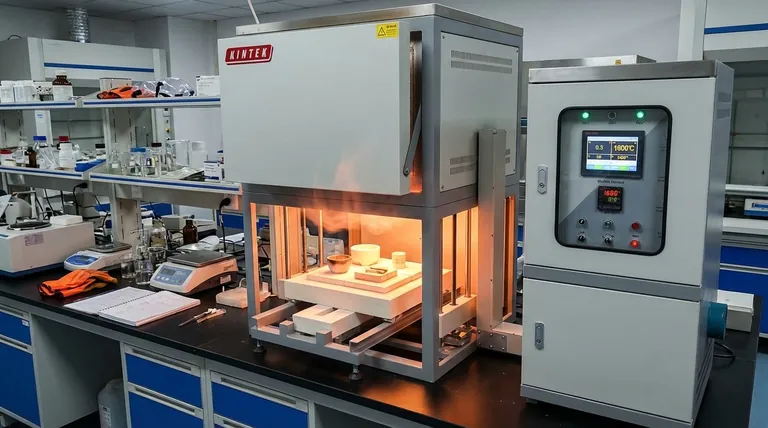
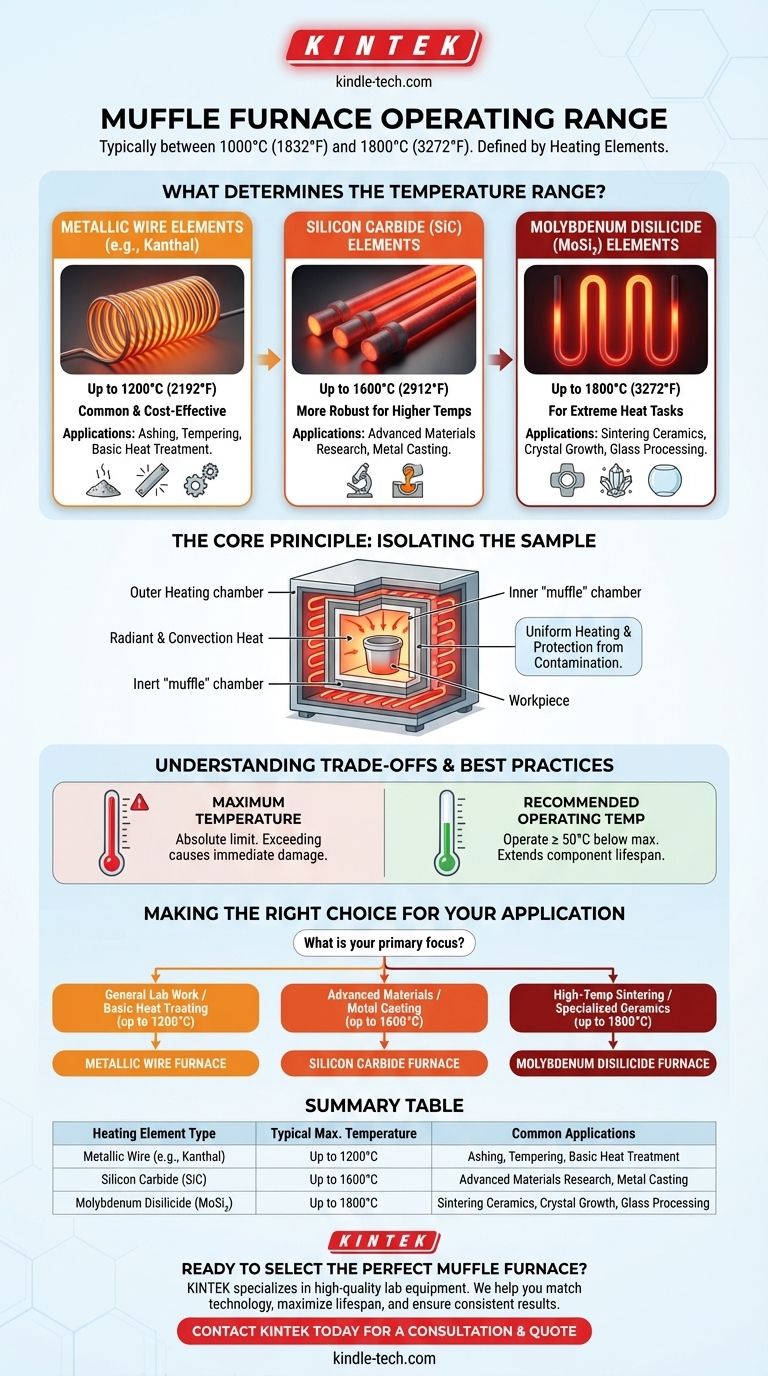
While there is no single answer, a muffle furnace's operating range is typically between 1000°C and 1800°C (1832°F to 3272°F). The specific maximum temperature is not an arbitrary limit but is directly determined by the type of heating elements used in its construction. This makes the selection of a furnace entirely dependent on the temperature requirements of your specific application.
A muffle furnace's temperature range is fundamentally limited by its heating elements. Common metallic elements reach up to 1200°C, while specialized materials like silicon carbide and molybdenum disilicide are required to achieve higher temperatures of 1600°C and 1800°C, respectively.

What Determines a Muffle Furnace's Temperature Range?
The furnace's capabilities are not defined by its size or shape, but by the physical limits of its core components. The heating elements are the primary factor dictating the achievable temperature.
The Role of the Heating Element
Heating elements are resistors that convert electrical energy into heat. Different materials have different melting points and resistance to high-temperature degradation, which sets the furnace's operational ceiling.
Common Metallic Wire Elements (~1000°C - 1200°C)
The most common and cost-effective muffle furnaces use heating elements made of metallic wire, such as Kanthal (an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy). These are ideal for a wide range of general-purpose applications like ashing, tempering, and basic metal heat treatment.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements (Up to 1600°C)
For processes requiring higher temperatures, such as advanced materials research or certain metal casting applications, furnaces employ silicon carbide heating elements. These are more robust and can reliably operate at significantly higher temperatures than standard metallic wires.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements (Up to 1800°C)
At the highest end of the spectrum are furnaces with molybdenum disilicide elements. These are used for highly demanding tasks like sintering advanced ceramics, growing crystals, or specialized glass processing that require extreme heat. Some specialized units may even exceed this range.
The Core Principle: Isolating the Sample
The term "muffle" refers to the core design principle of the furnace: a separated, inert inner chamber that isolates the material being heated.
A Chamber Within a Chamber
A muffle furnace contains an inner chamber (the "muffle") where the workpiece is placed. The heating elements heat this chamber from the outside.
Protection from Contamination
This design is critical because it separates the workpiece from any byproducts of the heat source. In older fuel-fired furnaces, this prevented contamination from combustion. In modern electric furnaces, it isolates the material from direct contact with the heating elements, ensuring purity and preventing electrical interference.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
The insulated muffle chamber allows for homogenous heating of the workpiece. Heat is transferred through a combination of radiant and convection methods, ensuring the entire sample reaches a uniform and stable temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Simply knowing the maximum temperature is not enough for effective and safe operation. The relationship between performance and component longevity is a critical trade-off.
Maximum vs. Recommended Operating Temperature
The "rated temperature" of a furnace is its absolute maximum limit. Exceeding this temperature can cause immediate and irreversible damage to the heating elements.
The Impact on Component Lifespan
For optimal longevity, it is best practice to operate a furnace at least 50°C below its maximum rated temperature. Consistently pushing the furnace to its absolute limit will significantly shorten the life of the heating elements, leading to more frequent and costly maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching its heating element technology to your specific temperature needs.
- If your primary focus is general lab work or basic heat treating (up to 1200°C): A furnace with standard metallic wire elements is the most cost-effective and common choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or specific metal casting (up to 1600°C): You will require a furnace equipped with silicon carbide heating elements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or specialized ceramics (up to 1800°C): Your work demands a high-performance furnace with molybdenum disilicide elements.
Understanding the direct link between heating elements and temperature empowers you to select the precise tool for your specific high-temperature task.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (e.g., Kanthal) | Up to 1200°C | Ashing, tempering, basic heat treatment |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Advanced materials research, metal casting |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C | Sintering ceramics, crystal growth, glass processing |
Ready to Select the Perfect Muffle Furnace?
Choosing the right furnace with the correct heating elements is critical for your lab's success and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces tailored to your specific temperature requirements and applications.
We help you:
- Match the right technology to your process needs, from basic ashing to advanced sintering.
- Maximize equipment lifespan by selecting a furnace that operates optimally within your required range.
- Ensure consistent, reliable results with equipment designed for precision and durability.
Don't compromise on your high-temperature processes. Let our experts guide you to the ideal solution.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the refractory material in a muffle furnace? Discover the High-Temperature Ceramic System
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of muffle furnace in soil laboratory? Essential for Accurate Soil Organic Matter Analysis
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method



















