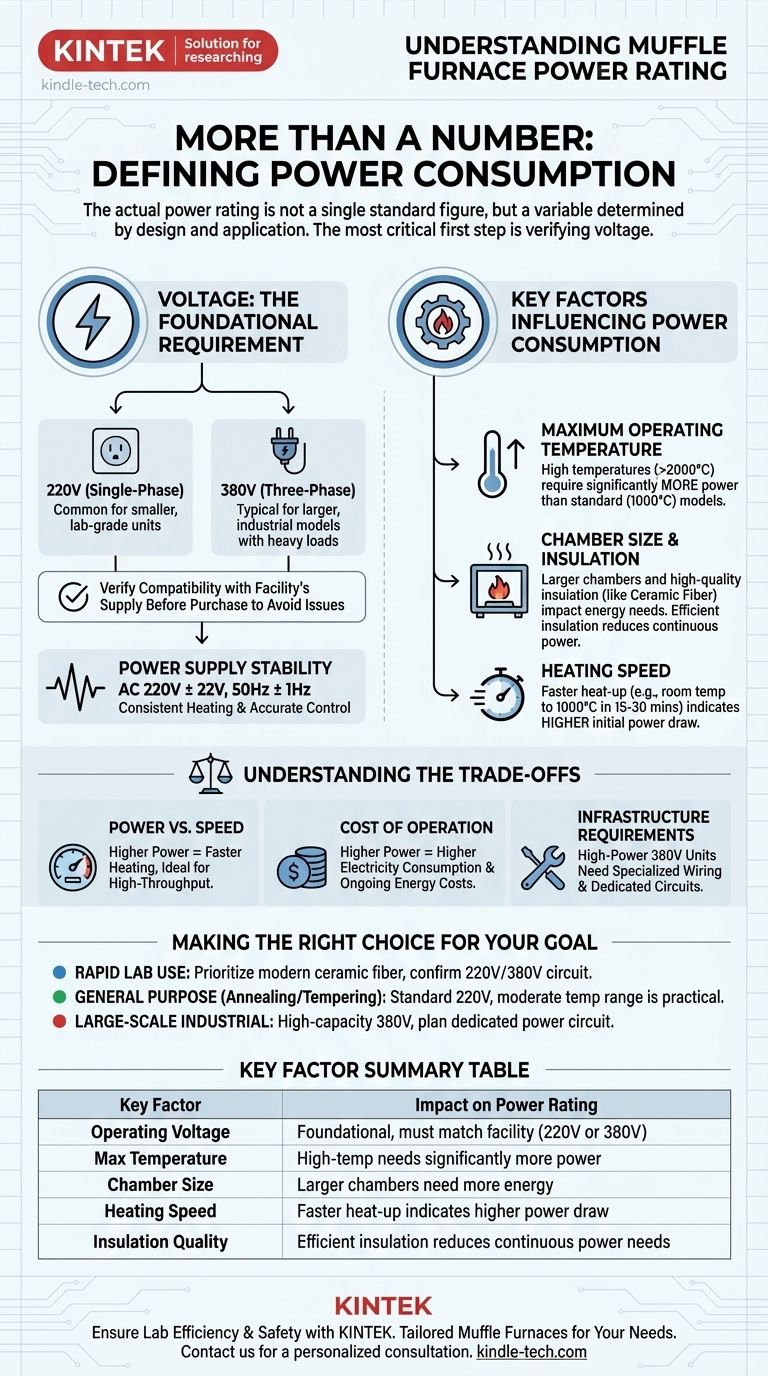
Determining the power rating of a muffle furnace is not about finding a single, standard number. The actual power consumption varies widely, but the most critical specification to verify first is the operating voltage, which is typically either 220V or 380V. This ensures the furnace is compatible with your facility's electrical supply, which is the foundational requirement for its operation.
The most important step is not to find a generic power rating, but to first confirm the required voltage (220V or 380V) for your specific model. The actual power consumption in kilowatts (kW) is a direct function of the furnace's size, maximum temperature, and heating technology.

Why Voltage is the First Specification to Check
Before you can understand the power draw in watts or kilowatts, you must ensure the furnace can connect to your power source. This is a fundamental step that precedes all other considerations.
The 220V vs. 380V Decision
Muffle furnaces are manufactured for different electrical systems. Smaller, laboratory-grade units often run on a standard 220V single-phase supply.
Larger, industrial models designed for heavy loads and higher temperatures typically require a more robust 380V three-phase supply.
Verifying this requirement before purchase is essential to prevent significant compatibility issues, installation delays, and potential damage.
Power Supply Stability
Beyond the correct voltage, a stable power source is crucial for performance and safety. The supply should conform to the manufacturer's specifications, often cited as AC 220V ± 22V with a frequency of 50Hz ± 1Hz, to ensure consistent heating and accurate temperature control.
Key Factors That Determine Power Consumption
Once voltage compatibility is confirmed, the actual power rating is determined by the furnace's design and intended application. Several key factors directly influence how much energy the unit consumes.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The single largest factor in a furnace's power rating is its maximum temperature. A furnace designed to reach over 2000°C will require substantially more power than a standard unit that operates around 1000°C.
Chamber Size and Insulation
A larger internal chamber, or muffle, requires more energy to heat its volume. The quality of the refractory material lining the chamber is also critical. High-efficiency insulation, like ceramic fiber, prevents heat loss and allows the furnace to maintain temperature with less continuous power.
Heating Speed
The speed at which a furnace reaches its set temperature is directly related to its power. Models with modern ceramic fiber insulation can heat from room temperature to 1000°C in as little as 15 to 30 minutes, which indicates a higher power draw during the initial heat-up phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a muffle furnace involves balancing performance needs with practical constraints. Higher power is not always better; it comes with clear trade-offs.
Power vs. Speed
A furnace with a higher power rating will generally reach its target temperature much faster. This is ideal for high-throughput environments but may be unnecessary for applications where slower, controlled heating is acceptable.
Cost of Operation
A higher power rating directly translates into higher electricity consumption. For continuous or frequent operation, the ongoing energy cost of a high-power furnace can be a significant factor in its total cost of ownership.
Infrastructure Requirements
A powerful 380V industrial furnace cannot be plugged into a standard wall outlet. It requires specialized wiring and a dedicated circuit installed by a qualified electrician, which can add significant cost and complexity to its installation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate furnace, align its electrical specifications with your primary application.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating for frequent laboratory use: Prioritize a modern ceramic fiber furnace and confirm your facility has the required 220V or 380V circuit to support its faster heating cycle.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose tasks like annealing or tempering: A standard 220V model with a moderate temperature range is often the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial sintering or material testing: You will almost certainly need a high-capacity, 380V furnace, and planning for its dedicated power circuit is a critical first step.
By matching the furnace's voltage, size, and temperature capabilities to your specific goal, you ensure a safe, efficient, and effective installation.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Power Rating |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | Foundational: Must match your facility's supply (220V or 380V). |
| Max Temperature | High-temp furnaces (e.g., >2000°C) require significantly more power. |
| Chamber Size | Larger chambers need more energy to heat the greater volume. |
| Heating Speed | Faster heat-up times (e.g., 15-30 min to 1000°C) indicate higher power draw. |
| Insulation Quality | Efficient insulation (e.g., ceramic fiber) reduces continuous power needs. |
Ensure Your Lab's Efficiency and Safety with the Right Muffle Furnace
Choosing a muffle furnace with the correct power rating and voltage is critical for your lab's productivity, safety, and operational costs. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces tailored to your specific voltage requirements (220V or 380V) and application needs—from rapid-heating ceramic fiber models for frequent use to robust industrial units for large-scale testing.
Our experts will help you navigate the specifications to find a furnace that delivers precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and reliable performance for your laboratory processes like annealing, sintering, or material testing.
Don't risk compatibility issues or subpar performance. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure your new muffle furnace is a perfect, powerful fit for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment affect surface roughness? Minimize Surface Degradation for Precision Parts
- What is furnace lining? The Engineered System Protecting Your High-Temperature Processes
- What are the safety precautions for muffle furnace? A Complete Guide to Safe High-Temperature Operation
- How do you choose calcination temperature? A Guide to Optimizing Material Properties
- What is the critical point of heat treatment? Master the Key to Steel Transformation



















