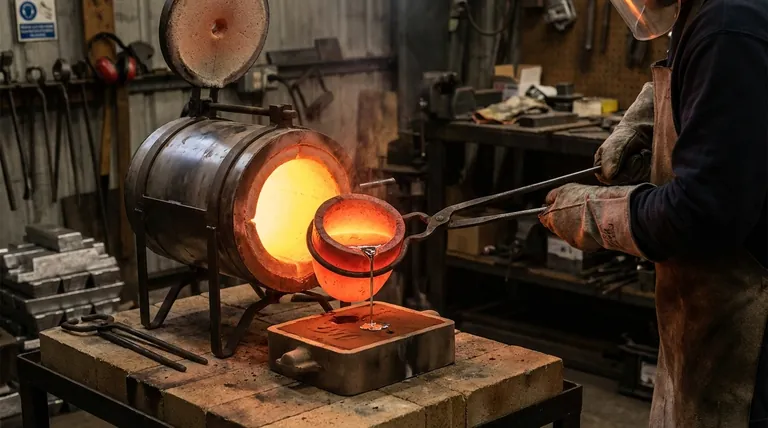
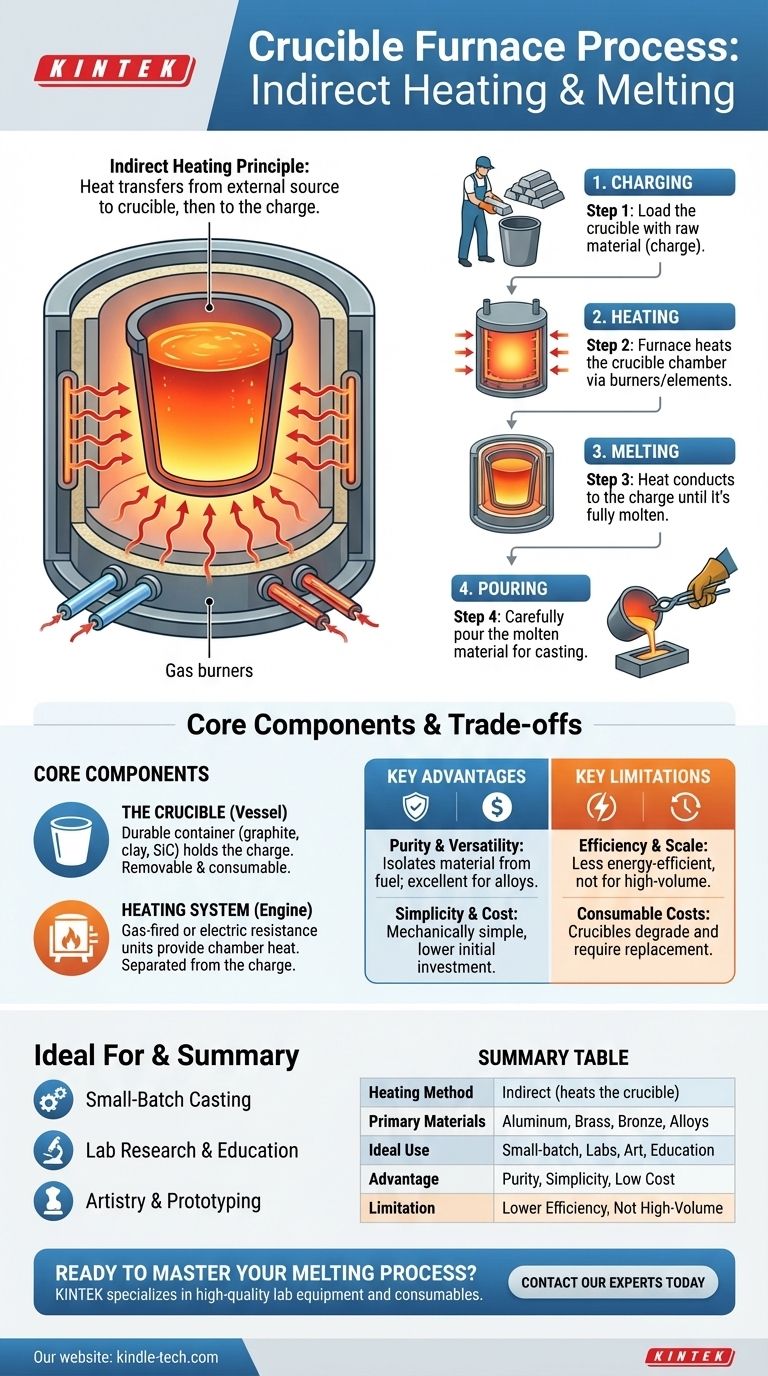
At its core, the crucible furnace process is a straightforward method of indirect heating. A material, typically metal, is placed inside a durable container called a crucible. The furnace then heats the outside of this crucible, transferring thermal energy through its walls until the material inside melts and is ready to be poured.
A crucible furnace operates on the simple principle of heating a container to melt its contents. This method's strength is its versatility for small-scale work, but its indirect heating approach also defines its limitations in terms of industrial efficiency and scale.

Deconstructing the Core Components
To understand the process, you must first understand its two essential parts. The furnace is a system built around separating the heat source from the material being melted.
The Crucible: The Heart of the Furnace
The crucible is the vessel that holds the charge, which is the term for the raw material to be melted. It is not part of the furnace itself but is a removable, consumable container.
These are made from refractory materials like graphite, clay, or silicon carbide that can withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock without contaminating the molten metal.
The Heating System: The Engine
The furnace provides a super-heated chamber for the crucible. Heat is generated by an external source that never directly touches the material being melted.
The two primary types are gas-fired furnaces, which use powerful burners, and electric resistance furnaces, which use heating elements similar to a kiln. Both are designed to heat the chamber, which then radiates heat onto the crucible.
The Step-by-Step Melting Process
The operational workflow is simple, which is one of its primary advantages. Each step is a distinct phase of transforming a solid into a liquid.
Step 1: Charging the Crucible
The process begins by "charging" the crucible, which means filling it with the solid material (e.g., aluminum ingots, scrap brass). The charged crucible is then placed into the center of the cold furnace.
Step 2: Applying Heat
The furnace is sealed, and the heating system is activated. The burners or electric elements heat the internal chamber of the furnace. This heat is transferred to the crucible's exterior walls through radiation and convection.
Step 3: Reaching a Molten State
As the crucible's temperature rises, it conducts heat inward, raising the temperature of the charge. The furnace temperature is carefully managed until the material inside becomes fully molten. The operator can visually inspect the melt or rely on a temperature control system.
Step 4: Pouring and Casting
Once the material is fully liquid and at the correct pouring temperature, the furnace is turned off. The glowing-hot crucible is carefully lifted out of the furnace with specialized tongs and then used to pour the molten material into a mold.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The simplicity of the crucible furnace is both its greatest strength and its primary weakness. Choosing one depends entirely on the requirements of your task.
Key Advantage: Purity and Versatility
Because the material is isolated within the crucible, it is protected from direct contact with the heat source or combustion byproducts. This makes it excellent for melting a wide range of materials, including aluminum, brass, and bronze, and for creating specific alloys where purity is key.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
Crucible furnaces are among the oldest and most mechanically simple furnace designs. This makes them relatively inexpensive to purchase and operate, especially for small workshops, laboratories, or hobbyist foundries.
Key Limitation: Efficiency and Scale
Indirect heating is inherently less energy-efficient than direct heating methods (like an induction furnace). A significant amount of energy is used to heat the furnace chamber and the crucible itself, not just the metal. This inefficiency makes them uneconomical for large-scale, high-volume industrial production.
Key Limitation: Consumable Costs
Crucibles are durable but not permanent. They are subject to intense thermal shock and will eventually degrade or crack, requiring replacement. This represents a recurring operational cost that must be factored in.
Is a Crucible Furnace Right for Your Goal?
To make the right choice, align the technology's capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is small-batch metal casting, artistry, or lab research: The crucible furnace offers an ideal balance of versatility, precise control, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is learning fundamental foundry principles: The crucible furnace provides a clear, hands-on demonstration of the core concepts of melting and casting.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, industrial-scale melting: You should investigate more energy-efficient direct-heating technologies like induction or arc furnaces.
Understanding this fundamental process empowers you to select the right tool for your specific melting task.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Crucible Furnace Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (heats the crucible container) |
| Primary Materials Melted | Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Alloys |
| Ideal For | Small-batch casting, art, labs, education |
| Key Advantage | Material purity, simplicity, low cost |
| Key Limitation | Lower energy efficiency, not for high-volume |
Ready to Master Your Melting Process?
Whether you're setting up a small foundry, advancing lab research, or creating intricate metal art, having the right equipment is crucial. The crucible furnace is a perfect starting point for its simplicity and versatility.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable crucibles and reliable furnace systems designed to meet the precise demands of laboratories, workshops, and educational institutions.
Let us help you achieve precise, pure melts every time.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss your specific needs and find the ideal crucible furnace solution for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are alumina crucibles selected for wood-plastic composite tests? Ensure Precision at 1000°C
- Why are zirconia crucibles preferred for high-temperature Ni3Al melting? Ensure Purity with Specialized Refractories
- What are most crucibles made of? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Selection
- Why is the design of laboratory-grade ceramic crucibles critical when determining the volatile matter content of flax straw?
- Why are high-temperature crucibles indispensable for metal passivation? Secure Your Laboratory Process Integrity
- What technical properties are required for crucibles used in high-temperature vacuum distillation? | KINTEK Solutions
- Do you need to heat the clean crucible before using it? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Process Accuracy
- How much heat can a crucible take? Choosing the Right Material for Your Melting Application



















