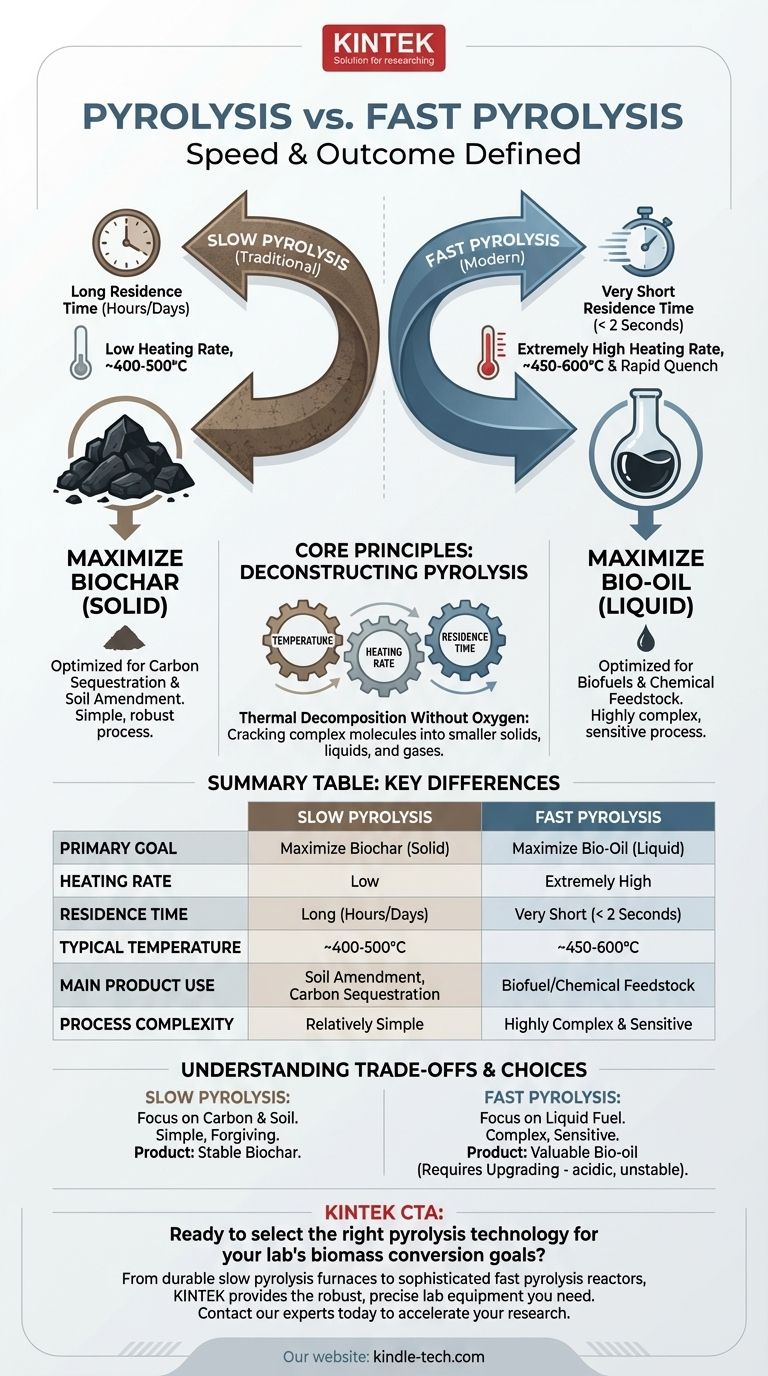
At its core, the difference between pyrolysis and what is specified as "fast pyrolysis" is a matter of speed and intended outcome. While both are methods of thermal decomposition without oxygen, standard (or slow) pyrolysis is a gradual process designed to maximize the output of solid biochar. Fast pyrolysis is an extremely rapid process, lasting mere seconds, engineered to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
While both processes convert biomass using heat in an oxygen-free environment, their goals are fundamentally different. Slow pyrolysis is optimized to create a stable solid (char), while fast pyrolysis is optimized to create a valuable liquid (bio-oil).

Deconstructing Pyrolysis: More Than Just Heat
To understand the distinction, we must first establish the core principles that govern both processes.
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
Pyrolysis is a process that breaks down organic materials, such as biomass or plastic, by heating them to high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen.
Without oxygen, the material doesn't combust (burn). Instead, its complex molecules crack and decompose into a mixture of smaller solids, liquids, and gases.
The Three Key Variables
The specific products you get from pyrolysis are determined by three "control knobs":
- Temperature: The peak temperature the material reaches.
- Heating Rate: How quickly the material is brought to that temperature.
- Residence Time: How long the material is held at that temperature.
The distinction between slow and fast pyrolysis is found in how these variables, particularly heating rate and residence time, are manipulated.
Slow Pyrolysis: The Path to Biochar
When people refer to "pyrolysis" without a qualifier, they are often referring to slow pyrolysis. This is the traditional method used for centuries to make charcoal.
Defining Characteristics
Slow pyrolysis uses a low heating rate and a very long residence time, often lasting several hours or even days. The process gives molecules ample time to break down and then rearrange.
The Primary Product: Biochar
The main goal of slow pyrolysis is to produce biochar, a stable, solid, carbon-rich material. While some liquid (tar) and gas are also produced, they are secondary byproducts.
The slow, prolonged heating allows for secondary reactions to occur, which polymerize and re-condense smaller molecules into the stable, aromatic carbon structure of biochar.
Fast Pyrolysis: The Race to Liquid Bio-oil
Fast pyrolysis is a more modern, advanced technology specifically engineered to prevent the formation of biochar and instead capture intermediate products.
Defining Characteristics
Fast pyrolysis is defined by an extremely high heating rate and a very short residence time, typically less than two seconds. The biomass is heated to a moderate temperature, often in the range of 450-600°C, and the resulting vapors are rapidly cooled, or "quenched."
The Primary Product: Bio-oil
The primary output of fast pyrolysis is bio-oil (also called pyrolysis oil), a dark, viscous liquid. Yields of this liquid can be as high as 75% by weight, with smaller amounts of biochar and non-condensable gases as co-products.
The rapid heating cracks the biomass into vapor molecules, and the immediate quenching prevents those vapors from undergoing the secondary reactions that would otherwise form more biochar or gas. It essentially "freezes" the decomposition process at the liquid stage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these processes involves significant technical and economic considerations.
Product Focus vs. Process Complexity
Slow pyrolysis is a relatively simple, robust, and forgiving process. Its primary output, biochar, is most valuable for carbon sequestration and soil amendment.
Fast pyrolysis is a much more complex and sensitive engineering challenge. It requires finely ground, dry feedstock for rapid heat transfer and sophisticated reactors. Its liquid product, bio-oil, is a dense energy carrier that can be upgraded into transportation fuels or chemical feedstocks, making it potentially more valuable.
Bio-oil Quality
It is critical to understand that bio-oil is not a "drop-in" replacement for crude oil. It is highly acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable. It contains significant amounts of water and oxygenated compounds, which must be removed through a costly upgrading process (like hydrotreating) before it can be used in conventional refineries or engines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of technology is dictated entirely by your desired end product.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil improvement: Slow pyrolysis is the optimal choice to maximize stable biochar production.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid biofuel or chemical feedstock: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary pathway to maximize bio-oil yield.
- If your primary focus is on-site power generation from waste: You might also consider gasification, a related process that operates at higher temperatures with a limited amount of oxygen to maximize the production of combustible gas (syngas).
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the precise thermochemical conversion technology that aligns with your specific material and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Slow Pyrolysis | Fast Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize Biochar (Solid) | Maximize Bio-Oil (Liquid) |
| Heating Rate | Low | Extremely High |
| Residence Time | Long (Hours/Days) | Very Short (< 2 Seconds) |
| Typical Temperature | ~400-500°C | ~450-600°C |
| Main Product Use | Soil Amendment, Carbon Sequestration | Biofuel/Chemical Feedstock |
| Process Complexity | Relatively Simple | Highly Complex & Sensitive |
Ready to select the right pyrolysis technology for your lab's biomass conversion goals?
Whether your research focuses on sustainable biochar production or advanced bio-oil refinement, KINTEK provides the robust, precise lab equipment you need. From durable slow pyrolysis furnaces to sophisticated fast pyrolysis reactors, our solutions are engineered for reliability and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's specialized lab equipment and consumables can accelerate your thermochemical conversion research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular RTP Heating Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















