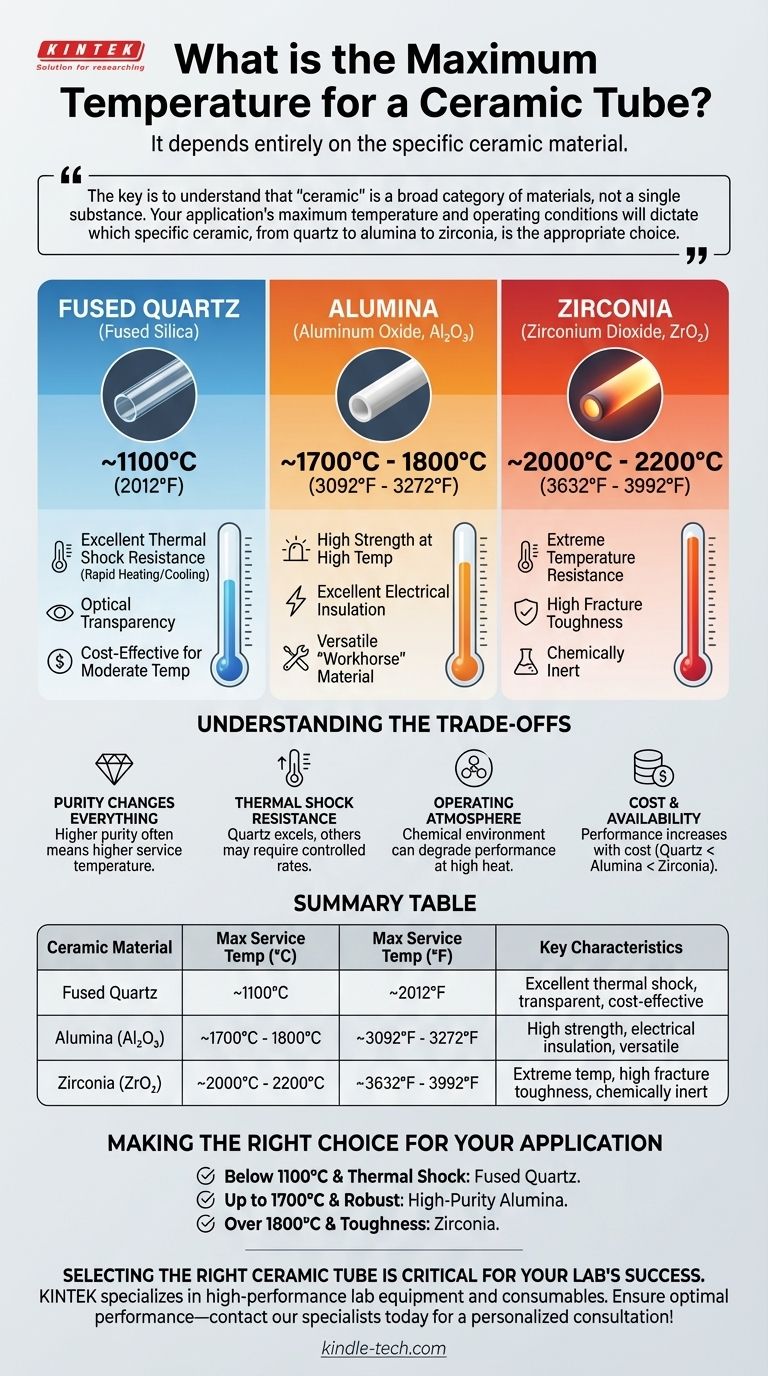
The maximum temperature for a ceramic tube is not a single value. It depends entirely on the specific type of ceramic material used. For example, a common transparent quartz tube can typically be used up to 1100°C (2012°F), while a high-purity alumina tube can withstand over 1700°C (3092°F), and specialized zirconia tubes can exceed 2000°C (3632°F).
The key is to understand that "ceramic" is a broad category of materials, not a single substance. Your application's maximum temperature and operating conditions will dictate which specific ceramic, from quartz to alumina to zirconia, is the appropriate choice.

Why Material Composition is Everything
Asking for the temperature limit of a "ceramic tube" is like asking for the speed limit of a "vehicle." A bicycle and a race car are both vehicles, but their performance capabilities are worlds apart. The same principle applies to technical ceramics.
Each material offers a unique profile of thermal resistance, durability, and cost.
Fused Quartz (Fused Silica)
Maximum Service Temperature: ~1100°C (2012°F)
Fused quartz is a high-purity glass known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance. You can heat it to high temperatures and cool it rapidly without cracking.
Its optical transparency also makes it ideal for applications where visual monitoring is necessary. It is often one of the most cost-effective choices for moderate high-temperature work.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃)
Maximum Service Temperature: ~1700°C - 1800°C (3092°F - 3272°F)
Alumina is arguably the most common and versatile technical ceramic for high-temperature applications. It is extremely hard, has excellent electrical insulation properties, and maintains its strength well at high temperatures.
It is the workhorse material for furnace tubes, insulators, and thermocouple protection tubes in a vast range of industries.
Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide, ZrO₂)
Maximum Service Temperature: ~2000°C - 2200°C (3632°F - 3992°F)
When applications push beyond the limits of alumina, zirconia is often the next step. It has one of the highest melting points of common oxides and exhibits excellent chemical inertness.
Zirconia is also known for its high fracture toughness, making it more resistant to mechanical stress than many other ceramics. It is used in ultra-high temperature furnaces, oxygen sensors, and crucibles for melting aggressive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is never about a single specification. The maximum temperature is a critical starting point, but other factors directly impact performance and longevity.
Purity Changes Everything
A higher-purity ceramic almost always has a higher service temperature. For instance, a 99.8% pure alumina tube will reliably perform at a higher temperature than a 95% pure alumina tube. Impurities can lower the melting point and degrade performance.
Thermal Shock Resistance
A material's ability to withstand rapid temperature changes is crucial. Quartz is the champion here. Many high-temperature ceramics, like alumina, require controlled heating and cooling rates to prevent cracking.
Operating Atmosphere
The chemical environment inside the tube matters. Certain atmospheres (like hydrogen) can react with and degrade specific ceramics at high temperatures, reducing their maximum effective service temperature and lifespan.
Cost and Availability
As performance increases, so does cost. Fused quartz is relatively inexpensive. High-purity alumina represents a moderate investment. Zirconia and other exotic ceramics are significantly more expensive and are reserved for applications where their extreme performance is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct tube requires balancing your technical requirements with your budget.
- If your primary focus is on applications below 1100°C requiring excellent thermal shock resistance or transparency: Fused quartz is the most effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is a robust, all-purpose solution for furnaces operating up to 1700°C: High-purity alumina offers the best balance of high performance, wide availability, and reasonable cost.
- If your primary focus is on extreme temperatures exceeding 1800°C or demanding high mechanical toughness: Zirconia is the necessary choice, though it comes at a significant cost premium.
Choosing the right ceramic tube is about matching the material's specific properties to your precise operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Material | Max Service Temperature (°C) | Max Service Temperature (°F) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | ~1100°C | ~2012°F | Excellent thermal shock resistance, transparent, cost-effective |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | ~1700°C - 1800°C | ~3092°F - 3272°F | High strength, excellent electrical insulation, versatile |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | ~2000°C - 2200°C | ~3632°F - 3992°F | Extreme temperature resistance, high fracture toughness, chemically inert |
Selecting the right ceramic tube is critical for your lab's success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including ceramic tubes made from quartz, alumina, and zirconia. Our experts will help you match the perfect material to your specific temperature requirements, operating atmosphere, and budget. Ensure optimal performance and longevity for your high-temperature applications—contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean an alumina tube furnace? Extend Tube Life with Proper Maintenance
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Purity
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control



















