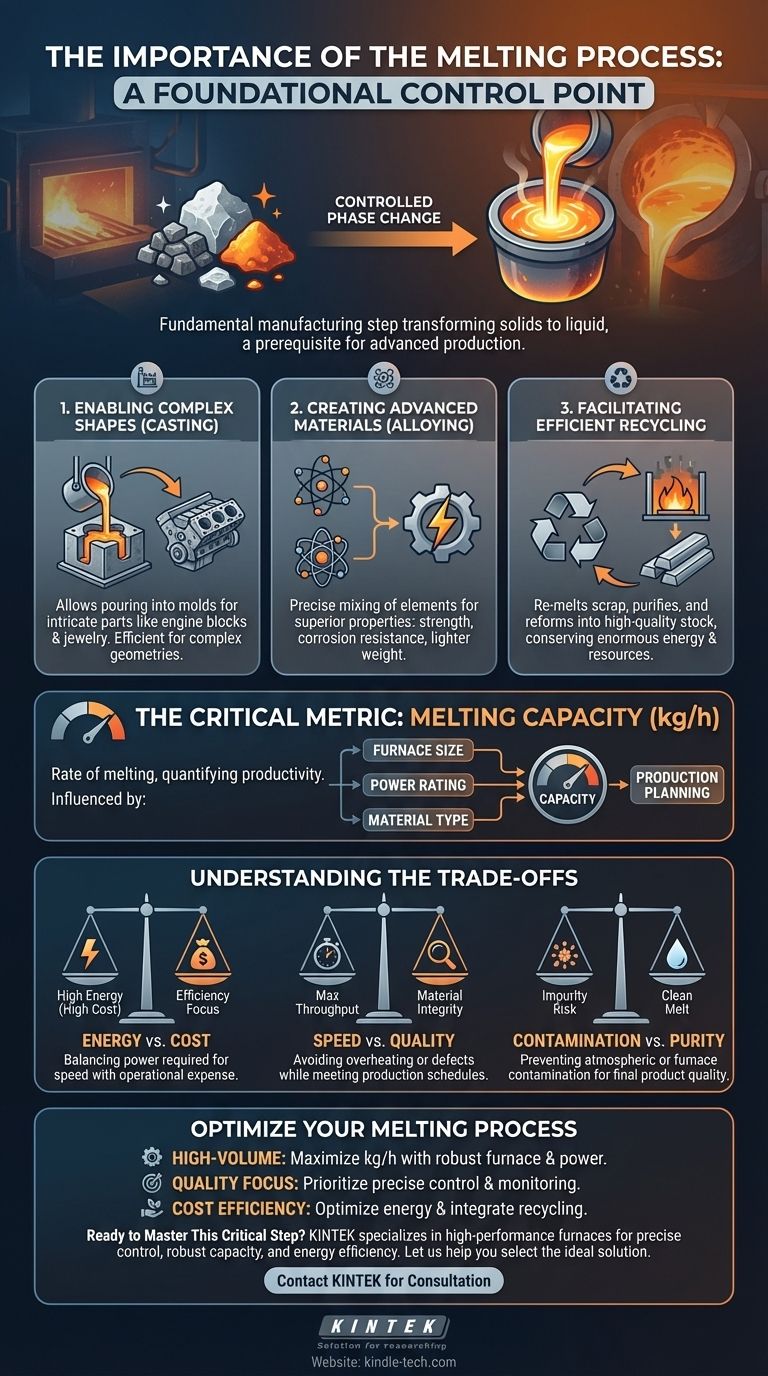
The importance of the melting process lies in its function as a fundamental manufacturing step that transforms solid raw materials into a liquid state. This controlled phase change is the critical prerequisite for producing a vast range of metal products through casting, creating advanced alloys, and enabling efficient recycling.
The melting process is more than a simple change of state; it is the foundational control point for manufacturing. How well you manage melting directly dictates production efficiency, final product quality, and your ability to meet production schedules.
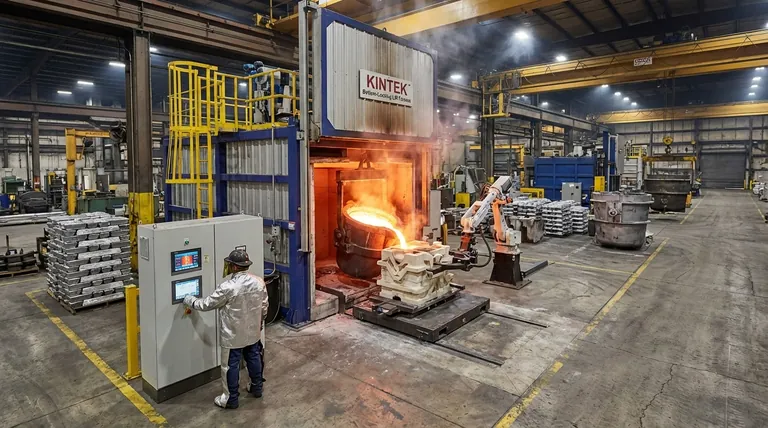

Why Melting is a Core Industrial Process
Melting is the gateway to manipulating materials in ways that are impossible in their solid form. It unlocks several essential manufacturing capabilities.
Enabling Complex Shapes through Casting
Once a material is in its liquid state, it can be poured into a mold of nearly any shape. This process, known as casting, is one of the most efficient ways to produce complex or intricate parts, from engine blocks to jewelry.
Creating Advanced Materials via Alloying
Melting allows for the precise mixing of different elements. This is the basis of alloying, where metals are combined to create new materials with superior properties like increased strength, corrosion resistance, or lighter weight.
Facilitating Efficient Recycling
The melting process is central to recycling metals. It allows scrap materials to be re-melted, purified, and reformed into new, high-quality stock, conserving enormous amounts of energy and natural resources compared to primary production.
The Critical Metric: Melting Capacity
To control the process, you must be able to measure it. The most important metric for any industrial melting operation is its capacity.
Defining Melting Capacity
Melting capacity is the rate at which a furnace can melt a material, measured in kilograms per hour (kg/h). It quantifies the furnace's productivity.
This capacity is not a fixed number; it depends on several factors.
Key Factors Influencing Capacity
Three primary variables determine a furnace's melting rate:
- Furnace Size: A larger furnace can hold and process more material at once.
- Power Rating: Higher power input provides more energy for heating, enabling a faster melt.
- Material Type: Different materials have unique melting points and thermal properties, affecting how much energy is required to liquefy them.
Impact on Production Planning
Understanding your melting capacity is essential for business operations. It allows you to accurately plan production schedules, forecast output, and determine the overall productivity of your facility.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, the melting process is not without its challenges. Success requires balancing competing priorities.
Energy Consumption vs. Cost
Melting is an extremely energy-intensive process. A higher melting rate often requires a significant increase in power, leading to higher operational costs. Efficiency is a constant concern.
Process Speed vs. Material Quality
Pushing for maximum throughput can compromise quality. Overheating can burn away valuable alloying elements, while insufficient heating can lead to defects. Proper control requires a balance between speed and precision.
Contamination and Purity
During its liquid phase, a material is vulnerable to contamination from the atmosphere or the furnace lining itself. Maintaining a clean melt is critical for preventing impurities that can cause defects in the final product.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your operational focus will determine how you approach and optimize the melting process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Your goal is to maximize melting capacity (kg/h) through proper furnace selection and efficient power management to meet demanding schedules.
- If your primary focus is material quality and purity: You must prioritize precise temperature control and process monitoring over raw speed to ensure alloy consistency and prevent defects.
- If your primary focus is cost efficiency: Your strategy should center on optimizing furnace energy consumption, minimizing material loss, and integrating efficient scrap recycling streams.
Ultimately, mastering the melting process is the first and most critical step toward controlling the quality and efficiency of your entire production line.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Enables Casting | Creates complex shapes by pouring liquid metal into molds. |
| Facilitates Alloying | Mixes elements to create materials with superior properties. |
| Drives Recycling | Re-melts scrap metal efficiently, conserving energy and resources. |
| Defines Capacity (kg/h) | Determines production rate, influenced by furnace size, power, and material. |
| Balances Trade-offs | Requires managing energy cost, process speed, and material purity. |
Ready to Optimize Your Melting Process?
Whether your goal is maximizing production volume, achieving superior material purity, or improving cost efficiency, the right equipment is the foundation of success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and industrial melting furnaces designed to deliver precise temperature control, robust capacity, and energy efficiency.
Let us help you master this critical step. Our experts will work with you to select the ideal furnace for your specific materials and production targets.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation and see how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the uniformity of e beam evaporation? Achieve Precise, Uniform Thin Films
- What advantage does the electric arc furnace present in comparison to the basic oxygen furnace? Unlock Flexibility & Sustainability
- What are the components of sintering? Master the 4-Step Process for Stronger Materials
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition
- Is laser sintering the same as melting? Understand the Key Differences for Your AM Process
- What are the 3 types of heat transfer? Master Conduction, Convection & Radiation for Your Lab
- What is the difference between sintering and powder metallurgy? Sintering is a Key Step Within the Process
- What is the physical Vapour deposition method for nanoparticles? A Top-Down Approach for High-Purity Nanomaterials



















