In short, an induction furnace is a powerful tool used for melting and heating electrically conductive materials, most notably metals like steel, iron, copper, and aluminum. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, generating heat directly within the material itself rather than relying on an external heat source. This method results in rapid, efficient, and highly uniform heating.
The true value of an induction furnace lies not just in what it does—heating and melting metals—but in how it does it: by generating heat directly inside the material for unparalleled speed, control, and compositional uniformity.

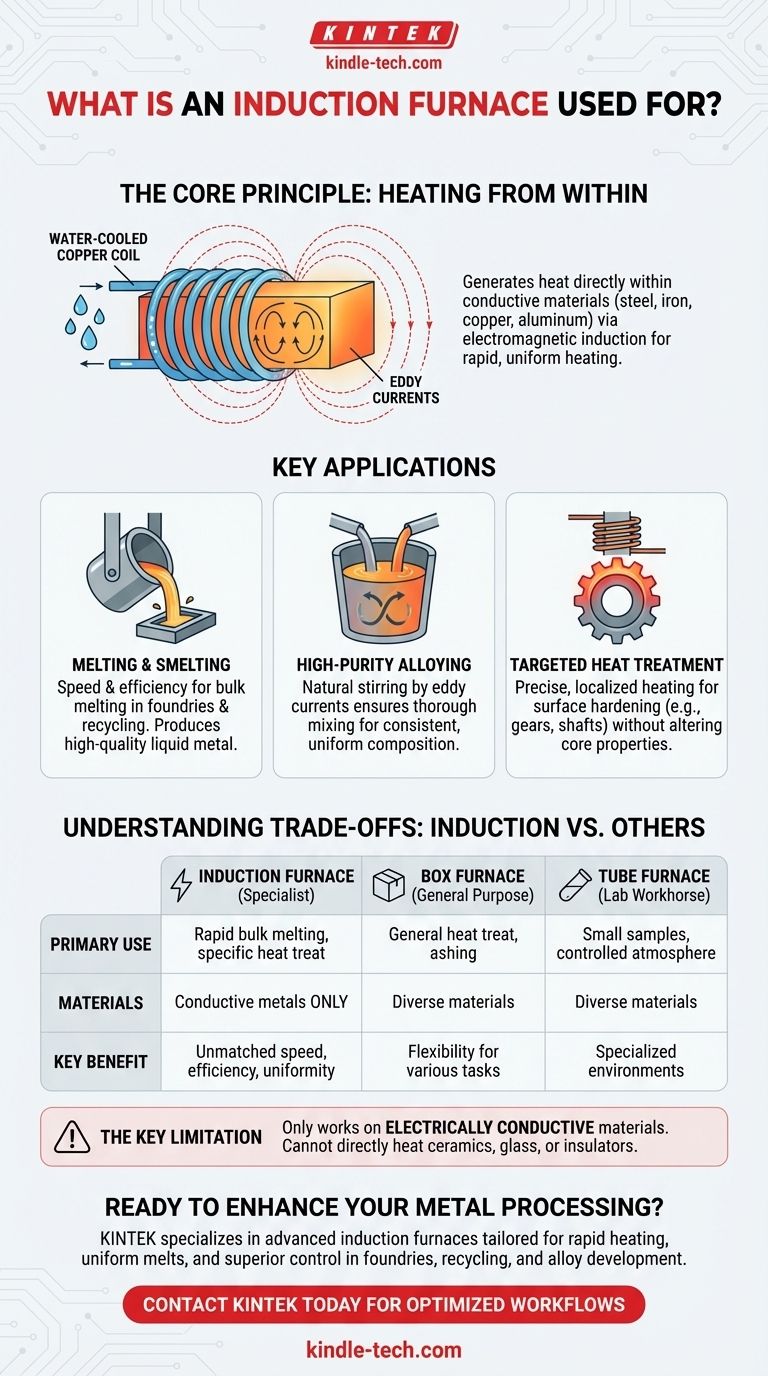
The Core Principle: Heating from Within
The induction furnace's unique capabilities stem directly from its method of heating. Understanding this principle is key to understanding its applications.
How Induction Heating Works
An induction furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil, called an inductor, to generate a powerful alternating magnetic field. When a conductive material is placed inside this field, it induces swirling electrical currents within the material, known as eddy currents. The material's natural resistance to these currents generates immense and immediate heat.
The Result: Speed and Purity
Because the heat is generated inside the material, the process is incredibly fast and efficient. There is no need to heat a chamber or wait for heat to transfer from an external element. This direct heating also stirs the molten metal, ensuring a uniform temperature and a homogenous chemical composition throughout the melt.
Key Applications of Induction Furnaces
While other furnaces can perform heat treatment, the induction furnace excels at tasks requiring speed, bulk melting, and high purity.
Melting and Smelting
This is the primary application for induction furnaces, especially in foundries and metal recycling facilities. Their speed and efficiency make them ideal for melting scrap metal and producing high-quality liquid metal for casting.
High-Purity Alloying
For industries that require precise metal alloys, the induction furnace is a critical tool. The natural stirring action caused by the eddy currents ensures that alloying elements are thoroughly mixed, resulting in a consistent and high-quality final product.
Targeted Heat Treatment
While box furnaces are used for general heat treatment, an induction furnace can be used for highly targeted processes. By designing a specific inductor coil, heat can be applied to a very precise area of a metal part, making it perfect for tasks like surface hardening gears or shafts without altering the core properties of the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Induction vs. Other Furnaces
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on the material and the process. The induction furnace is a specialist, not a generalist.
Induction Furnace vs. Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is a laboratory workhorse designed for versatility. It excels at processing small samples under controlled atmospheres for a wide variety of tasks like annealing, sintering, and coating. It is not designed for bulk melting.
Induction Furnace vs. Box Furnace
A box furnace, or muffle furnace, is a general-purpose tool for labs and workshops. It heats the entire chamber, which in turn heats the workpiece. It is ideal for heat treating small steel parts, ashing materials for analysis, or sintering ceramics, but it is far slower and less efficient for melting metal compared to an induction furnace.
The Key Limitation: Material Dependency
The most significant trade-off is that an induction furnace only works on electrically conductive materials. It cannot directly heat ceramics, glass, or other insulators, which limits its application compared to the more versatile box or tube furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate technology, you must align the furnace's heating method with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting large quantities of metal: The induction furnace is the superior choice for its unmatched speed, efficiency, and melt quality.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment or lab analysis of diverse materials: A box furnace offers the flexibility needed for tasks like annealing, tempering, and ashing.
- If your primary focus is research involving small samples or controlled atmospheres: A tube furnace provides the specialized environment required for processes like calcination or degassing.
Choosing the right furnace begins with understanding how its heating method aligns with your material and desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting & Smelting | Bulk metal melting in foundries | High speed and efficiency |
| High-Purity Alloying | Creating precise metal alloys | Uniform composition and mixing |
| Targeted Heat Treatment | Surface hardening of components | Precise, localized heating |
Ready to enhance your metal processing with precision and efficiency?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment, including induction furnaces tailored for your specific needs. Whether you're in metal recycling, foundry operations, or high-purity alloy development, our solutions deliver rapid heating, uniform melts, and superior control.
Contact us today to discuss how our induction furnaces can optimize your workflow and deliver consistent, high-quality results for your laboratory or production facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















