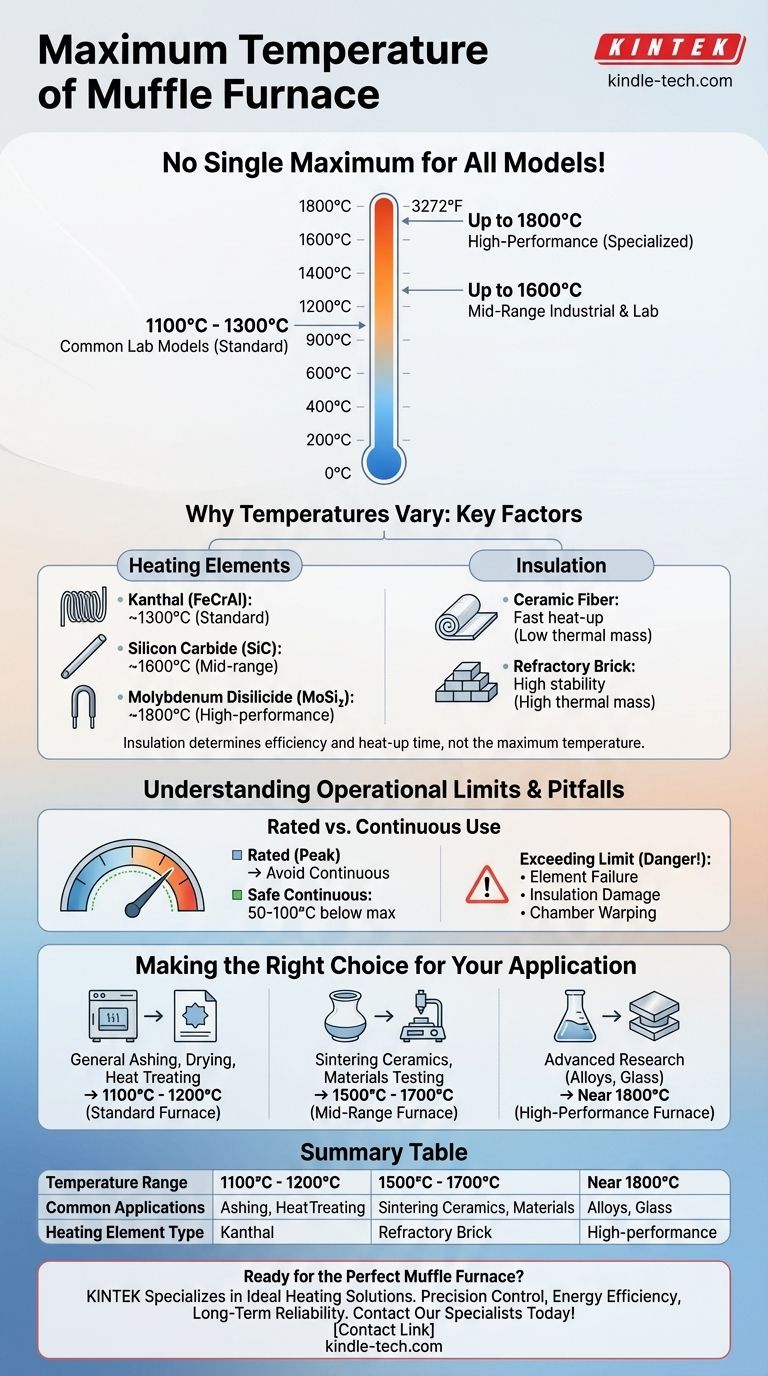
There is no single maximum temperature for all muffle furnaces. Instead, the maximum temperature is a specification determined by the manufacturer, with common laboratory models operating between 1100°C and 1300°C. However, high-performance furnaces designed for specialized applications can safely reach temperatures as high as 1800°C (3272°F).
A muffle furnace's maximum temperature is not a universal constant but a critical design limit. This limit is dictated by the materials used for its heating elements and insulation, requiring you to match the furnace's capabilities to your specific high-temperature application.

Why Maximum Temperatures Vary So Widely
The significant range in maximum temperatures across different muffle furnaces stems directly from their construction and intended purpose. The two most critical factors are the type of heating element used and the quality of the thermal insulation.
The Role of Heating Elements
The material of the heating element is the primary determinant of a furnace's peak temperature. Different materials have different physical limits before they degrade or fail.
- Kanthal (FeCrAl) Elements: Common in standard lab furnaces, these are cost-effective and reliable up to about 1300°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements: Used in mid-range industrial and lab furnaces, these allow for higher operating temperatures, typically up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements: Found in high-performance furnaces for advanced materials research, these can operate continuously at extreme temperatures, reaching up to 1800°C.
The Impact of Insulation
Insulation does not determine the maximum temperature, but it dictates how efficiently the furnace reaches and holds that temperature.
A furnace with low-thermal-mass insulation, like ceramic fiber, can heat up very quickly—sometimes in as little as 20 minutes. Conversely, a furnace built with dense refractory brick may take several hours to reach its maximum temperature but will hold that heat with greater stability.
Understanding Operational Limits and Pitfalls
Simply knowing the maximum temperature is not enough. To operate a muffle furnace safely and ensure its longevity, you must understand the difference between its peak rating and its practical, everyday working limits.
Rated Temperature vs. Continuous Use
The "maximum temperature" listed on a spec sheet is often a peak rating that should not be sustained for long periods. Continuously running a furnace at its absolute limit will drastically shorten the lifespan of its heating elements and insulation.
A safer and more common practice is to operate the furnace at 50-100°C below its maximum rated temperature for extended applications.
The Danger of Exceeding the Limit
Never attempt to operate a muffle furnace beyond its specified maximum temperature. Doing so can cause catastrophic failure of the heating elements, permanent damage to the insulation, and warping of the furnace chamber, leading to costly repairs and unsafe operating conditions.
Time to Reach Temperature
Be aware that reaching the target temperature is not instantaneous. The time required depends on the furnace's size, power, and insulation type. While a small lab unit might be ready in under an hour, larger industrial models can require several hours to heat-soak and stabilize.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires you to look beyond a single number and consider your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is general ashing, drying, or basic heat treating: A standard furnace with a maximum temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C is typically sufficient and the most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is sintering technical ceramics or testing materials: You will likely need a mid-range furnace capable of reaching 1500°C to 1700°C to achieve the desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is advanced research with high-temperature alloys or glasses: You must invest in a high-performance model with specialized elements that can reliably operate at or near 1800°C.
Ultimately, selecting a muffle furnace begins by matching your specific process temperature requirements to the unit's designed operational limits.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Heating Element Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1100°C - 1300°C | General ashing, drying, heat treating | Kanthal (FeCrAl) |
| Up to 1600°C | Sintering ceramics, materials testing | Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
| Up to 1800°C | Advanced alloys, glass research | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your lab's temperature requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in matching laboratories with the ideal heating solutions. Whether you need a standard 1200°C furnace for routine testing or a high-performance 1800°C model for advanced research, our experts will help you select equipment that delivers precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability.
We serve laboratories across various industries with:
- Precision temperature control systems
- Durable heating elements and insulation
- Equipment tailored to your specific process needs
Contact our heating specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you make biochar in a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Controlled Pyrolysis
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of heat transfer in a furnace? Mastering Conduction, Convection & Radiation
- What is the function of an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temp Processing
- What are the uses of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Essential for Drug Purity & Safety



















