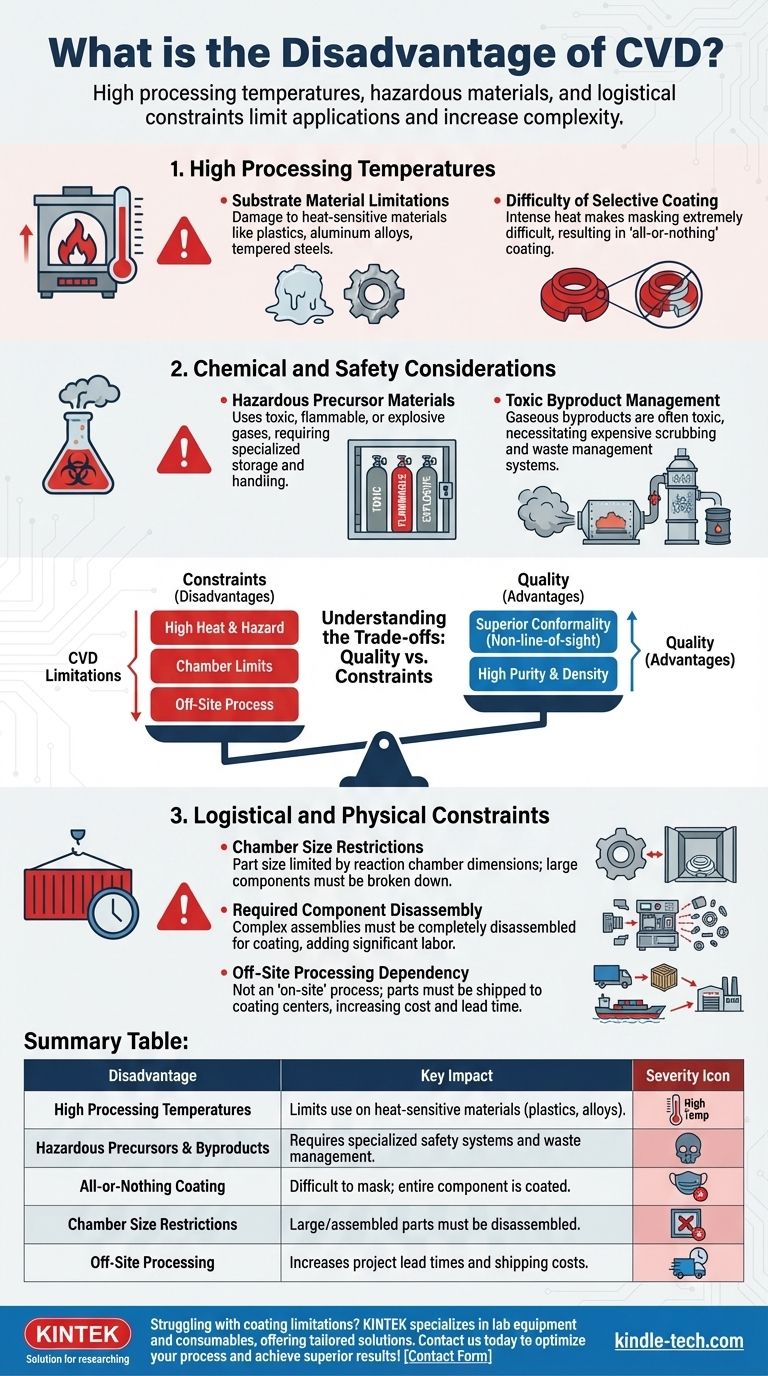
The primary disadvantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are its high processing temperatures, the use of hazardous materials, and significant logistical constraints. These factors limit the types of materials that can be coated and introduce complexities in safety and process management that are not present in other coating technologies.
While CVD produces exceptionally pure and uniform coatings, its major drawbacks—high heat, hazardous chemicals, and off-site processing—make it unsuitable for temperature-sensitive substrates, complex assemblies, and applications requiring rapid, on-site work.

The Challenge of High Processing Temperatures
The most frequently cited limitation of CVD is the requirement for very high temperatures to initiate the chemical reaction. This has direct consequences for the materials you can work with and how you can apply the coating.
Substrate Material Limitations
The high heat involved in the CVD process can damage or fundamentally alter the substrate being coated. Materials with low melting points or specific heat treatments, such as plastics, many aluminum alloys, or tempered steels, cannot withstand the typical CVD thermal environment.
Difficulty of Selective Coating
The intense heat makes it extremely difficult to mask off specific areas of a component. Most masking materials cannot survive the process, which often results in an "all-or-nothing" coating that covers the entire part, whether desired or not.
Chemical and Safety Considerations
CVD relies on chemical reactions involving volatile and often dangerous materials, creating significant safety and environmental management challenges.
Hazardous Precursor Materials
The process requires gaseous precursors, which can be toxic, flammable, or even explosive. This necessitates specialized storage, handling protocols, and safety systems, which increases both the complexity and the operational cost.
Toxic Byproduct Management
The chemical reactions that deposit the coating also produce gaseous byproducts. These byproducts are often toxic and must be captured and neutralized before they can be released, requiring expensive scrubbing and waste management systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Constraints
To make an informed decision, you must weigh CVD's disadvantages against its unique benefits. CVD is chosen despite these drawbacks because it offers unparalleled coating quality in certain aspects.
Advantage: Superior Conformality
CVD is a non-line-of-sight process. Because the precursor is a gas, it can flow into and coat complex internal geometries and intricate shapes with a completely uniform, homogeneous layer. This is something line-of-sight processes like PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) cannot achieve.
Advantage: High Purity and Density
The nature of the chemical reaction allows for the growth of extremely dense, pure, and strong coatings. For applications demanding the highest material quality and performance in harsh environments, this benefit can outweigh all the logistical hurdles.
The Inherent Conflict
The very thing that gives CVD its conformal coating advantage—its gaseous nature—is also linked to its "all-or-nothing" coating drawback. You trade selective application for the ability to coat everything, including internal cavities.
Logistical and Physical Constraints
Beyond the core process, CVD presents several practical challenges that affect project timelines and costs.
Chamber Size Restrictions
The size of the part you can coat is strictly limited by the dimensions of the reaction chamber. Large components cannot be coated without being broken down.
Required Component Disassembly
Because of the size limits and the need to coat individual surfaces, complex assemblies must be completely disassembled before coating. This adds significant labor for both breakdown and reassembly.
Off-Site Processing Dependency
CVD is not an "on-site" process that can be performed in the field. Parts must be shipped to a specialized coating center, which introduces shipping costs and extends project lead times.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use CVD should be based on a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and coating conformity on a heat-resistant component: CVD's disadvantages are likely acceptable trade-offs for its superior film quality and ability to coat complex internal surfaces.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material or a large, assembled part: The high heat and chamber size limitations make CVD a poor choice; you should explore lower-temperature alternatives like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround, cost-efficiency, or on-site application: The logistical requirements and hazardous material handling of CVD make other coating methods far more practical.
Ultimately, understanding these limitations is the key to leveraging CVD for its strengths while avoiding its significant operational pitfalls.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Processing Temperatures | Limits use on heat-sensitive materials like plastics and certain alloys. |
| Hazardous Precursors & Byproducts | Requires specialized safety systems and waste management. |
| All-or-Nothing Coating | Difficult to mask parts; entire component is coated. |
| Chamber Size Restrictions | Large or assembled parts must be disassembled for processing. |
| Off-Site Processing | Increases project lead times and shipping costs. |
Struggling with coating limitations? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for your laboratory needs. Whether you're dealing with temperature-sensitive substrates or complex geometries, our expertise helps you choose the right coating technology. Contact us today to optimize your process and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the substrate for CVD process? Choosing the Right Foundation for Your Thin Film
- What is the primary function of a High Vacuum CVD Furnace? Master High-Quality Graphene Synthesis
- What is CVD process? A Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition for High-Quality Thin Films
- Which method of CNTs production leads to high quality nanotubes in large-scale? Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
- What are the parameters for chemical vapour deposition? Master Temperature, Pressure & Gas Flow for Perfect Films
- What is the process of ALD deposition? Master Atomic-Level Thin Film Coating
- What is chemical vapor deposition at atmospheric pressure? A High-Speed, Low-Cost Thin Film Solution
- Which is advantage of sputtering? Unmatched Material Versatility and Superior Film Quality



















