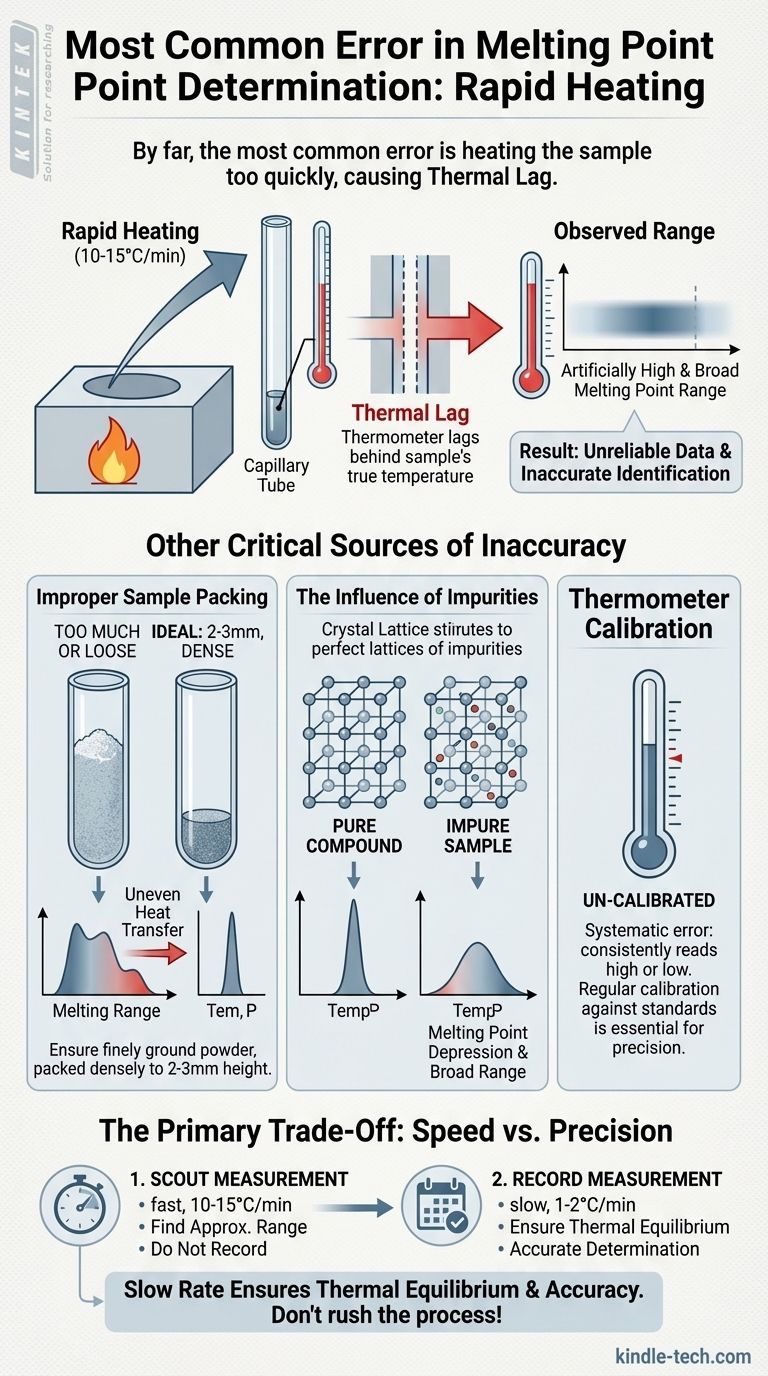
By far, the most common error in melting point determination is heating the sample too quickly. This fundamental mistake causes a lag between the temperature of the heating block and the temperature registered by the thermometer. The result is an observed melting point range that is artificially high and broader than the true value, undermining the reliability of the measurement.
The accuracy of a melting point measurement is directly tied to thermal equilibrium. Rushing the process breaks this equilibrium, making your thermometer an unreliable narrator of your sample's true physical state.

The Physics of a Flawed Measurement: Why Rapid Heating Fails
Melting point is a physical constant used for both identification and purity assessment. An accurate measurement hinges on the slow, controlled transfer of heat. When this principle is violated, the data becomes meaningless.
Understanding Thermal Lag
A melting point apparatus consists of a heating block, your sample in a capillary tube, and a thermometer. Heat does not transfer between these three components instantaneously. This delay is known as thermal lag.
The Thermometer's Deception
If you heat the block rapidly, its temperature rises much faster than the heat can transfer to, and be absorbed by, the sample and the thermometer.
When your sample begins to melt, the thermometer has not yet "caught up" to the sample's true temperature. You will only see and record the temperature after it has risen past the actual melting point.
The Consequence: An Inflated, Broad Range
This lag means you will always record a melting point that is higher than reality. Because the temperature is rising so quickly throughout the melting process, the range from the first drop of liquid (onset) to the fully molten state (clear point) will also appear artificially wide.
Other Critical Sources of Inaccuracy
While rapid heating is the primary culprit, other factors in your technique can also lead to poor results. These often manifest as a broad melting range, making it difficult to distinguish between poor technique and an impure sample.
Improper Sample Packing
Your sample should be a finely ground powder to ensure it heats uniformly. It must be packed densely into the capillary tube to a height of no more than 2-3 millimeters.
Using too much sample is a frequent mistake. A large sample size creates a significant temperature gradient across the material itself, meaning the bottom will melt long before the top, resulting in a very broad range.
Similarly, a loosely packed sample with air gaps will heat inefficiently. The trapped air acts as an insulator, slowing heat transfer and causing uneven melting.
The Influence of Impurities
This is not a technical error but a chemical principle that can be misinterpreted as one. Impurities disrupt a compound's crystal lattice structure.
This disruption lowers the energy required to break the solid-state bonds, causing the substance to melt at a lower temperature and over a wider range. This is known as melting point depression and is a key indicator of an impure sample.
Thermometer Calibration
An uncalibrated thermometer introduces a systematic error. If the thermometer consistently reads 2°C high, every measurement you take will be 2°C high, even with perfect technique. For precise work, thermometer calibration against known standards is essential.
The Primary Trade-Off: Speed vs. Precision
In any lab, time is a resource. However, with melting point determination, sacrificing time directly sacrifices accuracy.
The "Scout" Measurement
A common and valid technique is to perform a rapid "scout" melt on a preliminary sample. Heating quickly (10-15 °C per minute) allows you to find the approximate melting range in a short amount of time.
This scout value is never recorded as official data. Its only purpose is to identify the temperature range for a second, more careful measurement.
The "Record" Measurement
Once you know the approximate range, you allow the apparatus to cool significantly. You then prepare a fresh sample and heat it quickly to about 15-20 °C below the scout range.
At that point, you must slow the rate of heating down to 1-2 °C per minute. This slow rate ensures thermal equilibrium and allows for an accurate determination of the melting point range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach should be dictated by your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is identifying an unknown compound: You must prioritize accuracy. First, perform a rapid scout melt, then use a fresh sample to measure slowly (1-2 °C per minute) to get a sharp range to compare against literature values.
- If your primary focus is assessing the purity of a known compound: A sharp melting range that matches the literature value indicates high purity, while a broad and depressed range signifies the presence of impurities.
- If your primary focus is routine verification: Always ensure your sample is finely powdered and packed densely to a height of 2-3 mm to guarantee efficient, uniform, and repeatable heat transfer.
Mastering this technique comes down to one principle: granting your system the time it needs to achieve thermal equilibrium.
Summary Table:
| Error Type | Primary Consequence | Key Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Heating | Artificially high & broad melting range | Slow heating rate (1-2°C/min) near melting point |
| Improper Sample Packing | Broad, uneven melting range | Use finely ground powder, pack densely to 2-3mm height |
| Uncalibrated Thermometer | Systematic high/low readings | Regular calibration against known standards |
| Impure Sample | Melting point depression & broad range | Use pure compounds for identification |
Achieve precise and reliable melting point determinations with KINTEK's laboratory equipment.
Struggling with inconsistent results? Our specialized melting point apparatuses are designed to ensure optimal thermal equilibrium and accurate temperature control. Whether you're identifying unknown compounds or assessing purity, KINTEK provides the reliable tools and consumables your lab needs for flawless analysis.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's precision and efficiency.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys











