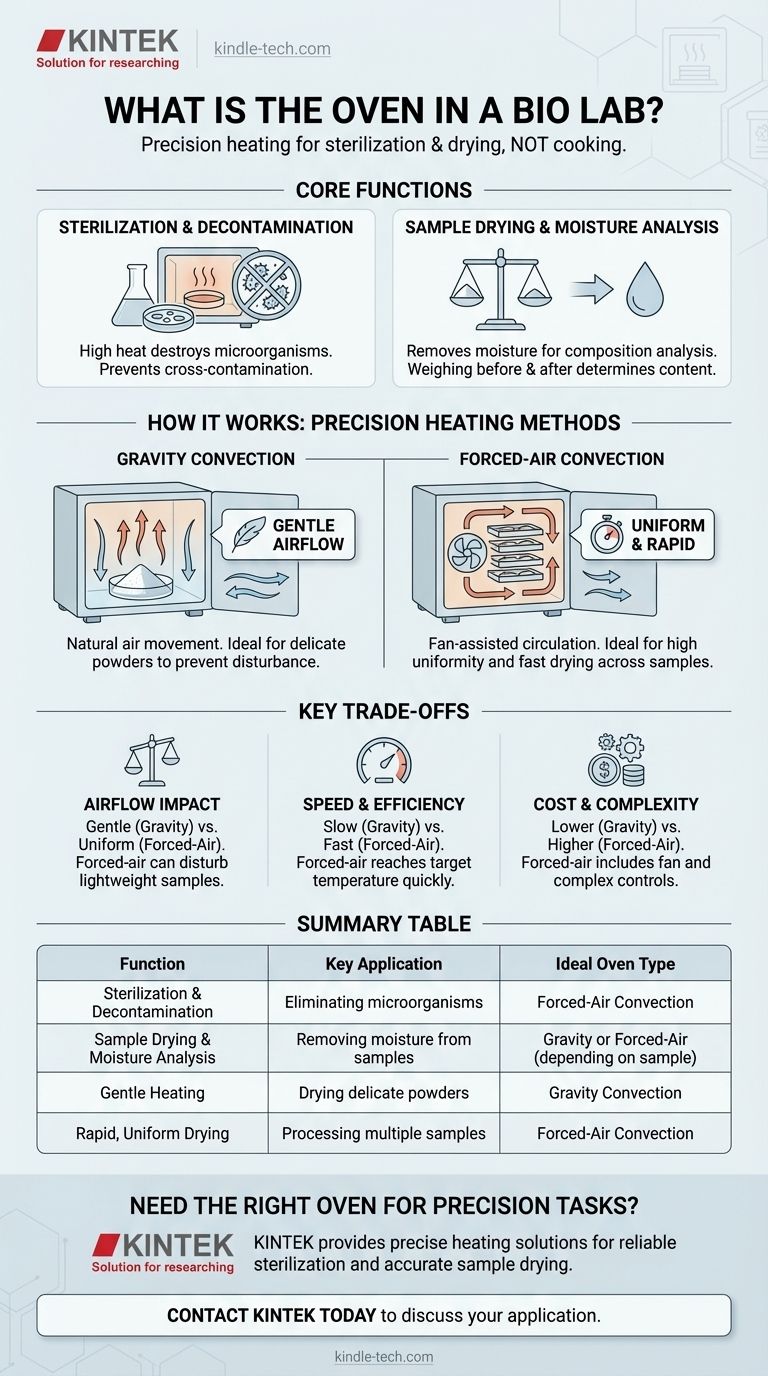
In a biology laboratory, an oven is a precision heating instrument used for high-temperature applications that require controlled and uniform thermal environments. Unlike a standard kitchen oven, a lab oven is engineered for specific scientific tasks such as sterilization, decontamination, and precisely drying biological or environmental samples.
A lab oven is not for cooking, but for creating a highly controlled, high-heat environment essential for sterilizing equipment and accurately removing moisture from scientific samples.

The Core Functions of a Laboratory Oven
A lab oven’s value comes from its ability to maintain precise and consistent temperatures, which is critical for repeatable scientific outcomes. Its applications generally fall into two primary categories.
Sterilization and Decontamination
The high heat inside a lab oven is used to destroy microorganisms and remove biological contaminants. This is a fundamental step in ensuring that lab equipment and glassware are sterile before an experiment begins, preventing cross-contamination that could invalidate results.
Sample Drying and Moisture Analysis
In biological and environmental studies, determining the moisture content of a sample is often a critical data point. A lab oven is used to dry out samples, such as soil or biological tissue, at a controlled temperature until all moisture has evaporated.
By weighing the sample before and after the drying process, a researcher can accurately calculate its initial moisture content. This is essential for understanding material composition and properties.
How Lab Ovens Achieve Precision Heating
The method of heat circulation is the key differentiator among lab ovens and dictates their ideal use case. The two most common types are gravity convection and forced-air convection.
Gravity Convection Ovens
These ovens rely on the natural movement of air. As the air at the bottom of the chamber is heated, it becomes less dense and rises. As it cools near the top, it falls, creating a gentle, continuous airflow.
This method is simple and effective for applications where a forceful airflow could disturb the sample, such as when drying fine powders.
Forced-Air (Mechanical) Convection Ovens
These ovens incorporate a fan to actively circulate the hot air throughout the chamber. This forced circulation creates a highly uniform temperature distribution and speeds up the heating and drying processes significantly.
This makes them ideal for applications requiring tight temperature uniformity across multiple samples or when rapid drying is necessary.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing between a gravity or forced-air oven depends entirely on the specific requirements of your experiment. Neither is universally superior.
The Problem of Airflow
The primary trade-off is between gentle heating and temperature uniformity. The fan in a forced-air oven ensures excellent uniformity but can disturb lightweight samples, potentially causing sample loss or cross-contamination between open containers.
Heating Speed and Efficiency
Gravity convection ovens heat up more slowly and can have greater temperature variations within the chamber. Forced-air ovens are faster and more efficient, bringing samples to the target temperature quickly and maintaining consistency throughout the space.
Cost and Complexity
Due to the addition of a fan and more complex airflow controls, forced-air ovens are typically more expensive and complex than their gravity convection counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct oven is critical for achieving accurate and reliable results.
- If your primary focus is drying delicate powders or samples that are sensitive to airflow: A gravity convection oven is the appropriate choice to prevent sample disturbance.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest temperature uniformity for multiple samples or require rapid drying: A forced-air convection oven will provide the speed and consistency you need.
Ultimately, the laboratory oven is a fundamental tool that enables researchers to control the critical variable of temperature with scientific precision.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Application | Ideal Oven Type |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization & Decontamination | Eliminating microorganisms from equipment | Forced-Air Convection |
| Sample Drying & Moisture Analysis | Removing moisture from biological/environmental samples | Gravity or Forced-Air (depending on sample) |
| Gentle Heating | Drying delicate powders or airflow-sensitive materials | Gravity Convection |
| Rapid, Uniform Drying | Processing multiple samples quickly with high consistency | Forced-Air Convection |
Need the Right Oven for Your Lab's Precision Tasks?
Choosing between a gravity convection and forced-air oven is critical for your experiment's success. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing the precise heating solutions your biology lab requires for reliable sterilization and accurate sample drying.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the ideal lab oven for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in W18Cr4V steel sample preparation? Expert Microstructural Drying Guide
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep



















