurate results.
Conversely, using an expensive muffle furnace for simple glassware drying is inefficient and unnecessary. The tool must match the task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilization, or low-temperature curing (below 300°C): A hot air oven provides efficient and uniform heating for general-purpose tasks.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature analysis, ashing, or heat-treating metals (above 500°C): A muffle furnace is required for its superior temperature capability and performance.
- If your primary focus is preventing any contamination of your sample during heating: The isolated chamber of a muffle furnace makes it the only suitable choice, regardless of temperature.
Ultimately, selecting the right thermal processing tool starts with a clear understanding of its core design and intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Fan-forced convection | Radiant heat via an insulated chamber |
| Max Temperature | ~300°C | Up to 1200°C+ |
| Sample Isolation | Sample exposed to air | Sample isolated from contaminants |
| Primary Use | Drying, sterilization, low-temperature curing | Ashing, sintering, high-temperature heat treatment |
Still unsure which thermal processing tool is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and expertise. Whether you require the uniform, low-temperature heating of a hot air oven for drying and sterilization, or the high-temperature, contaminant-free environment of a muffle furnace for ashing and sintering, we have the right solution for you.
Our team can help you select the perfect instrument to enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let us provide you with a tailored solution. Reach out now via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the results of calcination? A Guide to Purification and Material Transformation
- What PPE is required for a muffle furnace? Essential Gear for High-Temperature Safety
- What is a muffle oven used for? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment and Analysis
- What are the different types of ash analysis? Dry vs. Wet Ashing Methods Explained
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating



















