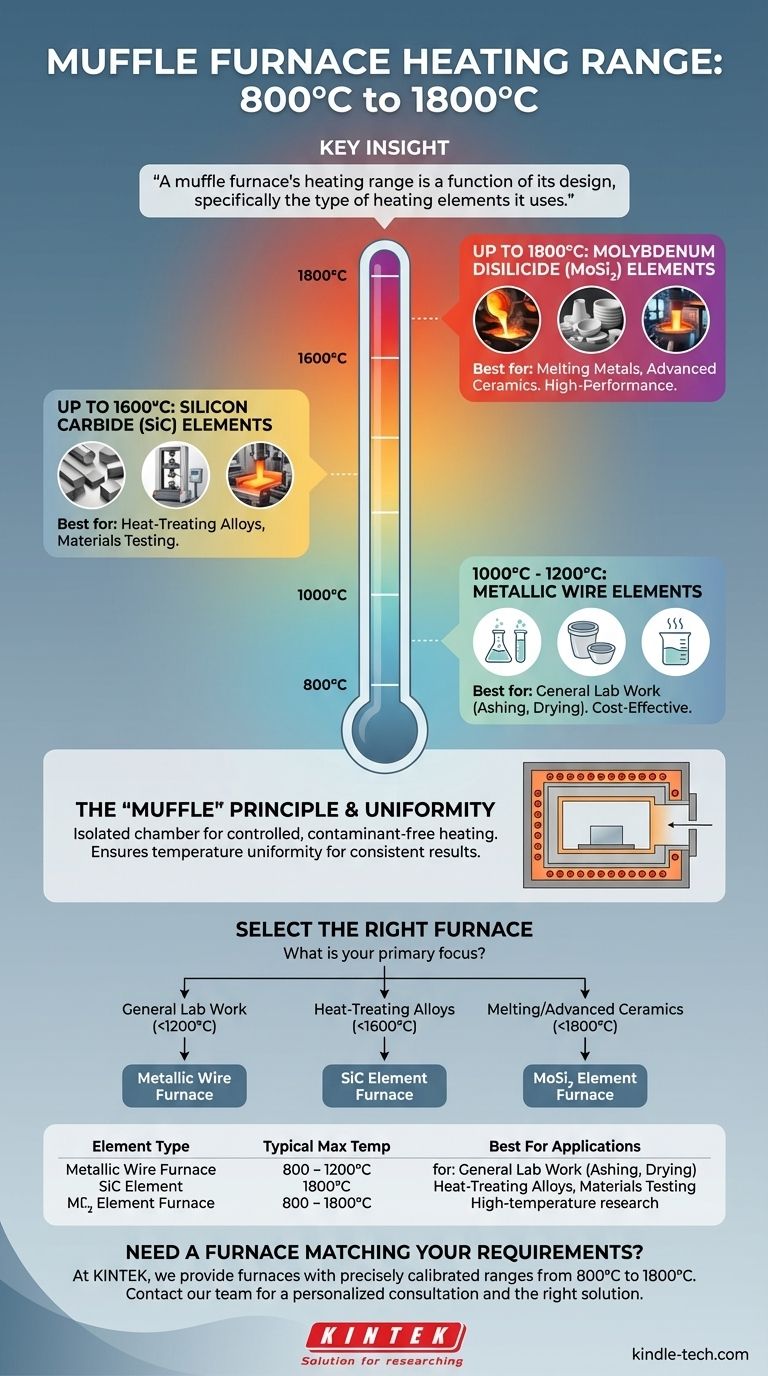
In practice, a muffle furnace typically operates within a broad temperature range of 800°C to 1800°C (1472°F to 3272°F). The specific maximum temperature a furnace can achieve is not a universal standard but is directly determined by the material used for its internal heating elements.
The critical takeaway is that a muffle furnace's heating range is a function of its design, specifically the type of heating elements it uses. Understanding this relationship is essential for selecting a furnace that meets the precise requirements of your high-temperature application without over-investing in unnecessary capabilities.

What Defines a Muffle Furnace's Temperature?
A muffle furnace's primary advantage is its ability to heat materials in a controlled environment, free from contamination. This is achieved through its core design, where the heating source and the material being processed are separated.
The Decisive Role of Heating Elements
The maximum attainable temperature is dictated by the physical limits of the heating elements. Different materials are used to achieve different heat levels.
-
Metallic Wire Elements: These are the most common, typically found in general-purpose lab furnaces. They reliably achieve maximum temperatures between 1000°C and 1200°C.
-
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements: For applications requiring higher heat, furnaces use silicon carbide elements. These can sustain operational temperatures up to 1600°C.
-
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements: Used for the most demanding high-temperature processes, these advanced elements allow furnaces to reach up to 1800°C.
The "Muffle" Design Principle
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's internal chamber, which is sealed off from the heating elements. This design is crucial because it isolates the workpiece from any byproducts of combustion or direct radiation effects from the elements themselves.
In modern electric furnaces, this separation prevents contamination and ensures that the heat treatment occurs in a clean, controlled atmosphere. This is vital for processes like ashing, heat treating, or materials research where purity is paramount.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
Modern muffle furnaces are engineered for superior temperature uniformity. The insulated chamber minimizes heat loss and allows a combination of radiant and convection heat transfer to work together.
This ensures that the entire workpiece is heated evenly, which is critical for consistent and repeatable results in processes like metal casting, annealing, or ceramic firing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While the maximum temperature is a key specification, it's not the only factor. A practical decision involves balancing performance, cost, and operational requirements.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
There is a direct correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its cost. Furnaces with advanced molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are significantly more expensive than standard metallic-wire models.
It is crucial to match the furnace's capability to your actual application needs to avoid unnecessary expense.
Atmosphere and Contamination Control
The fundamental design of a muffle furnace provides a baseline level of atmosphere control by separating the sample from contaminants. This is its main purpose.
If your process requires a specific inert or reactive gas environment (like nitrogen or argon), you may need a specialized furnace with gas-purging capabilities, which is a feature beyond the standard muffle design.
Safety and Operating Environment
A muffle furnace is a powerful piece of equipment that demands a safe workspace. The operating environment must be clear of any flammable materials, explosive substances, or corrosive gases that could react at high temperatures or damage the furnace components.
How to Select the Right Furnace for Your Application
Choosing the correct furnace means aligning its specifications with your specific technical goals. Always select a furnace whose maximum temperature comfortably exceeds your highest anticipated process temperature.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing or drying (up to 1200°C): A standard furnace with metallic heating elements is the most cost-effective and appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating specialized alloys or materials testing (up to 1600°C): You will need a furnace equipped with silicon carbide (SiC) elements.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or working with advanced ceramics (up to 1800°C): Your application demands a high-performance furnace using molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements.
- If you anticipate future needs for higher temperatures: Investing in a furnace with a higher maximum temperature now can provide valuable flexibility and prevent the need for another purchase later.
Ultimately, identifying your core temperature requirements is the first and most important step toward making an informed decision.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Best For Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire | 1000°C - 1200°C | General lab work (ashing, drying) |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Heat-treating alloys, materials testing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C | Melting metals, advanced ceramics |
Need a muffle furnace that perfectly matches your temperature requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces with precisely calibrated heating ranges from 800°C to 1800°C. Whether you're performing basic ashing or advanced materials testing, our experts will help you select the ideal furnace with the right heating elements for your specific application—ensuring optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and safety.
Let's discuss your high-temperature needs! Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and get the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the heat transfer of a muffle furnace? Understanding Indirect Heating for Purity
- What does 'sintered' mean and why is it important to understand? Unlock Advanced Materials & Manufacturing
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and hot air oven? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What is the effect of calcination temperature on the properties of nanoparticles? Master the Trade-Off for Optimal Performance
- What is the function of muffle furnace in food industry? Ensure Accurate Ash Determination for Quality Control



















