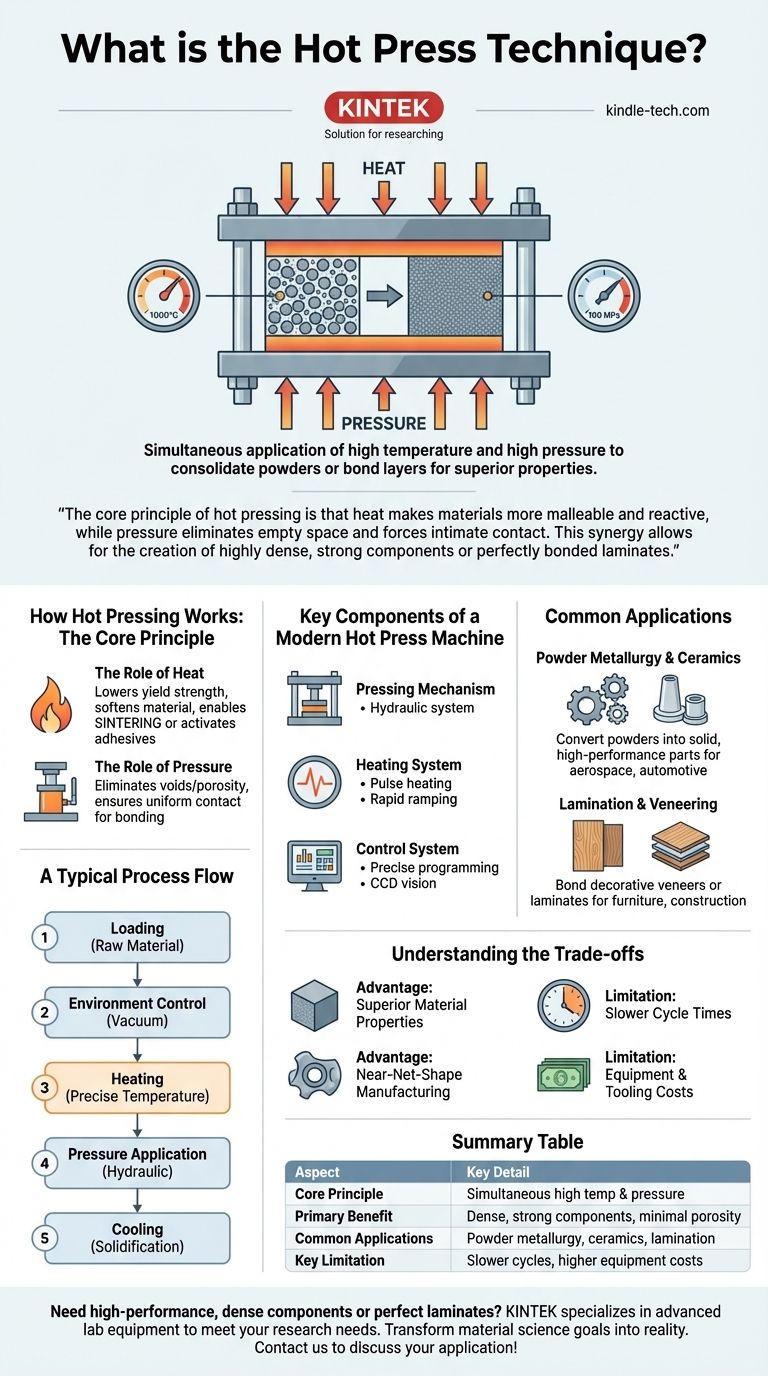
The hot press technique is a manufacturing process that simultaneously applies high temperature and high pressure to a material. This combined action is used to consolidate powders into a solid, dense form or to bond layers of materials together, resulting in a final product with superior mechanical properties.
The core principle of hot pressing is that heat makes materials more malleable and reactive, while pressure eliminates empty space and forces intimate contact. This synergy allows for the creation of highly dense, strong components or perfectly bonded laminates that are unattainable with pressure or heat alone.
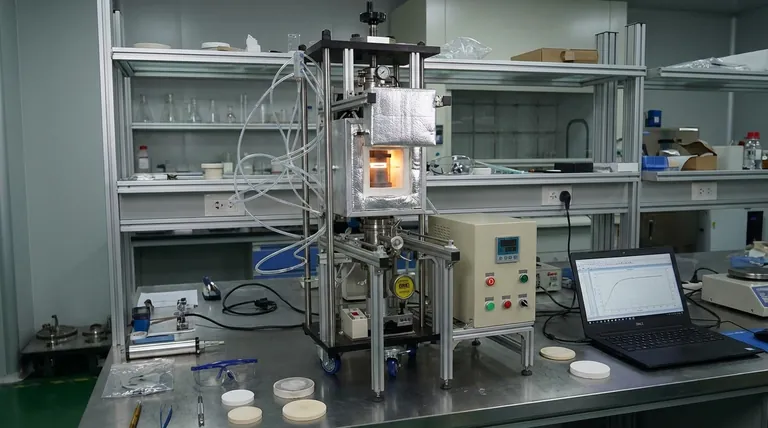

How Hot Pressing Works: The Core Principle
The effectiveness of the hot press technique comes from the distinct but complementary roles of heat and pressure, which are applied in a highly controlled environment.
The Role of Heat
Heat is the first critical ingredient. It significantly lowers the material's yield strength, essentially softening it and making it easier to shape and compact.
For powders like ceramics or metals, heating brings the material to a temperature where the particles can begin to fuse, a process known as sintering. For laminates, heat activates thermal-set adhesives, preparing them for a permanent bond.
The Role of Pressure
While the material is hot and pliable, a powerful force is applied. This pressure, typically generated by a hydraulic system, serves two primary functions.
First, it physically forces the material particles or layers together, eliminating voids and porosity. Second, it ensures complete and uniform contact across the entire surface, which is critical for both sintering and adhesive bonding.
A Typical Process Flow
While specific parameters vary, a typical hot pressing cycle follows these general steps:
- Loading: The raw material (powder or layered sheets) is placed into a die or onto the press platform.
- Environment Control: For sensitive materials, the chamber may be evacuated to create a vacuum, preventing oxidation.
- Heating: The material is heated to a precise, predetermined temperature using systems like induction coils or heating pipes.
- Pressure Application: Once at temperature, hydraulic pressure is applied and held for a specific duration.
- Cooling: The component is cooled, often under pressure, to solidify its new shape and structure.
Key Components of a Modern Hot Press Machine
Modern hot press machines are sophisticated pieces of equipment designed for precision, control, and repeatability.
The Pressing Mechanism
The machine's foundation is often a rigid four-column, three-plate structure that ensures stability and alignment under extreme force. The pressure itself is almost always generated by a hydraulic system, which allows for very high, balanced, and controllable pressure application.
The Heating System
Precise temperature is managed through advanced technology. Pulse heating allows for rapid temperature ramping and multi-stage control, ensuring the material follows an exact thermal profile. This is monitored in real-time to guarantee consistency.
The Control System
An automated control panel is the brain of the operation. It allows an operator to set, store, and execute complex programs that dictate temperature, pressure, and timing. Advanced systems may also include a CCD vision system for perfect alignment of components before pressing.
Common Applications of the Hot Press Technique
This technique is valued in industries where material density, strength, and surface bonding are critical performance metrics.
Powder Metallurgy and Ceramics
Hot pressing is a premier method for converting metallic or ceramic powders into solid, high-performance parts. The process minimizes porosity, leading to components with exceptional strength and durability that are used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications.
Lamination and Veneering
In the furniture and construction industries, hot pressing is used to bond decorative veneers or durable laminates onto core boards like particleboard or MDF. The heat activates the glue, and the pressure ensures a flawless, permanent bond for creating panel furniture, wooden doors, and partition walls.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any manufacturing process, hot pressing has clear advantages and specific limitations that make it suitable for certain applications over others.
Advantage: Superior Material Properties
The primary benefit is the final product quality. By drastically reducing or eliminating porosity, hot pressing produces parts that are significantly denser and stronger than those made with "cold pressing" or pressureless sintering.
Advantage: Near-Net-Shape Manufacturing
For powdered materials, the technique can produce complex parts that are very close to their final dimensions, reducing the need for subsequent costly machining.
Limitation: Slower Cycle Times
The process of heating the material and the die, holding it at temperature, and then cooling it down is inherently time-consuming. This makes hot pressing slower than processes like cold pressing, limiting its throughput for high-volume production.
Limitation: Equipment and Tooling Costs
Hot press machines are complex and represent a significant capital investment. Furthermore, the dies used must be able to withstand extreme temperature and pressure cycles, adding to the operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether hot pressing is the correct technique depends entirely on the required properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-performance parts from powders: Hot pressing is an ideal choice for achieving superior mechanical strength by eliminating internal voids.
- If your primary focus is producing durable, laminated surfaces: The technique provides an unmatched ability to create a strong, permanent, and seamless bond for veneers and laminates.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: You may want to consider alternative methods, as the cycle times and equipment costs of hot pressing can be prohibitive.
Ultimately, the hot press technique excels at transforming raw materials into consolidated, high-value products where structural integrity is paramount.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Simultaneous application of high temperature and high pressure |
| Primary Benefit | Creates dense, strong components with minimal porosity |
| Common Applications | Powder metallurgy, ceramics, lamination, and veneering |
| Key Limitation | Slower cycle times and higher equipment costs |
Need to create high-performance, dense components or perfect laminates? The hot press technique is the key to achieving superior material properties. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including hot press systems, to meet the demanding needs of research and development laboratories. Let our expertise help you transform your material science goals into reality. Contact us today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve High Densification in Al-Ti-Zr Synthesis
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production



















