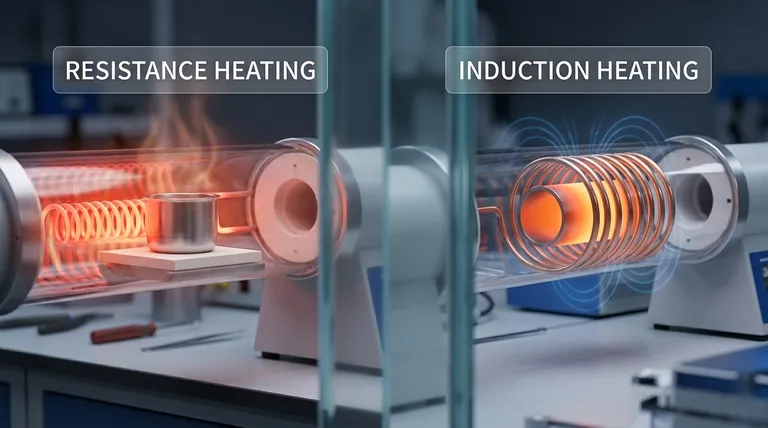
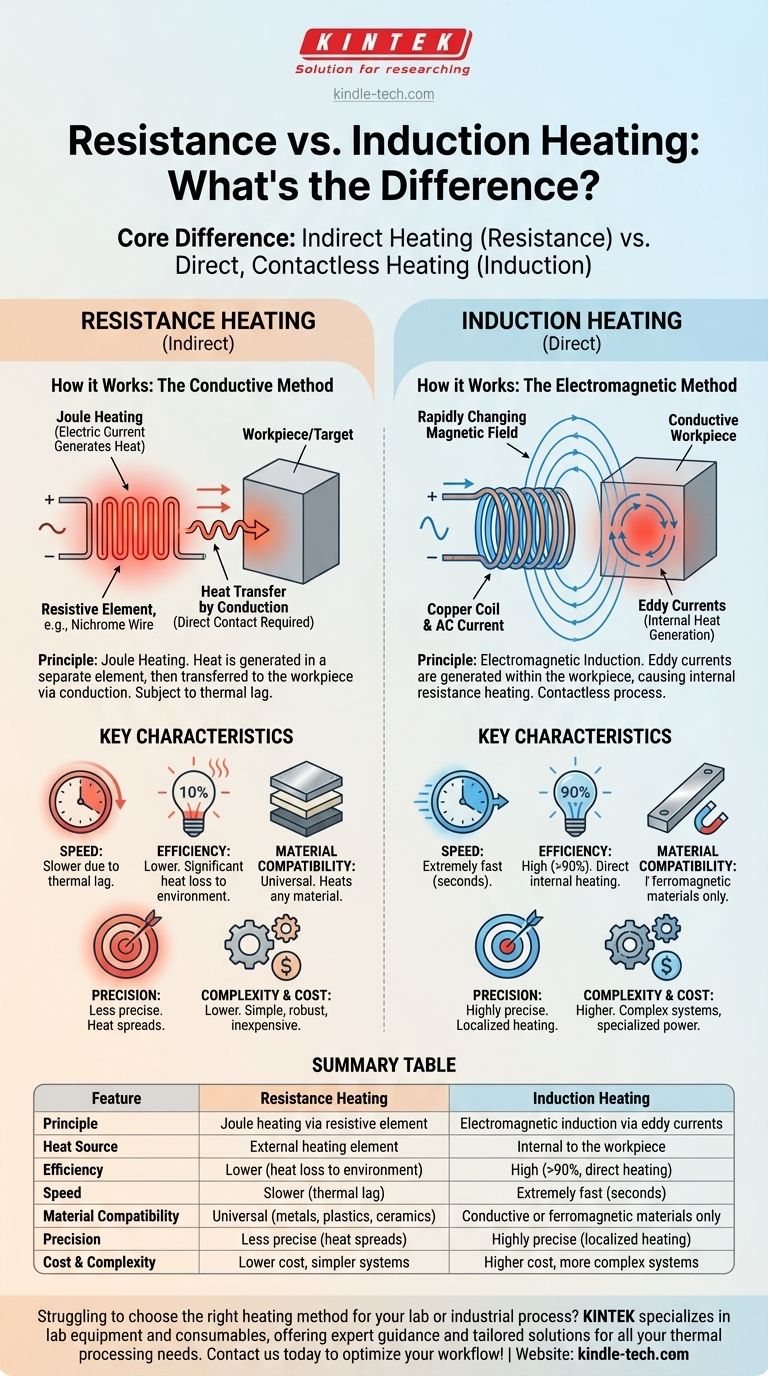
The core difference between resistance and induction heating lies in how heat is generated and where it originates. Resistance heating uses a hot element to conduct heat to a target, like a pan on an electric stove. In contrast, induction heating uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the target itself, with no physical contact from the heat source.
Resistance heating is an indirect method where a component is heated and then transfers that heat to your part. Induction heating is a direct method where the part itself becomes its own heat source. This distinction is the root of all the major differences in speed, efficiency, and application between the two technologies.
How Resistance Heating Works: The Conductive Method
The Principle of Joule Heating
Resistance heating is based on a simple principle known as Joule's First Law. When an electrical current passes through a material with high electrical resistance, such as a nichrome wire, the friction of the moving electrons generates heat.
The heating element is designed to get very hot while carrying this current. This is the same principle that makes the coils on an electric range or the wires in a toaster glow red.
Heat Transfer by Conduction
Once heat is generated in the resistive element, it must be transferred to the workpiece. This happens primarily through conduction, meaning the hot element must be in direct physical contact with, or very close to, the target material.
This is why a resistive soldering iron is a "two-piece" system: heat is created in a separate heater cartridge and must travel along the metal tip to reach the solder joint. This transfer process introduces a delay, known as thermal lag.
How Induction Heating Works: The Electromagnetic Method
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
Induction heating operates on Faraday's Law of Induction. First, a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through a copper coil, creating a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
When an electrically conductive workpiece (like a piece of steel) is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are called eddy currents.
Internal Heat Generation
These eddy currents are not coming from an external source; they are generated directly inside the workpiece. As these currents flow against the material's own electrical resistance, they rapidly generate immense heat.
The workpiece itself becomes the heater. This is a contactless process, as the coil generating the field never touches the part being heated. It explains why an induction system can have a "one-piece" tip—the tip itself is the part being heated internally by the field.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Efficiency and Speed
Induction is significantly more energy-efficient (often over 90%) because heat is generated precisely where it's needed—inside the part. Very little energy is wasted heating the surrounding air. This also makes it extremely fast, with heating occurring in seconds.
Resistance heating is less efficient. A great deal of heat is lost to the environment from the glowing-hot element and during the slow conductive transfer to the workpiece.
Material Compatibility
Resistance heating is universal. It can heat any material—metal, plastic, ceramic, or liquid—as long as heat can be conducted to it.
Induction heating has a critical limitation: it only works on materials that are electrically conductive (like metals) or ferromagnetic. It has no effect on non-conductive materials like glass, plastic, or most ceramics.
Precision and Control
Induction offers exceptionally precise control. By designing the shape of the coil and controlling the frequency and power, you can heat a very specific area of a part to a precise temperature, leaving the surrounding areas cool.
Resistance heating is less precise. Heat tends to "soak" and spread through conduction, making it difficult to heat a localized area without affecting the rest of the part. This is what creates the "high-temperature insulation problem" in some furnaces—the entire chamber gets hot.
Complexity and Cost
Resistance heating systems are simple, robust, and relatively inexpensive to build and maintain. The technology is straightforward and has been used for over a century.
Induction heating systems are more complex and costly. They require a specialized power supply to generate the high-frequency current, a carefully designed copper coil, and often a cooling system for the coil itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between these technologies requires matching their fundamental characteristics to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is low cost and simplicity for general-purpose heating: Resistance heating is the clear and reliable choice for applications like room heaters, ovens, and basic soldering.
- If your primary focus is speed, energy efficiency, and precision on a conductive part: Induction heating offers superior performance for industrial processes like heat treating, brazing, or high-speed soldering.
- If you are working with non-conductive materials like plastics or ceramics: Resistance heating is your only viable option, as induction will have no effect.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction—heating from the outside versus heating from the inside—is the key to selecting the most effective technology for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Resistance Heating | Induction Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Joule heating via resistive element | Electromagnetic induction via eddy currents |
| Heat Source | External heating element | Internal to the workpiece |
| Efficiency | Lower (heat loss to environment) | High (often >90%, direct heating) |
| Speed | Slower (thermal lag) | Extremely fast (seconds) |
| Material Compatibility | Universal (metals, plastics, ceramics) | Conductive or ferromagnetic materials only |
| Precision | Less precise (heat spreads) | Highly precise (localized heating) |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler systems | Higher cost, more complex systems |
Struggling to choose the right heating method for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and tailored solutions for all your thermal processing needs. Whether you're working with conductive metals, plastics, or ceramics, we can help you select the most efficient and precise heating technology. Contact us today to optimize your workflow and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity



















