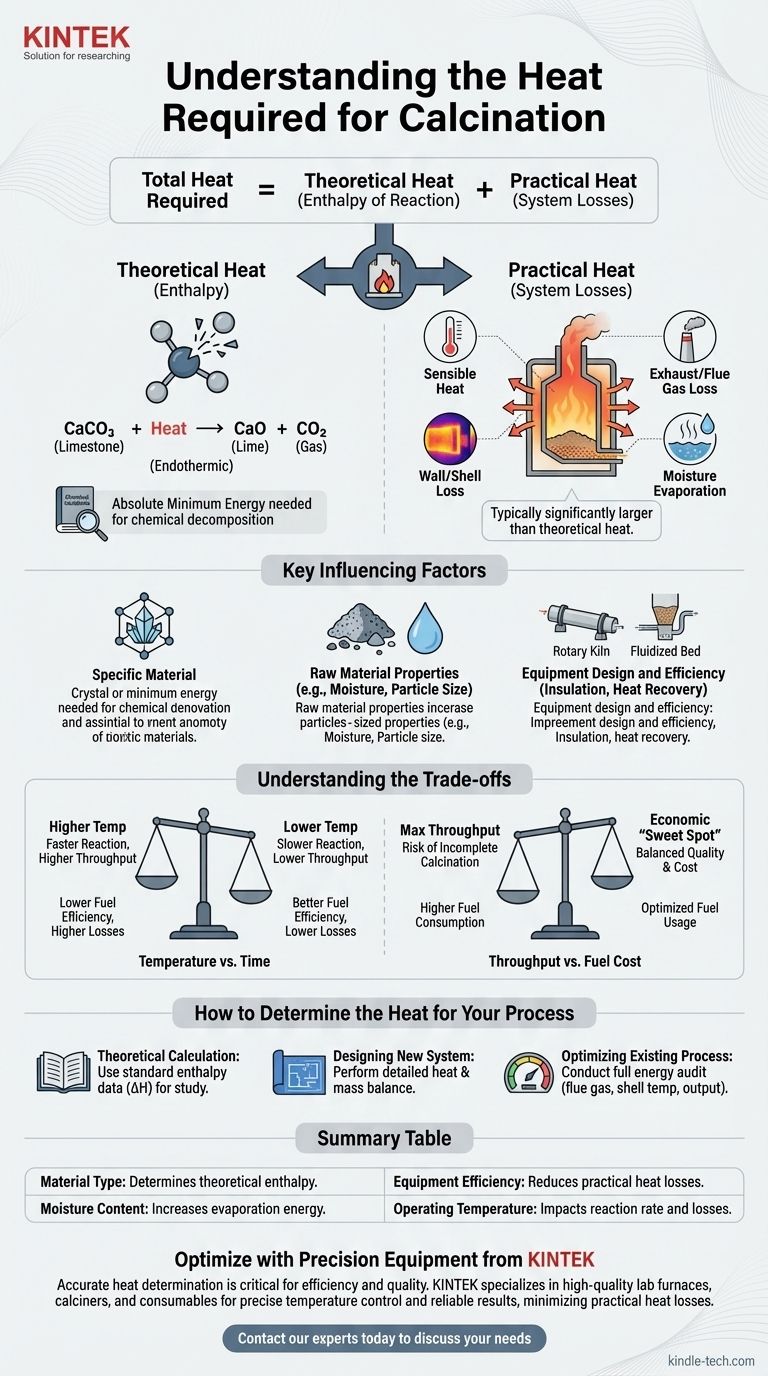
The heat required for calcination is not a single, universal value. It is a variable quantity that depends entirely on the specific material being processed, the underlying chemical reaction, and the efficiency of the equipment used, such as a furnace or calciner. Calculating this value requires understanding both chemical principles and real-world system inefficiencies.
The total heat required for any calcination process is the sum of two distinct components: the theoretical heat of reaction needed to break the material's chemical bonds and the practical heat losses inherent in the operating system. A successful analysis must account for both.

The Two Components of Calcination Heat
To understand the energy demands of calcination, we must separate the theoretical minimum from the practical realities of industrial equipment.
Theoretical Heat (Enthalpy of Reaction)
This is the absolute minimum amount of energy required by the laws of chemistry to drive the decomposition reaction.
This value is fixed for a given chemical transformation. For example, the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) is an endothermic reaction, meaning it must absorb a specific amount of energy to proceed.
This theoretical energy requirement can be calculated or found in chemical engineering handbooks for most common materials.
Practical Heat (System Losses)
This is all the additional energy that must be supplied to a real-world system beyond the theoretical minimum. In most industrial operations, this component is significantly larger than the theoretical heat of reaction.
Major sources of practical heat loss include:
- Sensible Heat: Energy used to heat the material itself up to the required reaction temperature.
- Exhaust/Flue Gas Loss: Heat carried away by the hot gases leaving the calciner.
- Wall/Shell Loss: Heat that radiates and convects away from the outer surfaces of the furnace or kiln.
- Moisture Evaporation: Energy consumed to turn any water present in the raw material into steam before the calcination reaction can even begin.
Key Factors That Influence Heat Requirement
The final energy consumption figure is a result of several interacting variables. Understanding these factors is crucial for process design and optimization.
The Specific Material
Different materials have vastly different chemical bonds and decomposition temperatures. The energy needed to drive water from gypsum is much lower than the energy needed to decompose calcium carbonate.
Raw Material Properties
The physical state of the material matters. Fine powders heat up more uniformly than large rocks, and high initial moisture content can dramatically increase energy consumption due to the high heat of vaporization of water.
Equipment Design and Efficiency
The type of equipment used, such as a rotary kiln, shaft furnace, or fluidized bed calciner, has a massive impact on heat transfer.
Factors like the quality of insulation, the effectiveness of air seals, and the presence of heat recovery systems (like preheaters that use hot exhaust gas to warm up incoming material) are primary drivers of overall thermal efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a calcination process involves balancing competing operational goals. Ignoring these trade-offs often leads to inefficiency or poor product quality.
Temperature vs. Time
Higher operating temperatures can accelerate the calcination reaction, increasing throughput. However, this often leads to greater heat loss through the equipment shell and flue gases, reducing fuel efficiency.
Conversely, lower temperatures conserve energy but require the material to spend more time in the calciner, which can limit the production rate.
Throughput vs. Fuel Cost
Pushing for maximum production output can lead to incomplete calcination or require forcing so much fuel into the system that overall efficiency plummets.
Finding the economic "sweet spot" requires carefully balancing the value of the final product against the cost of the fuel consumed per ton.
How to Determine the Heat for Your Process
There is no single formula, but you can determine the heat requirement by focusing on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is a theoretical calculation for study: Find the standard enthalpy of reaction (ΔH) for your specific chemical decomposition in a thermodynamics data reference.
- If your primary focus is designing a new system: You must perform a detailed heat and mass balance that accounts for material properties, equipment specifications, and all potential heat losses.
- If your primary focus is optimizing an existing process: Conduct a full energy audit on your equipment, measuring flue gas temperatures, product output, and shell temperatures to identify and quantify major sources of heat loss.
Ultimately, accurately determining the heat of calcination moves beyond a single number to a comprehensive analysis of your specific material and system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Heat Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Determines the theoretical enthalpy of reaction (e.g., limestone vs. gypsum). |
| Moisture Content | High moisture significantly increases energy needed for evaporation. |
| Equipment Efficiency | Better insulation and heat recovery systems reduce practical heat losses. |
| Operating Temperature | Higher temperatures can increase reaction rate but also heat losses. |
Optimize your calcination process with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Accurately determining heat requirements is critical for efficiency and product quality. Whether you are designing a new system or optimizing an existing one, the right lab equipment is essential for accurate thermal analysis and material testing.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces, calciners, and consumables that provide the precise temperature control and reliability needed for your research and process development. Our solutions help you minimize practical heat losses and achieve optimal results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific calcination needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What is a laboratory furnace called? A Guide to Muffle and Tube Furnaces
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a normal furnace? Ensuring Sample Purity with Indirect Heating
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method



















