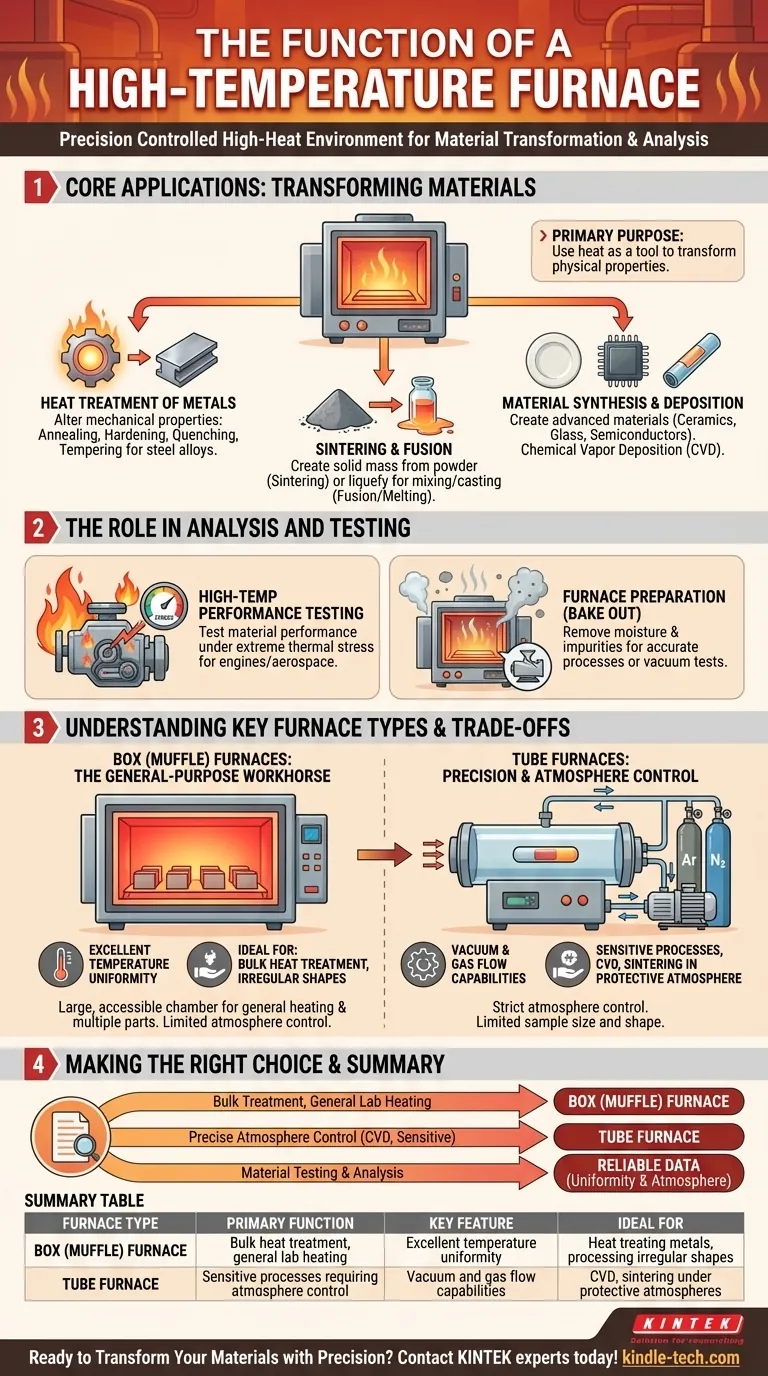
At its core, a high-temperature furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed to create a precisely controlled, high-heat environment. Its function is to fundamentally alter or test materials through processes like heat treatment of metals, sintering ceramics from powders, melting glass, or conducting elemental analysis.
The primary purpose of a high-temperature furnace is not simply to generate heat, but to use that heat as a tool to transform a material's physical properties, create new solid materials from powders, or prepare samples for highly accurate analysis.
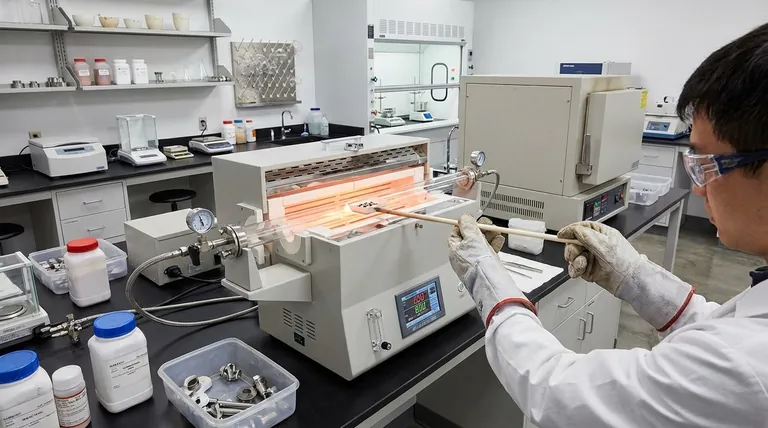

Core Applications: Transforming Materials
The most common use for these furnaces is to induce specific physical or chemical changes in a material that are only possible at elevated temperatures.
Heat Treatment of Metals
This is a foundational application for altering the mechanical properties of steel alloys and other metals.
Processes include annealing to soften a metal and improve ductility, hardening and quenching to increase strength, and tempering to reduce brittleness after hardening.
Sintering and Fusion
These processes involve creating a solid mass from a starting material that is not yet solid.
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. This is used for metals, ceramics, and even some organic compounds.
Fusion, dissolution, and melting are used to liquefy materials like glass or metals for mixing, casting, or analysis.
Material Synthesis and Deposition
Beyond simply modifying existing materials, these furnaces are critical for creating new ones.
They are used in the preparation of advanced ceramics, glass, and semiconductors.
Specialized tube furnaces are also used for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a process where volatile chemical precursors react to produce a high-quality, solid thin film on a substrate.
The Role in Analysis and Testing
A furnace's stable, high-temperature environment is also essential for quality control, research, and material characterization.
High-Temperature Performance Testing
Engineers and scientists use furnaces to test how materials and physical components perform under extreme thermal stress. This helps determine their suitability for high-heat applications like engines or aerospace components.
Furnace Preparation for Accurate Measurement
Before sensitive work, a furnace may undergo a high-temperature dry run, or "bake out."
This function removes residual moisture and impurities that could otherwise interfere with a process or compromise the accuracy of an experiment, such as a vacuum leak-rate test.
Understanding Key Furnace Types and Their Trade-offs
The function you can perform is often dictated by the furnace's design. The two most common types present a clear trade-off between volume and atmospheric control.
Box (Muffle) Furnaces: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A box or muffle furnace is essentially a chamber with heating elements on all sides, ensuring excellent temperature uniformity.
Its large, accessible chamber is ideal for general laboratory heating, bulk heat treatment of multiple parts, or processing irregularly shaped objects. However, controlling the atmosphere inside (e.g., creating a vacuum) is more difficult.
Tube Furnaces: Precision and Atmosphere Control
A tube furnace heats a cylindrical tube through which the sample is passed or placed.
Its design is perfect for applications requiring strict atmosphere control. It is easily sealed to enable processes in a vacuum or under a flow of specific gases (atmosphere protection sintering). The trade-off is the limited sample size and shape, which must fit within the tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace is critical to achieving your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is bulk metal heat treatment or general-purpose lab heating: A box (muffle) furnace provides the necessary space and temperature uniformity for these tasks.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control for sensitive materials or CVD: A tube furnace is non-negotiable, as it is specifically designed for vacuum or controlled gas environments.
- If your primary focus is material testing and analysis: Your choice will depend on sample shape and atmosphere needs, but ensuring the furnace provides certified temperature uniformity is the most critical factor for reliable data.
Ultimately, understanding the specific function you need to perform is the first step in selecting the right high-temperature tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Function | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Box (Muffle) Furnace | Bulk heat treatment, general lab heating | Excellent temperature uniformity | Heat treating metals, processing irregular shapes |
| Tube Furnace | Sensitive processes requiring atmosphere control | Vacuum and gas flow capabilities | CVD, sintering under protective atmospheres |
Ready to Transform Your Materials with Precision?
Choosing the right high-temperature furnace is critical for achieving reliable results in heat treatment, sintering, or material analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs.
Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace for your application, whether you require the uniform heating of a box furnace or the precise atmosphere control of a tube furnace.
Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















