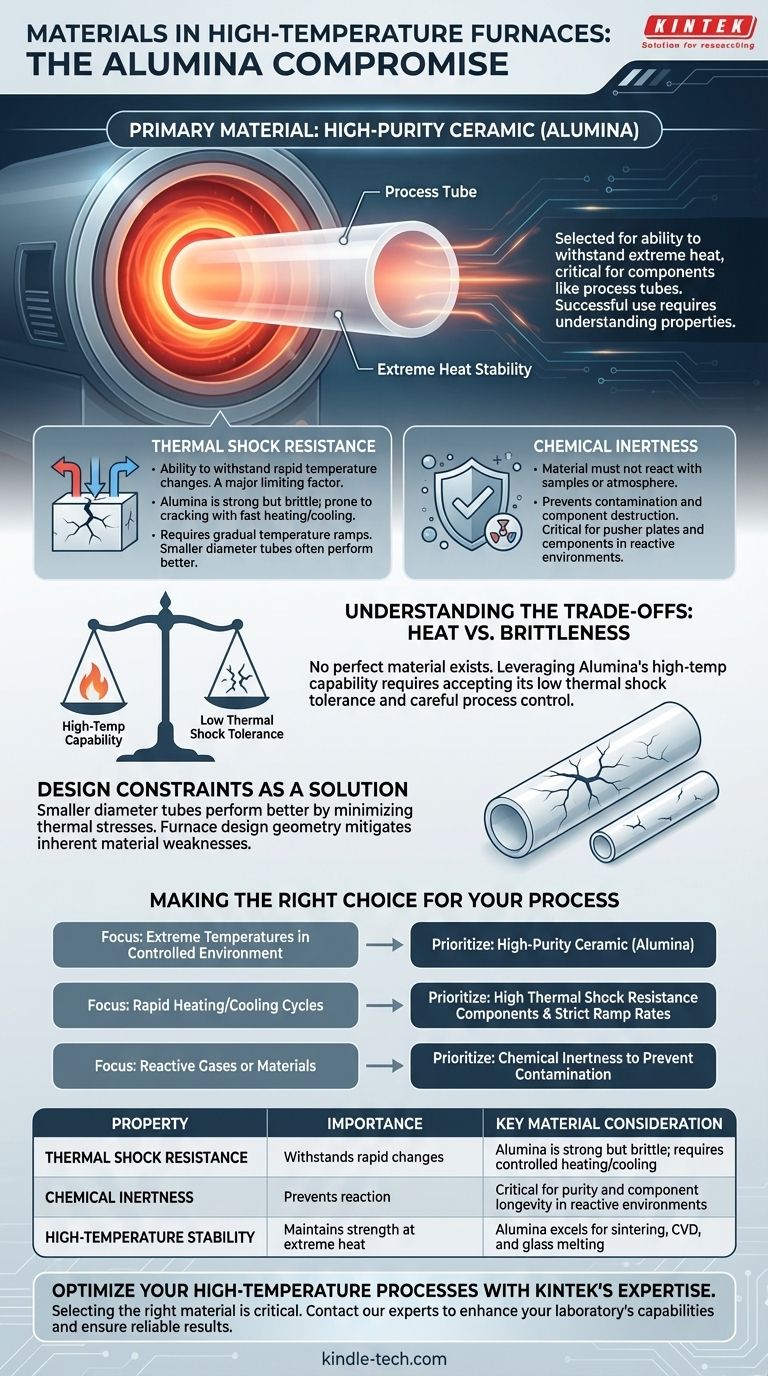
For high-temperature furnaces, the primary material used for critical components like process tubes is a high-purity ceramic, most commonly Alumina. This material is selected for its ability to withstand extreme heat, but its successful use depends heavily on understanding its specific properties and limitations, such as its susceptibility to thermal shock.
The choice of material for a high-temperature furnace is not about finding a single substance that does everything. It is a strategic decision based on balancing critical properties—primarily thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness—against the specific demands of the furnace's application.
Why Material Selection Dictates Furnace Performance
A high-temperature furnace is a system where different parts are made of different materials, each chosen for a specific job. The most critical component is often the one directly containing the process, which must endure the most extreme conditions.
The Core Component: Ceramic Tubes
For many applications like tube furnaces, Alumina is the material of choice for the process tube. Its primary advantage is its excellent stability and strength at very high temperatures.
These furnaces are essential for processes like vacuum sintering, atmosphere protection sintering, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) experiments, where maintaining a controlled, high-heat environment is paramount.
The First Critical Property: Thermal Shock Resistance
A material's ability to withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking is called thermal shock resistance. This is a major limiting factor for many furnace ceramics.
Alumina, while strong at high heat, can be brittle and prone to cracking if heated or cooled too quickly. This is why furnace operating procedures often specify gradual temperature ramps. The references note that smaller diameter Alumina tubes generally have better thermal shock performance.
The Second Critical Property: Chemical Inertness
The furnace material must not react with the substance being processed or the atmosphere inside the furnace. This property is known as chemical inertness.
For example, a furnace part like a pusher plate must endure a highly reducing atmosphere for long periods without degrading. Lack of chemical inertness can lead to contamination of the sample and destruction of the furnace components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no perfect material, and every choice involves compromises. Understanding these trade-offs is key to operating high-temperature equipment successfully and avoiding costly failures.
The Alumina Compromise: Heat vs. Brittleness
Alumina is an exceptional material for holding high temperatures, making it ideal for glass melting or testing ceramics. However, its inherent brittleness makes it vulnerable.
This creates a direct operational trade-off. To leverage Alumina's high-temperature capability, you must accept its low tolerance for thermal shock, which requires careful control over heating and cooling rates.
Design Constraints as a Solution
The observation that smaller diameter tubes perform better is a classic engineering solution to a material limitation. By reducing the size, the thermal stresses across the material are minimized during temperature changes.
This demonstrates that furnace design is deeply intertwined with the properties of the materials used. The geometry and dimensions of components are often chosen specifically to mitigate a material's inherent weaknesses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application dictates which material property you must prioritize. Use these principles to guide your thinking, whether you are selecting a new furnace or developing a process for an existing one.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures in a controlled environment: Your furnace will rely on a high-purity ceramic like Alumina for the core process chamber or tube.
- If your process involves rapid heating or cooling cycles: You must prioritize components designed for high thermal shock resistance and adhere strictly to the manufacturer's specified ramp rates.
- If you are working with reactive gases or materials: Your primary concern must be chemical inertness to prevent contamination and ensure the longevity of the furnace.
Understanding these foundational material properties empowers you to move beyond simply using a furnace to strategically leveraging it for reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Property | Importance for High-Temp Furnaces | Key Material Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid temperature changes | Alumina is strong but brittle; requires controlled heating/cooling |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reaction with samples/furnace atmosphere | Critical for purity and component longevity in reactive environments |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains strength and integrity at extreme heat | Alumina excels, making it ideal for sintering, CVD, and glass melting |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's expertise. Selecting the right furnace material is critical for the success and safety of your lab work. Whether your priority is extreme temperature stability, thermal shock resistance, or chemical inertness for sensitive applications, KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure reliable, repeatable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Protective Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes
- What is the primary function of an Alumina (Al2O3) tube in LLZTO sintering? Optimize Your Thermal Processing
- What are the primary functions of high-purity Alumina (Al2O3) tubes? Ensure Precision in Molten Salt Corrosion Tests
- Why is high-purity alumina preferred over mullite for CNT synthesis? Ensure Structural Stability at 1420°C
- What is the function of corundum tubes in high-temperature refractory corrosion experiments? Ensure Data Integrity



















