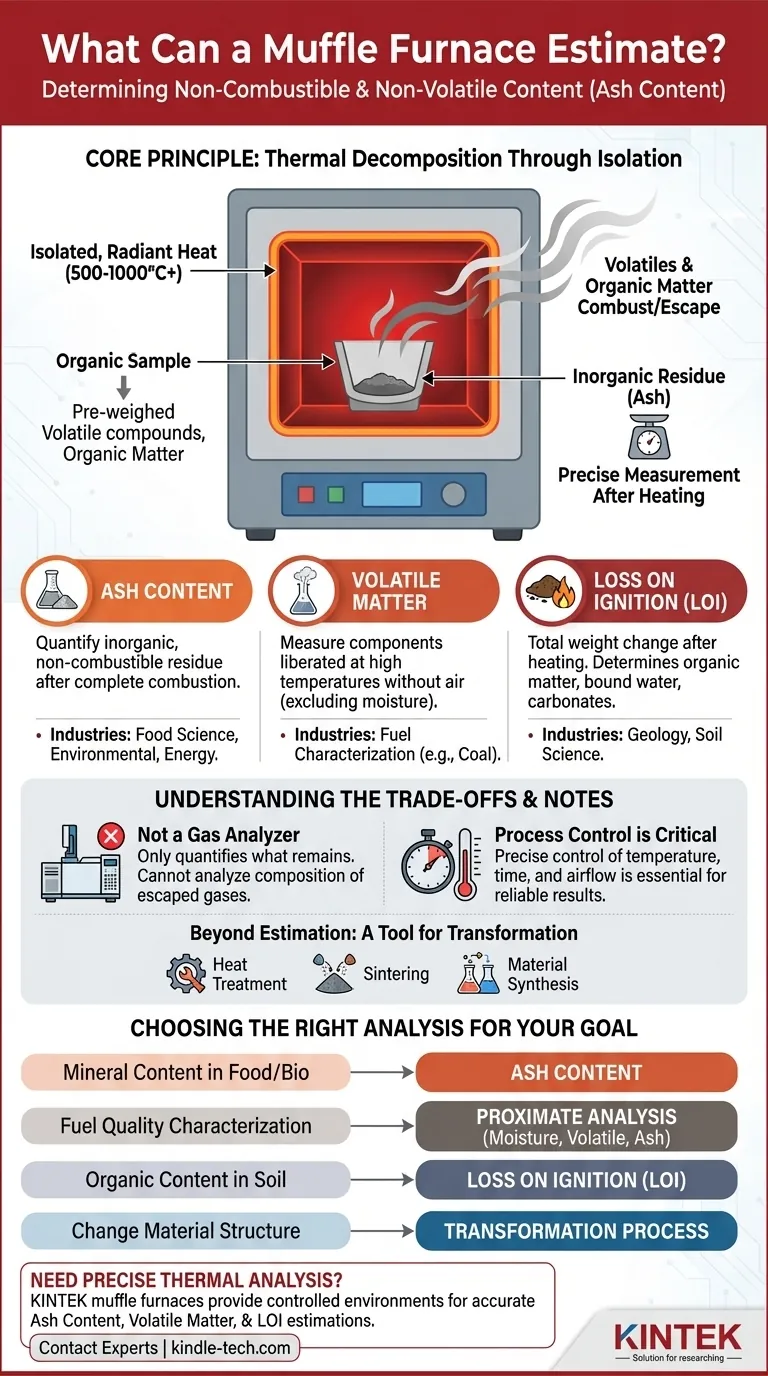
Primarily, a muffle furnace is used to estimate the amount of non-combustible and non-volatile material within a sample. This is most commonly referred to as determining the ash content. By exposing a sample to extremely high, controlled temperatures in an isolated chamber, the furnace burns away all organic and volatile components, leaving behind only the inorganic residue for measurement.
The core function of a muffle furnace in estimation is to separate materials based on their thermal properties. It uses intense, clean heat to eliminate volatile and combustible parts of a sample, allowing you to precisely quantify the stable, inorganic matter that remains.

The Core Principle: Characterization Through Thermal Decomposition
A muffle furnace is more than just a high-temperature oven. Its design is key to its function in quantitative analysis.
What Makes a Muffle Furnace Unique?
The name comes from the "muffle," which is a sealed, insulated inner chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements and any flame or combustion byproducts.
This creates an environment of pure, radiant heat. This isolation is critical for preventing contamination of the sample, ensuring that any weight loss is due only to changes within the sample itself, not reactions with external gases.
The Process of Thermal Analysis
The fundamental process is one of thermal decomposition. A pre-weighed sample, held in a high-temperature crucible, is placed inside the furnace.
The furnace is heated to a specific, high temperature (often 500-1000°C or higher) for a set duration. The intense heat causes the organic matter to combust and volatile compounds to turn into gas and escape.
Key Estimations and Analyses Performed
By carefully weighing the sample before and after heating, several key characteristics can be estimated.
Determining Ash Content
This is the most common analytical use. Ash is the inorganic, non-combustible residue left after complete combustion.
This analysis is vital in quality control for industries like food science (to measure mineral content), environmental testing (for analyzing sludge or waste), and energy (for determining the ash in coal or biomass).
Measuring Volatile Matter
Volatile matter refers to the components of a sample (excluding moisture) that are liberated at high temperatures in the absence of air.
For this test, a sample is heated to a specific temperature (e.g., 950°C for coal) for a precise amount of time. The resulting weight loss represents the volatile matter content, which is a key parameter in fuel characterization.
Loss on Ignition (LOI)
Loss on Ignition is a broader test that measures the total weight change of a sample after being heated to a high temperature.
While often used to determine organic matter content, LOI can also measure the loss of other volatile components, such as bound water in minerals or carbonates in geological samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specific tool with inherent limitations. Understanding these is key to accurate analysis.
It Is Not a Gas Analyzer
A muffle furnace only helps you quantify what remains. It does not analyze the composition of the gases that are burned off or volatilized. For that, you would need more complex equipment like a thermogravimetric analyzer coupled with a mass spectrometer (TGA-MS).
Process Control is Critical
The final results are entirely dependent on precise control of temperature, heating time, and airflow. Inconsistent procedures will lead to unreliable estimations. The rate of temperature increase (the "ramp") can also significantly impact the results.
Beyond Estimation: A Tool for Transformation
It's important to recognize that estimation is only one facet of a muffle furnace's utility. Its primary industrial purpose is often not analysis but material transformation, including:
- Heat Treatment: Hardening, annealing, or tempering metals to alter their physical properties.
- Sintering: Fusing ceramic or metal powders into a solid object.
- Material Synthesis: Creating new compounds or alloys at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The analysis you perform is dictated by the information you need to extract from your sample.
- If your primary focus is determining the total mineral content of a food or biological sample: Your goal is to measure ash content through complete combustion.
- If your primary focus is characterizing fuel quality, like coal: You will perform a proximate analysis, which involves separate estimations for moisture, volatile matter, and ash.
- If your primary focus is assessing the organic content of soil or sediment: You will perform a Loss on Ignition (LOI) test to measure the weight lost upon heating.
- If your primary focus is changing a material's structure: You are performing a heat treatment or synthesis process, not an estimation.
By providing a clean and controlled high-temperature environment, the muffle furnace empowers you to precisely separate and quantify the fundamental components of your material.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Type | Primary Use | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Ash Content | Quantify inorganic residue | Food Science, Environmental Testing, Energy |
| Volatile Matter | Measure combustible components | Fuel Characterization |
| Loss on Ignition (LOI) | Determine organic matter/water loss | Geology, Soil Science |
Need precise thermal analysis for your lab?
KINTEK's muffle furnaces provide the controlled, high-temperature environment essential for accurate ash content, volatile matter, and LOI estimations. Our lab equipment ensures reliable, contamination-free results for your quality control and research needs.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Does casting change material properties? Understand the Microstructural Impact on Performance
- What are the parts of a muffle furnace? Uncover the Core Components for Precision Heating
- What is dry ashing? A Reliable Method for Analyzing Inorganic Composition
- What is the function of an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temp Processing
- What is a muffle furnace used for ash determination? Achieve Precise Inorganic Analysis



















