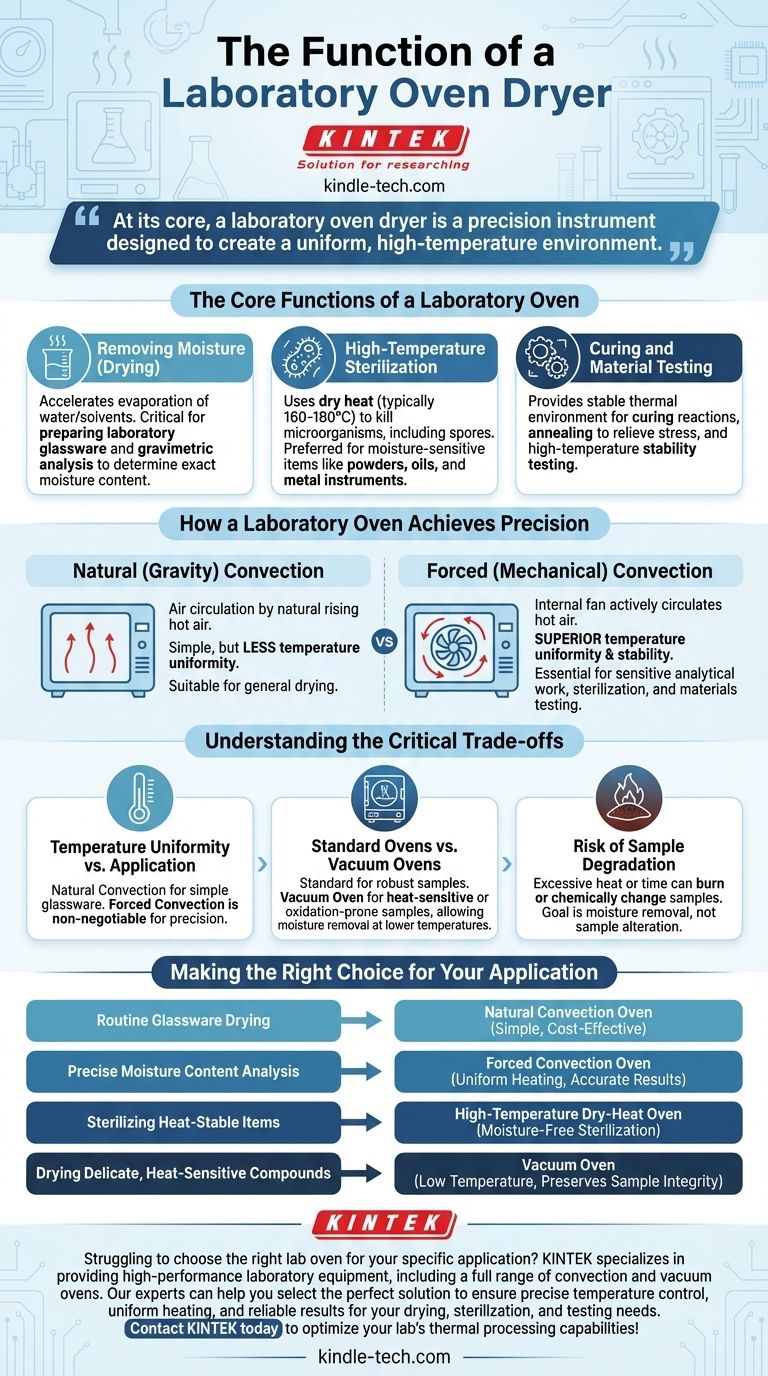
At its core, a laboratory oven dryer is a precision instrument designed to create a uniform, high-temperature environment. Its primary function is to remove moisture from lab equipment and samples through heating, but its applications extend to dry-heat sterilization, curing materials, and conducting high-temperature stability testing.
The function of a lab oven goes far beyond simple drying. It is a critical tool for ensuring the accuracy, purity, and safety of scientific experiments by providing precise thermal control for drying, sterilizing, and testing.

The Core Functions of a Laboratory Oven
A laboratory oven is a versatile workhorse, but its functions can be grouped into three primary categories. Each leverages the principle of controlled thermal convection to achieve a specific outcome.
Removing Moisture (Drying)
This is the most common and intuitive function. The oven's heat accelerates the evaporation of water and other solvents from objects placed inside.
This is critical for preparing laboratory glassware, ensuring that no residual moisture can dilute reagents or contaminate subsequent experiments.
It is also fundamental to gravimetric analysis, where a sample is heated until it reaches a constant weight. The weight difference before and after drying reveals its exact moisture content, a vital parameter in fields from food science to environmental testing.
High-Temperature Sterilization
A laboratory oven can perform dry-heat sterilization, a method used to kill all microorganisms, including bacterial spores.
This process is distinct from an autoclave, which uses pressurized steam (moist heat). Dry heat requires higher temperatures (typically 160-180°C) and longer exposure times.
It is the preferred method for sterilizing items that cannot be exposed to moisture, such as powders, oils, metal instruments, or certain types of glassware that might be damaged by steam.
Curing and Material Testing
Ovens provide the stable thermal environment needed for material science applications.
This includes curing, a process where heat is used to induce a chemical reaction that hardens a material, such as an epoxy or polymer.
They are also used for annealing, which involves heating and slowly cooling glass or metal to relieve internal stresses. Furthermore, ovens are used to test the thermal stability and performance of materials under prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
How a Laboratory Oven Achieves Precision
The effectiveness of a lab oven hinges on its ability to distribute heat evenly. This is achieved through one of two convection methods.
Natural (Gravity) Convection
In these more basic ovens, air circulation relies on the natural principle that hot air rises and cooler air sinks. This creates a gentle airflow.
While simple and cost-effective, this method results in less temperature uniformity throughout the chamber, making it suitable for general drying but not for applications requiring high precision.
Forced (Mechanical) Convection
These ovens use an internal fan to actively circulate the hot air throughout the chamber.
This forced airflow ensures superior temperature uniformity and stability, leading to faster drying times and more consistent, repeatable results. This design is essential for sensitive analytical work, sterilization, and materials testing.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing and using a lab oven requires understanding its limitations and the different technologies available for specific needs.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Application
For simply drying glassware, a natural convection oven is often sufficient. However, for applications where every sample must be exposed to the exact same temperature, such as in quality control testing or sterilization, a forced convection oven is non-negotiable.
Standard Ovens vs. Vacuum Ovens
A standard lab oven is unsuitable for samples that are heat-sensitive or prone to oxidation. High heat can degrade or destroy delicate biological compounds.
For these applications, a vacuum oven is required. By reducing the ambient pressure inside the chamber, a vacuum oven lowers the boiling point of water, allowing moisture to be removed at a much lower temperature, thereby protecting the sample.
Risk of Sample Degradation
The goal of drying is to remove moisture, not to alter the sample itself. Setting the temperature too high or heating for too long can burn or chemically change the sample, leading to inaccurate analytical results. It is crucial to use established protocols or determine the optimal temperature and time for each specific material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct process, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is routine glassware drying: A simple, cost-effective natural convection oven will meet your needs perfectly.
- If your primary focus is precise moisture content analysis: A forced convection oven is essential to ensure uniform heating and achieve accurate, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-stable powders or metal tools: A high-temperature dry-heat oven is the correct choice, ensuring moisture-free sterilization.
- If your primary focus is drying delicate, heat-sensitive compounds: You must use a vacuum oven to remove moisture at a low temperature, preserving the integrity of your sample.
Ultimately, understanding the function of a laboratory oven is about using controlled heat to achieve a specific, reliable, and repeatable outcome.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Application | Recommended Oven Type |
|---|---|---|
| Removing Moisture (Drying) | Preparing glassware, gravimetric analysis | Forced Convection (for precision) |
| High-Temperature Sterilization | Sterilizing powders, oils, metal tools | High-Temperature Dry-Heat Oven |
| Curing & Material Testing | Annealing, epoxy curing, stability testing | Forced Convection Oven |
| Drying Heat-Sensitive Samples | Preserving delicate biological compounds | Vacuum Oven |
Struggling to choose the right lab oven for your specific application? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance laboratory equipment, including a full range of convection and vacuum ovens. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to ensure precise temperature control, uniform heating, and reliable results for your drying, sterilization, and testing needs. Contact KINTEK today to optimize your lab's thermal processing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What temperature does porcelain fire at? A Guide to the 1222°C-1300°C Range for Perfect Results
- What precautions should be taken when using a muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- What are the benefits of integrating a high-precision electronic balance with a high-temperature furnace for TGA?
- What function does a muffle furnace serve during the isothermal aging of AFA alloys? Optimize Microstructural Control
- Can a muffle furnace be used for pyrolysis? How to adapt it for oxygen-free thermal decomposition
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in Nb-O coated NMC powder preparation? Optimize Your Material Purity
- How does sintering temperature affect mechanical properties? Optimize Strength and Durability
- How is a high-temperature box resistance furnace utilized in the preparation of IrO2/Ti electrodes? Expert Guide



















