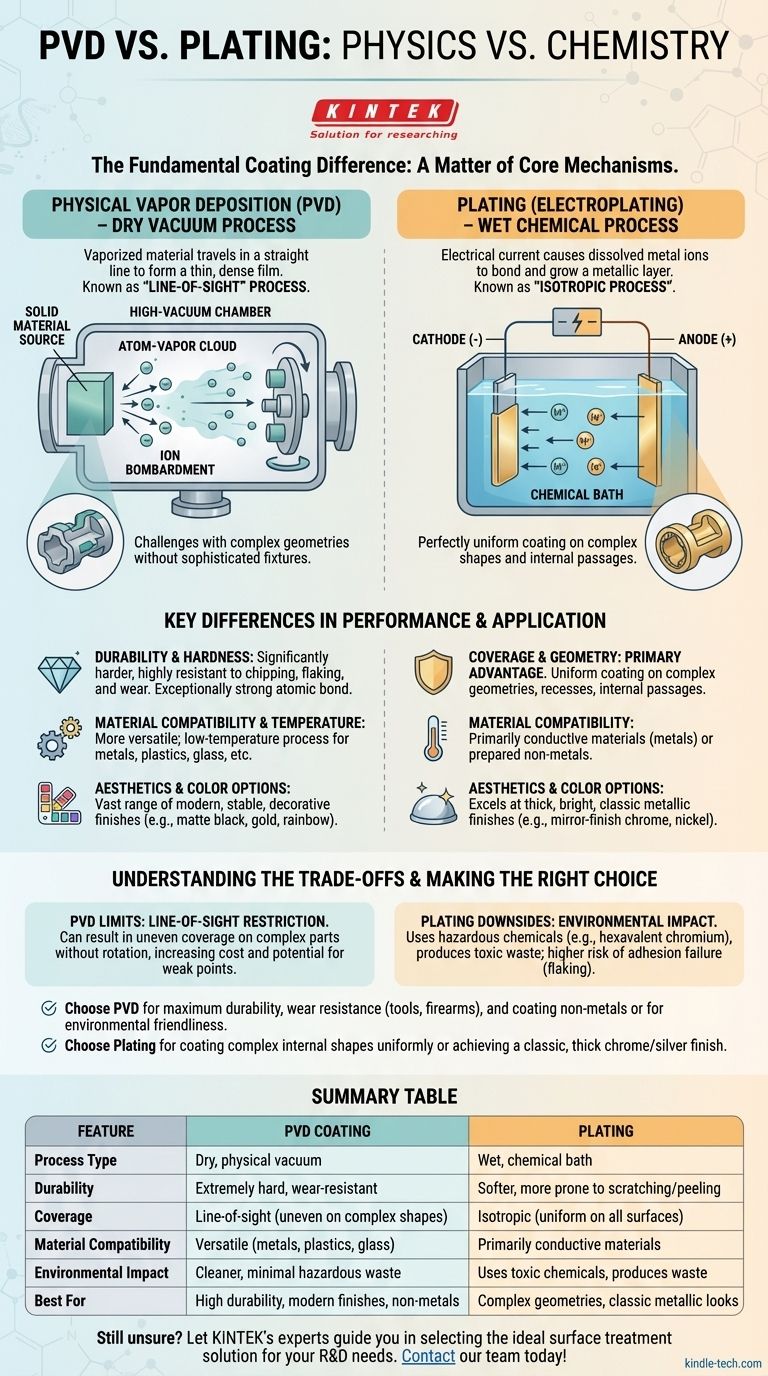
At its core, the difference between PVD and plating is a matter of physics versus chemistry. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a dry vacuum process that physically deposits a thin film of material onto a surface, atom by atom. Traditional plating, or electroplating, is a wet chemical process that uses an electrical current in a liquid bath to grow a layer of metal onto a conductive part.
The central decision between PVD and plating is a trade-off. You must choose between PVD's superior hardness and material versatility versus plating's ability to uniformly coat complex shapes with a thick, classic metallic finish.

How Each Process Fundamentally Works
To understand which method is right for your application, you must first grasp the fundamental difference in how the coating is applied.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Vacuum-Based Film
PVD takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. A solid source material is vaporized by a physical process, such as sputtering (bombarding it with ions).
This vaporized material then travels in a straight line through the vacuum and condenses on the target object, forming a very thin, dense, and highly adherent film.
Because the material travels in a straight line, PVD is known as a "line-of-sight" process. Any surface not directly exposed to the vapor source will not be coated.
Plating: A Chemical Bath Process
Plating occurs in a liquid chemical solution. In the most common method, electroplating, the object to be coated is submerged in the bath and acts as the cathode (negative electrode).
An electrical current is passed through the solution, causing dissolved metal ions to migrate and bond to the object's surface, effectively "growing" a metallic layer.
Because the object is fully immersed, this is an isotropic process. The coating forms uniformly on all surfaces the liquid can touch, including complex internal channels and holes.
Key Differences in Performance and Application
The differences in process lead to vastly different outcomes in durability, appearance, and suitable use cases.
Durability and Hardness
PVD coatings are significantly harder, more durable, and more corrosion-resistant than most plated finishes. The atomic bond created in the PVD process is exceptionally strong, making it highly resistant to chipping, flaking, and wear.
Plating, while protective, is a softer layer that is more susceptible to scratching and can peel if the surface preparation or process is flawed.
Coverage and Geometry
This is plating's primary advantage. Its isotropic nature ensures a perfectly uniform coating on parts with complex geometries, deep recesses, or internal passages.
PVD’s line-of-sight nature makes it challenging to coat complex shapes evenly without sophisticated fixtures to rotate the part during the process.
Material Compatibility and Temperature
PVD is more versatile. It is a low-temperature process that can be used to coat a wide range of materials, including plastics, glass, and heat-sensitive metals, in addition to standard steels and alloys.
Electroplating generally requires the substrate to be electrically conductive, limiting its application to metals or specially prepared non-metals.
Aesthetics and Color Options
PVD offers a vast range of modern, decorative finishes (e.g., matte black, gold, rose gold, bronze, and even iridescent rainbow colors) that are highly stable.
Plating excels at producing thick, bright, classic metallic finishes, such as mirror-finish chrome, nickel, or silver.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; choosing the wrong one for your goal can lead to failure.
The Limits of PVD
The primary drawback is the "line-of-sight" restriction. Without careful part rotation, it can result in uneven or incomplete coverage on complex parts, leading to weak points for wear and corrosion. This added complexity can increase costs.
The Downsides of Plating
The most significant concern with traditional plating is its environmental impact. The process often uses hazardous chemicals (like hexavalent chromium) and produces toxic waste that requires careful disposal. Furthermore, adhesion failure, resulting in flaking or peeling, is a more common failure mode than with PVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements should dictate your choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and wear resistance: Choose PVD for its superior hardness and adhesion, ideal for tools, firearms, and high-end watches.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal shapes uniformly: Choose plating, as the liquid bath will provide perfect coverage where a line-of-sight process cannot.
- If your primary focus is a classic, thick chrome or silver finish: Plating is the traditional and most effective method for achieving this specific aesthetic.
- If your primary focus is environmental friendliness or coating non-metals: PVD is the cleaner, more versatile process suitable for plastics, composites, and other materials.
Understanding the core mechanism—a physical film versus a chemical bath—is the key to selecting the right coating for your specific need.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Dry, physical vacuum process | Wet, chemical bath process |
| Durability | Extremely hard, wear-resistant | Softer, more prone to scratching/peeling |
| Coverage | Line-of-sight (uneven on complex shapes) | Isotropic (uniform on all surfaces) |
| Material Compatibility | Versatile (metals, plastics, glass) | Primarily conductive materials |
| Environmental Impact | Cleaner, minimal hazardous waste | Uses toxic chemicals, produces waste |
| Best For | High durability, modern finishes, non-metals | Complex geometries, classic metallic looks |
Still unsure which coating process is best for your parts? Let KINTEK's experts guide you. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables for surface treatment R&D, helping you select the ideal PVD or plating solution for enhanced durability, performance, and aesthetics. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts



















