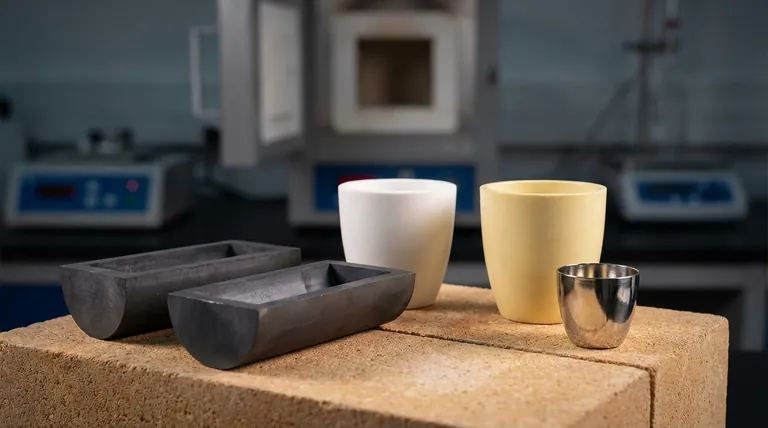
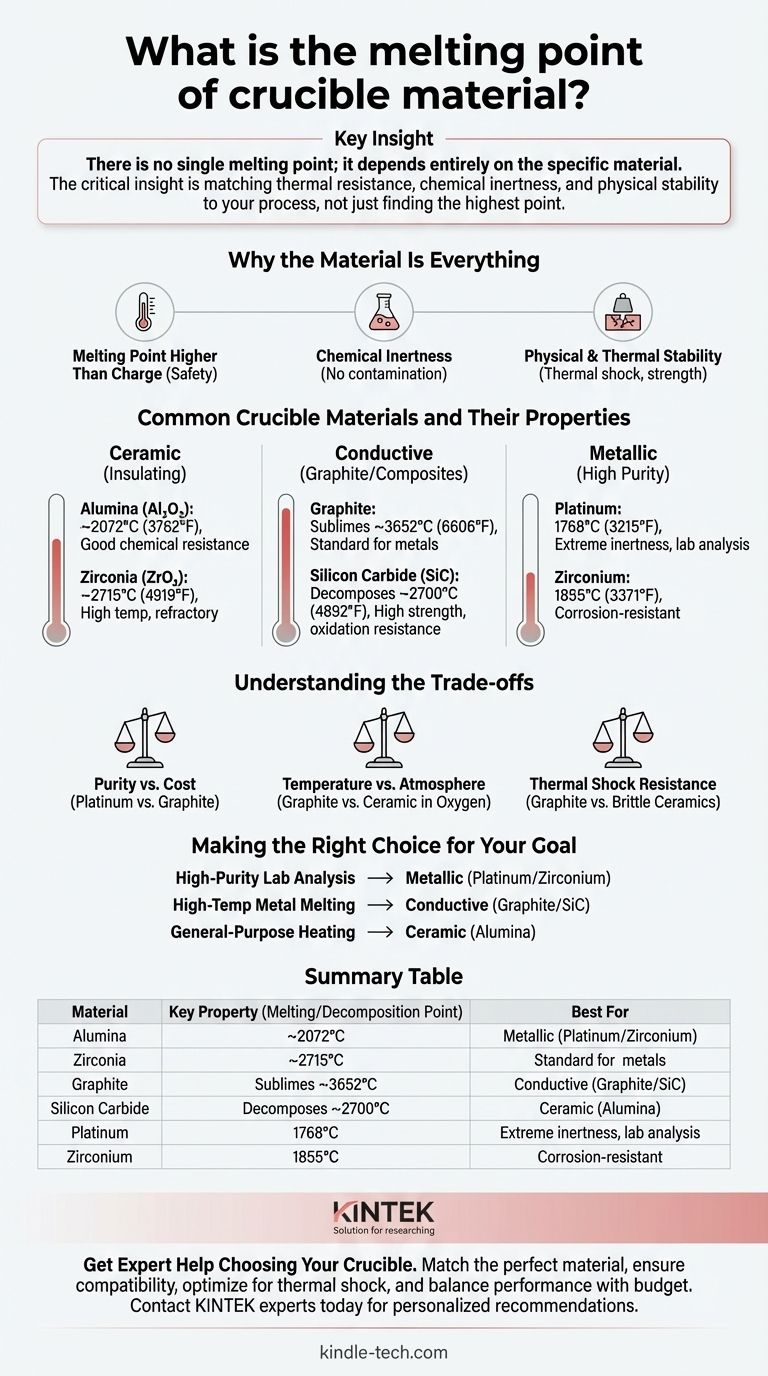
There is no single melting point for a crucible; the value depends entirely on the specific material it is made from. These materials are chosen based on the application, with melting points ranging from approximately 1770 °C (3220 °F) for platinum to over 3650 °C (6600 °F) for graphite, which sublimes rather than melts.
The critical insight is that choosing a crucible is not about finding the highest possible melting point. It's about selecting a material whose thermal resistance, chemical inertness, and physical stability are precisely matched to the substance being heated and the specific process conditions.

Why the Material Is Everything
A crucible’s primary job is to contain a substance while it is heated to extreme temperatures. To do this successfully, the crucible material must meet several non-negotiable criteria beyond simply not melting.
A Melting Point Higher Than the Charge
The most obvious requirement is that the crucible must remain solid at temperatures well above the melting point of the material it holds, known as the "charge." This safety margin prevents catastrophic failure and loss of the melt.
Chemical Inertness
A crucible must not react with the molten material it contains. Chemical reactions can contaminate the melt, altering its properties, and can also degrade the crucible itself, leading to structural failure.
Physical and Thermal Stability
The material must withstand the stress of rapid temperature changes (thermal shock) without cracking. It must also be physically strong enough at high temperatures to hold the weight of the molten charge without deforming.
Common Crucible Materials and Their Properties
Crucibles are generally classified into a few key categories, each with distinct properties suited for different tasks.
Ceramic Crucibles (Insulating)
These are often used for their excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance.
- Alumina (Al₂O₃): A very common and cost-effective choice, it has a melting point of approximately 2072 °C (3762 °F). It offers good resistance to chemical attack.
- Zirconia (ZrO₂): Used for higher temperature applications, Zirconia has a melting point of around 2715 °C (4919 °F) and is exceptionally refractory.
Conductive Crucibles (Graphite and Composites)
These materials are often used in induction furnaces where the crucible itself needs to heat up.
- Graphite: A unique material that does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimes (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at around 3652 °C (6606 °F). It is the standard for melting many non-ferrous and ferrous metals.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): A composite of graphite and silicon carbide, this material offers superior strength and oxidation resistance compared to pure graphite. It begins to decompose at approximately 2700 °C (4892 °F).
Metallic Crucibles (High Purity)
Used in laboratory settings where preventing even trace contamination is the highest priority for accurate chemical analysis.
- Platinum: With a melting point of 1768 °C (3215 °F), platinum is prized for its extreme inertness, making it ideal for sample preparation in analytical chemistry.
- Zirconium: Another high-purity option with a melting point of 1855 °C (3371 °F), it is also highly resistant to corrosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible involves balancing performance requirements with practical limitations. A higher melting point is not always better if it comes with unacceptable trade-offs.
Purity vs. Cost
Platinum offers unparalleled purity for lab analysis but is prohibitively expensive for large-scale industrial melting. Graphite is far more economical for bulk processes but may not be suitable for high-purity applications.
Temperature vs. Atmosphere
Graphite has an exceptional temperature ceiling but will rapidly oxidize and burn away in an oxygen-rich atmosphere. In such cases, a ceramic crucible like Alumina or Zirconia is required, even if its ultimate temperature limit is lower than graphite's sublimation point.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Some ceramic materials, while having very high melting points, are brittle and can crack if heated or cooled too quickly. Clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucibles often provide better resistance to thermal shock, making them more durable in rapid-cycle operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection must be guided by your primary objective. Match the crucible material to the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity lab analysis: Choose a metallic crucible like platinum or zirconium to minimize sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is melting metals at very high temperatures: A graphite or silicon carbide crucible is the standard choice, provided the atmosphere is controlled.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in an open atmosphere: An alumina ceramic crucible offers an excellent balance of temperature resistance, chemical stability, and cost.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of your target material and your furnace environment is the key to selecting a crucible that performs safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Property (Melting/Decomposition Point) | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | ~2072°C (3762°F) | General-purpose heating, cost-effective applications |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | ~2715°C (4919°F) | Very high-temperature applications |
| Graphite | Sublimes at ~3652°C (6606°F) | Melting metals in controlled atmospheres |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Decomposes at ~2700°C (4892°F) | High-strength, oxidation-resistant applications |
| Platinum | 1768°C (3215°F) | High-purity lab analysis, minimal contamination |
| Zirconium | 1855°C (3371°F) | Corrosion-resistant, high-purity applications |
Get Expert Help Choosing Your Crucible
Selecting the right crucible material is critical for your lab's safety, efficiency, and results. The wrong choice can lead to contamination, equipment failure, or inaccurate data.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and expertise. We can help you:
- Match the perfect crucible material to your specific application and temperature requirements
- Ensure chemical compatibility with your samples to prevent contamination
- Optimize for thermal shock resistance and durability in your processes
- Balance performance with budget constraints without compromising quality
Don't leave your crucible selection to chance. Contact our experts today for personalized recommendations and ensure your lab operates at peak performance with the right equipment for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- What are five applications of soldering? From Electronics to Art, Master Material Joining



















