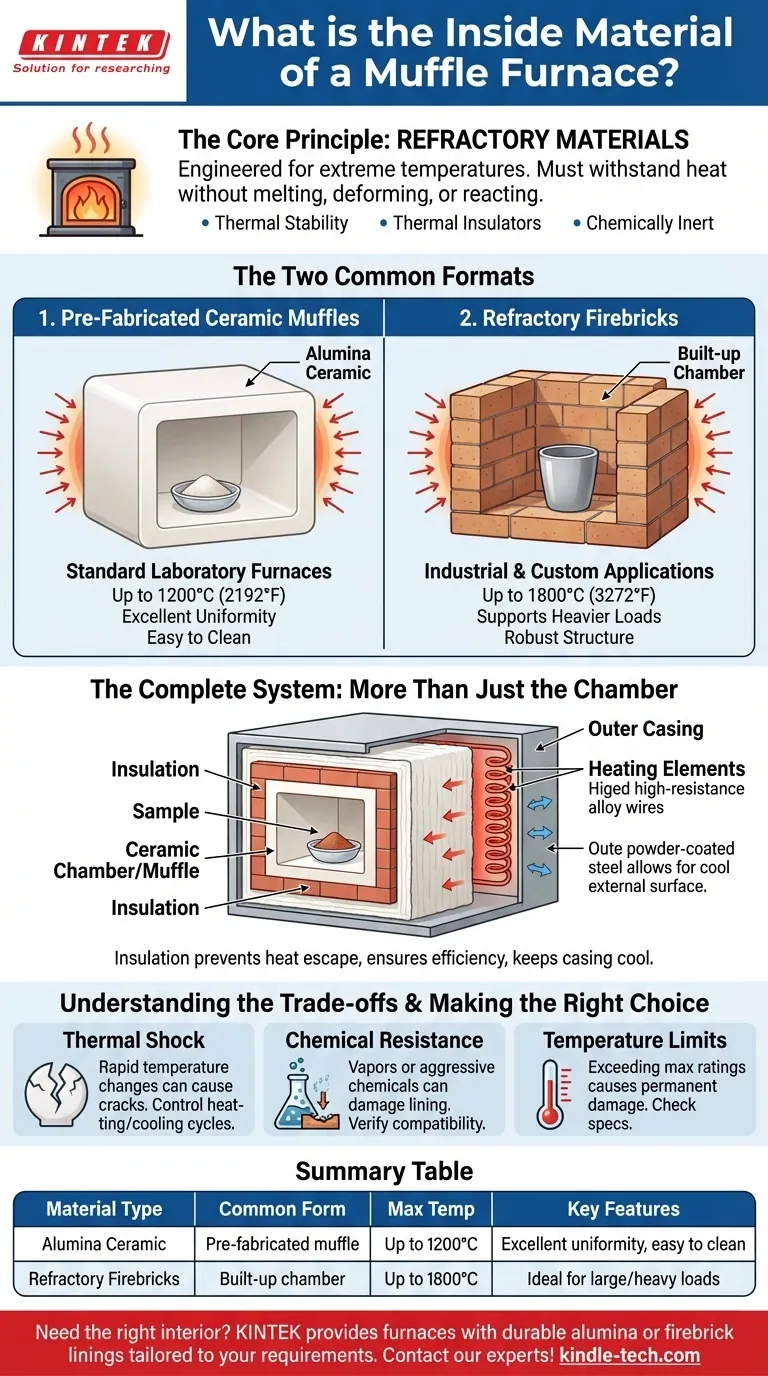
At its core, the inside of a muffle furnace is made from high-performance refractory materials. This category includes specific materials like dense ceramics (such as alumina) which are often formed into a single chamber, or individual refractory firebricks that are built up to form the interior.
The choice of material for a furnace's inner chamber is a critical engineering decision. The entire function of the furnace depends on using materials that can withstand extreme temperatures without melting, deforming, or reacting with the sample being heated.

The Core Principle: Refractory Materials
The term "refractory" is key to understanding a muffle furnace's construction. It describes a class of materials specifically designed to maintain their strength and chemical properties at very high temperatures.
Why Ceramics are the Standard
The inner chamber is almost universally made of a ceramic material. This is because ceramics possess the essential properties needed for a high-temperature environment.
These properties include exceptional thermal stability, meaning they don't break down or melt at temperatures that can exceed 1200°C (2192°F). They are also excellent thermal insulators and are generally chemically inert, preventing contamination of the samples inside.
The Two Common Formats
Depending on the furnace's size and intended maximum temperature, this ceramic interior is constructed in one of two ways.
1. Pre-Fabricated Ceramic Muffles Most standard laboratory muffle furnaces use a single, pre-formed chamber called a muffle. This muffle is often made from high-purity ceramic compounds like alumina.
This single-piece construction ensures excellent temperature uniformity and provides a smooth, easy-to-clean surface.
2. Refractory Firebricks For larger industrial furnaces or certain custom applications, the inner chamber is constructed from individual refractory firebricks.
These bricks are mortared together, similar to conventional masonry, to build a robust chamber capable of supporting heavier loads and reaching temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F).
The Complete System: More Than Just the Chamber
The ceramic chamber is the heart of the furnace, but it works as part of a system. It contains the sample and the heat, but it is itself surrounded by other critical components.
The Role of Insulation
Directly outside the ceramic muffle or firebrick lining is a thick layer of insulation. This material, often a ceramic fiber blanket, is crucial for preventing heat from escaping.
This insulation ensures the furnace operates efficiently and keeps the external steel casing cool enough to be safe.
Heating Elements and Casing
The heating elements, typically made of a high-resistance alloy wire, are positioned around the outside of the ceramic chamber. They generate the intense heat that radiates inward.
Finally, an outer casing, usually made of powder-coated or stainless steel, provides structural support and protects all the internal components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the materials used in muffle furnaces have inherent limitations that users must understand to ensure longevity and proper function.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
Ceramics, despite their heat resistance, can be brittle. Heating or cooling the furnace too rapidly can cause thermal shock, leading to cracks in the muffle or firebricks.
This is why controlled heating and cooling cycles are essential for preserving the furnace's interior.
Chemical Resistance is Not Absolute
While highly resistant to corrosion, the ceramic chamber can be damaged by certain aggressive chemicals or vapors at high temperatures.
Always verify that the materials you are heating will not react with or etch the furnace's alumina or firebrick lining.
Maximum Temperature Limits
Different refractory materials have different maximum operating temperatures. A standard ceramic muffle may be rated for 1200°C, while specialized firebrick furnaces can handle 1800°C. Exceeding these limits can cause permanent damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The internal material directly impacts the furnace's capability. Understanding this helps you select or operate the equipment correctly.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory ashing or heat-treating: A standard furnace with a pre-fabricated alumina muffle provides the necessary performance and uniformity.
- If you require a very large chamber or ultra-high temperatures (above 1400°C): A furnace constructed from high-grade refractory firebricks is necessary for structural integrity.
- If you are working with potentially corrosive substances: Verify the chemical compatibility of your samples with the specific ceramic lining to prevent damage.
Ultimately, the refractory lining is the critical component that enables the precise and extreme heating required for modern scientific and industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Form | Max Temperature | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramic | Pre-fabricated muffle | Up to 1200°C | Excellent uniformity, easy to clean |
| Refractory Firebricks | Built-up chamber | Up to 1800°C | Ideal for large/heavy loads |
Need a muffle furnace with the right interior for your application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing furnaces with durable alumina or firebrick linings tailored to your temperature and sample requirements. Contact our experts today to ensure optimal performance and longevity for your laboratory processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the precaution of furnace? Essential Safety Steps to Protect Operators and Equipment
- What is the critical point of heat treatment? Master the Key to Steel Transformation
- What are the safety precautions for muffle furnace? A Complete Guide to Safe High-Temperature Operation
- How do you set up a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Accurate Operation
- How do you handle a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe & Accurate Operation



















