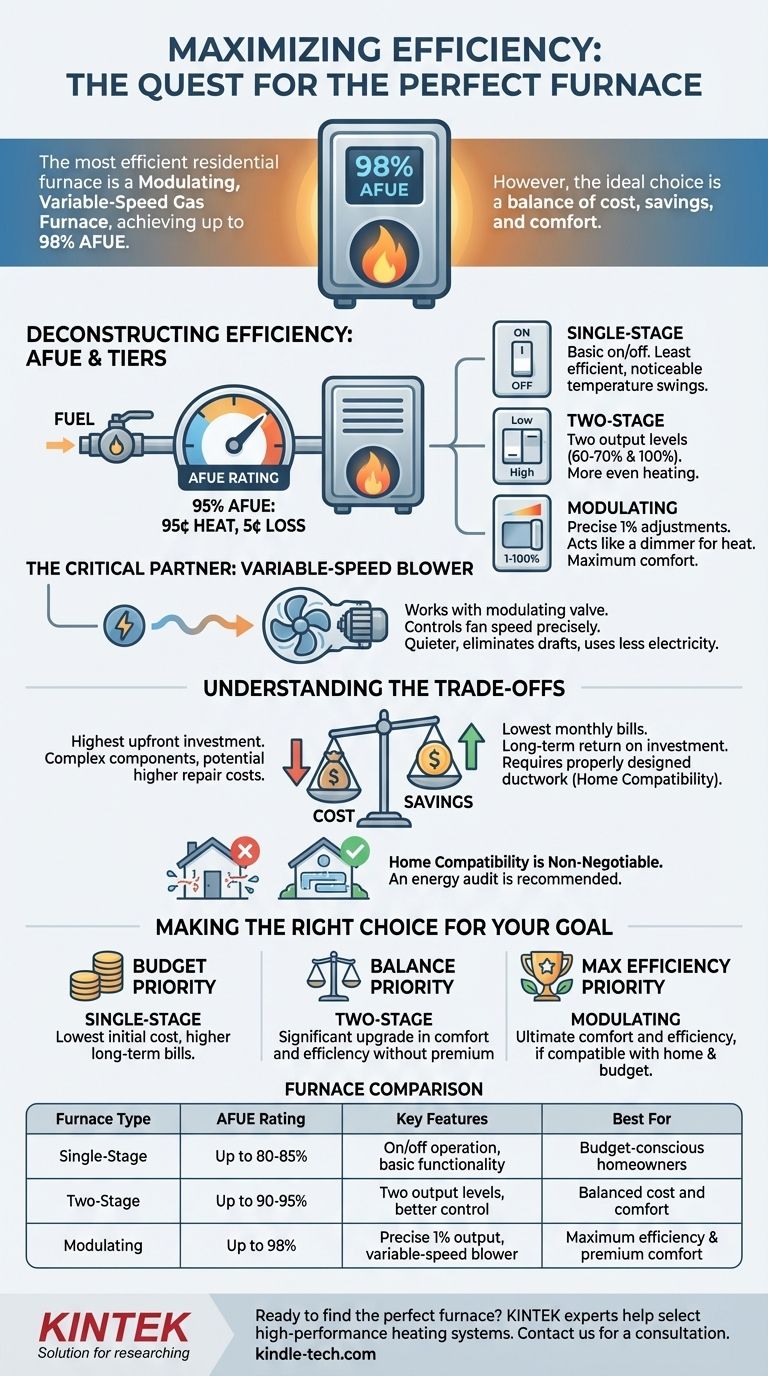
The most efficient residential furnace available today is a modulating, variable-speed gas furnace. This type of system can achieve an Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating of up to 98%, meaning only 2% of the fuel is lost during the combustion process. However, this peak efficiency comes with the highest upfront cost and requires specific home conditions, like properly designed ductwork, to perform correctly.
Choosing a furnace is not just about chasing the highest efficiency number. The most practical and efficient solution for your home involves a critical balance between the furnace's upfront cost, its long-term energy savings, and its ability to deliver consistent comfort.

Deconstructing Furnace Efficiency
True efficiency is a combination of a furnace's technical capabilities and its compatibility with your home. Understanding the core components and ratings is the first step to making an informed decision.
Understanding AFUE Ratings
The primary metric for furnace efficiency is its AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) rating. This percentage tells you how much of the fuel consumed is converted directly into usable heat for your home over the course of a year.
A furnace with a 95% AFUE rating means that for every dollar you spend on fuel, 95 cents becomes heat, and 5 cents are lost through the exhaust. Higher AFUE ratings signify greater efficiency and lower long-term fuel costs.
The Three Tiers of Gas Furnaces
Residential gas furnaces are generally categorized into three distinct performance tiers, each offering a different level of efficiency and comfort.
-
Single-Stage Furnaces: This is the most basic design. It operates on a simple "on/off" principle, running at 100% capacity whenever it's on. This can lead to noticeable temperature swings and is the least efficient option.
-
Two-Stage Furnaces: This model offers a significant improvement by operating at two levels: a low-output stage (around 60-70% capacity) and a high-output stage (100%). It runs on the lower, more efficient stage most of the time, only using full power on the coldest days. This results in more even heating and better efficiency.
-
Modulating Furnaces: This is the most advanced and efficient type. Instead of one or two set levels, a modulating furnace can adjust its heat output in tiny increments, often as fine as 1%. It acts like a dimmer switch for your heat, constantly matching its output to your home's precise needs.
The Role of the Variable-Speed Blower
The gas valve determines heat output, but the blower motor distributes that heat. A variable-speed blower is a critical partner to a modulating gas valve.
It precisely controls the speed of the fan, moving air more slowly and quietly for longer periods. This combination eliminates uncomfortable drafts, maintains a highly stable temperature, and uses significantly less electricity than a standard single-speed blower.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The most technologically advanced option is not always the most practical choice. Objectively weighing the costs against the benefits is essential.
The Cost vs. Savings Equation
A top-tier modulating furnace is the most expensive to purchase and install. While it will deliver the lowest monthly gas bills, the upfront investment can be substantial.
You must calculate the payback period—the time it takes for the energy savings to offset the higher initial cost. In some cases, a mid-range two-stage furnace may offer a more sensible financial return.
Home Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
A high-performance furnace cannot compensate for a low-performance home. A modulating furnace requires properly sized and well-sealed ductwork to function as designed.
Installing a 98% AFUE furnace in a home with leaky, undersized ducts is a wasted investment. The system will struggle to distribute air, negating many of its efficiency and comfort benefits. An energy audit is often a wise first step.
Complexity and Repair Costs
Advanced systems contain more sophisticated components and electronics. While modern furnaces are reliable, the potential repair costs for a modulating furnace's complex circuit boards or gas valve can be higher than for a simple single-stage unit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace based on a clear assessment of your budget, your home's characteristics, and your personal comfort priorities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost: A single-stage furnace is the most budget-friendly initial purchase, but it will have the highest long-term energy bills and least consistent comfort.
- If your primary focus is a balance of cost and comfort: A two-stage furnace offers a significant upgrade in comfort and efficiency over a single-stage model without the premium price of a modulating unit.
- If your primary focus is maximum efficiency and ultimate comfort: A modulating, variable-speed furnace is the clear winner, provided it is compatible with your home's ductwork and your budget allows for the investment.
Ultimately, the most efficient furnace is the one that is correctly sized and professionally installed to meet the unique demands of your home.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | AFUE Rating | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Stage | Up to 80-85% | On/off operation, basic functionality | Budget-conscious homeowners |
| Two-Stage | Up to 90-95% | Two output levels, better temperature control | Balanced cost and comfort |
| Modulating | Up to 98% | Precise 1% output adjustments, variable-speed blower | Maximum efficiency and premium comfort |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your home's unique needs? The experts at KINTEK specialize in helping homeowners and professionals select and maintain high-performance heating systems. We provide the right equipment and guidance to ensure your system delivers maximum efficiency, comfort, and reliability. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let us help you achieve optimal home heating performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process



















