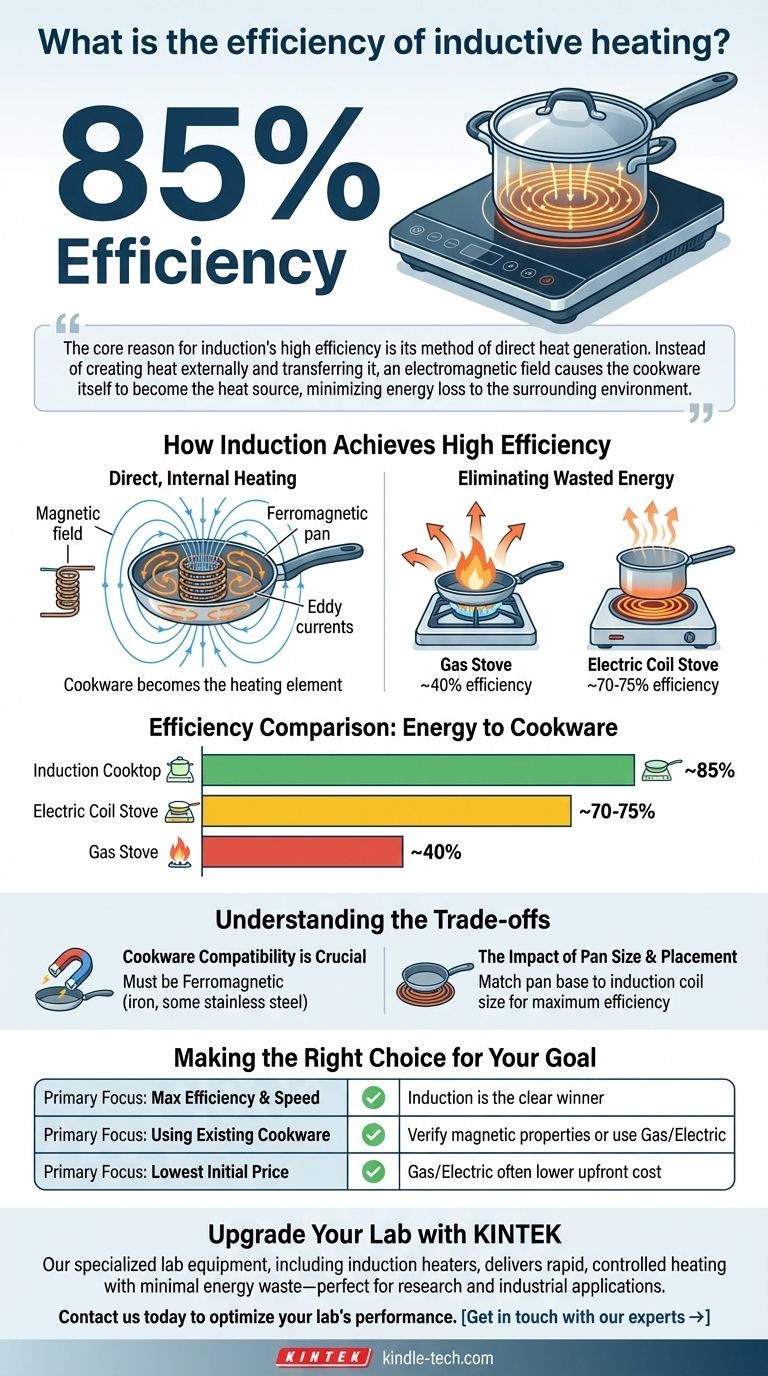
In practice, the efficiency of inductive heating is remarkably high. For common applications like residential induction cooktops, energy is transferred to the cookware with approximately 85% efficiency. This makes it one of the most direct and least wasteful methods for heating available.
The core reason for induction's high efficiency is its method of direct heat generation. Instead of creating heat externally and transferring it, an electromagnetic field causes the cookware itself to become the heat source, minimizing energy loss to the surrounding environment.

How Induction Achieves High Efficiency
Induction doesn't work like a traditional stove. It's a fundamentally different process that eliminates the intermediate steps where energy is typically wasted.
Direct, Internal Heating
An induction system uses an electromagnetic coil to create a rapidly alternating magnetic field.
When compatible cookware (made of a magnetic material like iron) is placed in this field, the field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal of the pot or pan.
The natural electrical resistance of the metal fights against these currents, and this struggle instantly generates heat. The cookware itself becomes the heating element.
Eliminating Wasted Energy
Traditional cooking methods are inherently less efficient because they rely on heat transfer.
With a gas stove, much of the heat from the flame flows around the pot and into the air, not into your food. This results in an efficiency of only around 40%.
With a conventional electric stove, the glowing coil must first heat itself and the glass or ceramic surface before it can begin to transfer heat to the pot. Energy is lost to the air and the cooktop itself during this transfer, leading to an efficiency of approximately 70-75%.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, the induction method comes with specific requirements and considerations.
Cookware Compatibility is Crucial
The primary requirement for induction is that your cookware must be ferromagnetic. This means it must be made of a material that can sustain a magnetic field, such as cast iron or certain types of stainless steel.
Materials like aluminum, copper, or glass will not heat up on an induction surface because the magnetic field cannot induce the necessary currents within them. An easy test is to see if a magnet sticks firmly to the bottom of the pan.
The Impact of Pan Size and Placement
For maximum efficiency, the size of the induction coil in the cooktop should match the size of the pan's base.
Using a pan that is much smaller than the coil can reduce efficiency, as some of the magnetic field will not be acting on the cookware. Modern induction cooktops are increasingly better at detecting pan size and adjusting the field accordingly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if induction is right for you depends on balancing efficiency with other practical factors.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and speed: Induction is the clear winner, heating faster and wasting far less energy than gas or conventional electric.
- If your primary focus is using all of your existing cookware: You must first verify that your pots and pans are magnetic; otherwise, a conventional electric or gas cooktop would be more suitable.
- If your primary focus is the lowest initial purchase price: Gas and conventional electric cooktops typically have a lower upfront cost than induction models.
Ultimately, induction's efficiency translates directly into faster cooking times and lower energy consumption.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Typical Efficiency | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Cooktop | ~85% | Direct internal heating of cookware |
| Electric Coil Stove | ~70-75% | Indirect heating with surface loss |
| Gas Stove | ~40% | Significant heat loss to surrounding air |
Upgrade your lab with the precision and efficiency of KINTEK's induction heating solutions.
Our specialized lab equipment, including induction heaters and compatible consumables, is designed to deliver rapid, controlled heating with minimal energy waste—perfect for research, sample preparation, and industrial applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our induction technology can optimize your lab's performance and reduce operational costs.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- Why is high-precision temperature control at 630°C necessary for Al-Sc vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Alloy Stability
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot-pressing furnace? Superior Copper-Graphite Composite Production
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?



















