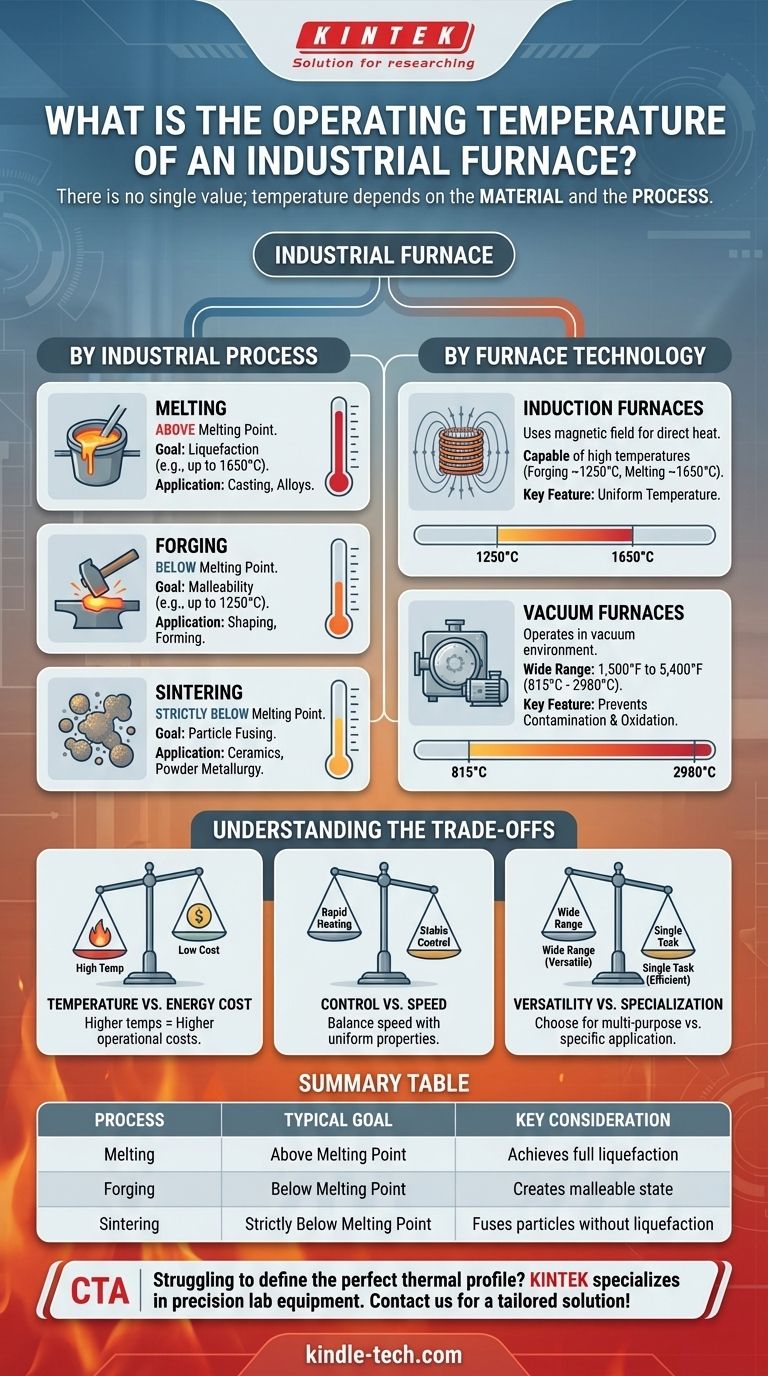
There is no single operating temperature for an industrial furnace; the required temperature is dictated entirely by the material being processed and the specific industrial application. While some systems operate at over 5,000°F (~2760°C), others are designed for much lower temperatures to achieve specific material transformations without melting. The type of furnace technology and the intended process are the two factors that define the operating range.
The operating temperature of an industrial furnace is not a fixed value but a critical parameter determined by two factors: the specific industrial process (like melting, forging, or sintering) and the underlying technology of the furnace itself (such as induction or vacuum).

How Industrial Processes Dictate Temperature
The primary factor determining a furnace's operating temperature is its purpose. The temperature must be precisely controlled to achieve a specific change in the material.
For Melting
To melt a material, the furnace must operate at a temperature above its melting point.
For example, an induction furnace used for melting can reach up to 1650°C (3002°F). This ensures the material becomes fully liquid, which is essential for casting and creating alloys.
For Forging
Forging requires making a material malleable and easy to shape without liquefying it. This means the temperature must be high, but remain below the melting point.
An induction furnace used for forging might operate at temperatures up to 1250°C (2282°F). This brings steel to a plastic state, allowing it to be shaped by force.
For Sintering
Sintering is a process used to create solid objects from powders, such as in ceramics or powder metallurgy. It requires heating the material to fuse the particles together.
Crucially, sintering furnaces must maintain temperatures strictly below the material's melting point. The goal is to bond the particles, not to liquefy the entire mass.
How Furnace Technology Determines Capability
Different types of furnaces are engineered to achieve different temperature ranges and heating characteristics, making them suitable for specific tasks.
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces use an alternating magnetic field to generate heat directly within the material.
This technology is capable of reaching very high temperatures for both forging (1250°C) and melting (1650°C). A key advantage is the "stirring effect" of the magnetic field, which promotes a highly uniform temperature throughout the material.
Vacuum Furnaces
Vacuum furnaces are highly versatile systems that can operate across a very wide temperature spectrum.
Their maximum operating temperatures can range from 1,500°F to 5,400°F (approximately 815°C to 2980°C). The vacuum environment prevents contamination and oxidation, making them ideal for processing high-performance alloys and reactive metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace and its operating temperature involves balancing competing priorities. An ideal furnace minimizes material waste and production cost, but this requires careful consideration of the trade-offs.
Temperature vs. Energy Cost
Higher operating temperatures demand significantly more energy. Pushing a furnace to its maximum thermal capacity dramatically increases operational costs, affecting the final cost of the manufactured product.
Control vs. Speed
While a fast heating speed is often desirable for production efficiency, it can come at the cost of control. The best systems offer both rapid heating and stable, uniform temperature control, preventing thermal shock or inconsistent material properties.
Versatility vs. Specialization
A vacuum furnace with a wide temperature range offers great versatility for a research lab or a facility handling many different processes. However, a furnace designed for a single task, like sintering, will often be more efficient and precise for that specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines the required thermal profile. To select the correct furnace and operating temperature, you must first define the intended material transformation.
- If your primary focus is melting materials: You need a furnace, like an induction furnace, capable of exceeding the material's melting point, often up to 1650°C.
- If your primary focus is shaping or forging: Your goal is malleability, requiring a furnace that can precisely hold temperatures below melting, such as 1250°C for steel.
- If your primary focus is sintering powders: You must select a system that guarantees temperatures are kept strictly below the material's melting point to fuse particles without liquefaction.
Ultimately, selecting the right industrial furnace is about matching the equipment's thermal capabilities to the precise needs of your material and process.
Summary Table:
| Process | Typical Temperature Goal | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Melting | Above material melting point (e.g., up to 1650°C) | Achieves full liquefaction for casting/alloys |
| Forging | Below material melting point (e.g., up to 1250°C) | Creates malleable, plastic state for shaping |
| Sintering | Strictly below material melting point | Fuses powder particles without liquefaction |
Struggling to define the perfect thermal profile for your material process? The right furnace temperature is critical for efficiency, quality, and cost. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including industrial furnaces for melting, forging, and sintering. Our experts will help you select the ideal system to match your material's exact requirements, ensuring optimal performance and control. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a tailored solution! Reach out via our contact form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















