At its most fundamental level, a vacuum furnace consists of three primary components: a hermetically sealed chamber, a vacuum system to remove the air, and a heating system to treat the material inside. These parts work together to create a highly controlled, oxygen-free environment, which is essential for processes like brazing, sintering, and heat-treating sensitive metals without causing surface reactions like oxidation.
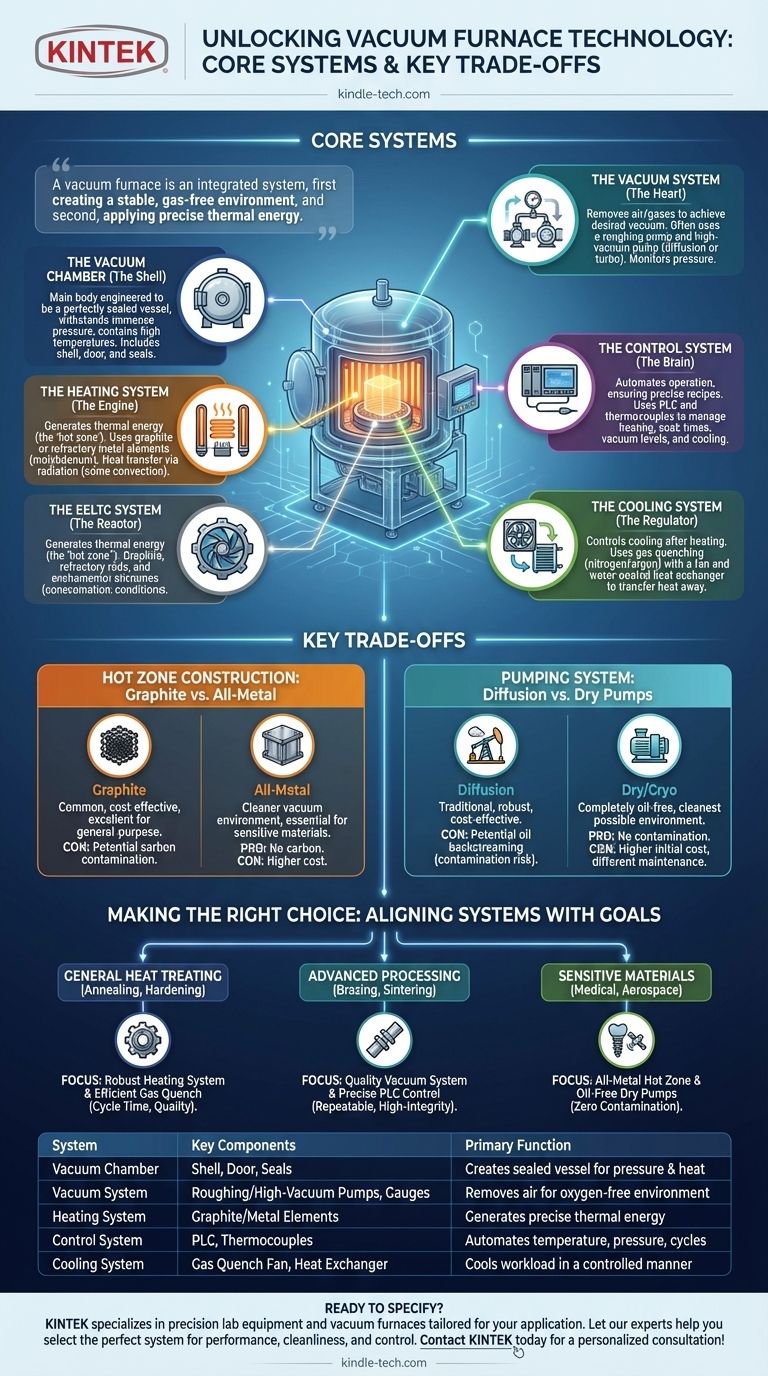
A vacuum furnace isn't just a collection of parts, but an integrated system designed to perform two critical functions in sequence: first, to create a stable, gas-free environment (a vacuum), and second, to apply precise thermal energy within that environment.

The Core Systems of a Vacuum Furnace
To understand how a vacuum furnace operates, it's best to think of it in terms of its functional systems. Each system is responsible for one aspect of creating the perfect processing conditions.
The Vacuum Chamber (The Shell)
The vacuum chamber is the main furnace body, engineered to be a perfectly sealed vessel. It includes the furnace shell, the door or furnace cover, and high-integrity seals.
This chamber must withstand immense external atmospheric pressure when the internal vacuum is created, all while containing the high temperatures generated by the heating system.
The Vacuum System (The Heart)
This is the system that gives the furnace its name. It is responsible for removing air and other gases from the chamber to achieve the desired level of vacuum.
It typically consists of a series of pumps—often a "roughing pump" to remove the bulk of the air, followed by a "high-vacuum pump" (like a diffusion or turbomolecular pump) to achieve lower pressures. A measurement system with vacuum gauges monitors the pressure throughout the process.
The Heating System (The Engine)
Located inside the chamber, the heating system generates the thermal energy required for the process. This system is often called the "hot zone."
Heating elements are typically made of graphite or refractory metals like molybdenum. The heat is transferred to the workload primarily through radiation, though some furnaces use fans to circulate inert gas (convection) for more uniform heating.
The Control System (The Brain)
The control system is the central nervous system that automates and manages the furnace's operation. It ensures the process follows a precise, pre-programmed recipe.
This system is composed of thermocouples for temperature measurement and a programmable logic controller (PLC) or computer for temperature and vacuum control. It manages heating rates, soak times, vacuum levels, and cooling cycles with high precision.
The Cooling System (The Regulator)
Once the heating cycle is complete, the workload must be cooled in a controlled manner. This is the job of the cooling system.
Most modern vacuum furnaces use a gas quenching system. An inert gas like nitrogen or argon is rapidly circulated through the hot zone by a high-power fan, transferring heat away from the parts and to a water-cooled heat exchanger.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The specific components used in a vacuum furnace are chosen based on its intended application, leading to important trade-offs in performance, cost, and capability.
Hot Zone Construction: Graphite vs. All-Metal
The materials used for the heating elements and insulation inside the furnace are a critical choice.
Graphite-based hot zones are common, cost-effective, and excellent for general-purpose heat treating. However, they can be a source of carbon, which may be undesirable for certain materials.
All-metal hot zones, built from molybdenum or tungsten, provide a much cleaner vacuum environment. They are essential for processing highly sensitive or reactive materials like medical implants and aerospace components but come at a higher cost.
Pumping System: Diffusion vs. Dry Pumps
The type of high-vacuum pump used impacts cleanliness and maintenance.
Oil diffusion pumps are a traditional, robust, and cost-effective technology for creating a high vacuum. Their primary drawback is the potential for oil vapor to "backstream" into the furnace chamber, which can contaminate sensitive parts.
Cryopumps or dry pumps offer a completely oil-free alternative, ensuring the cleanest possible environment. This is critical for medical and electronics applications, but these pumps have a higher initial cost and different maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these systems allows you to evaluate a furnace based on your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating (annealing, hardening): Pay closest attention to the robustness of the heating system and the efficiency of the gas quench cooling system, as these dictate cycle time and part quality.
- If your primary focus is advanced processing (brazing, sintering): The quality of the vacuum system and the precision of the PLC control system are paramount for achieving repeatable, high-integrity results.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive materials (medical, aerospace): An all-metal hot zone and an oil-free dry pumping system are non-negotiable to prevent any possibility of contamination.
By breaking the furnace down into its functional systems, you can move past a simple list of parts and begin to understand the technology on a deeper, more practical level.
Summary Table:
| System | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Shell, Door, Seals | Creates a sealed vessel to withstand pressure and heat |
| Vacuum System | Roughing Pump, High-Vacuum Pump, Gauges | Removes air to create an oxygen-free environment |
| Heating System (Hot Zone) | Graphite or Metal Heating Elements | Generates precise thermal energy for processing |
| Control System | PLC, Thermocouples | Automates and manages temperature, pressure, and cycle times |
| Cooling System | Gas Quench Fan, Heat Exchanger | Cools the workload in a controlled manner after heating |
Ready to specify the right vacuum furnace for your application?
The specific configuration of these parts—whether you need a robust graphite hot zone for general heat treating or a clean, all-metal system for sensitive aerospace components—directly impacts your results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision vacuum furnaces tailored for brazing, sintering, and heat-treating.
Let our experts help you select a system that delivers the performance, cleanliness, and control your process demands. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space



















