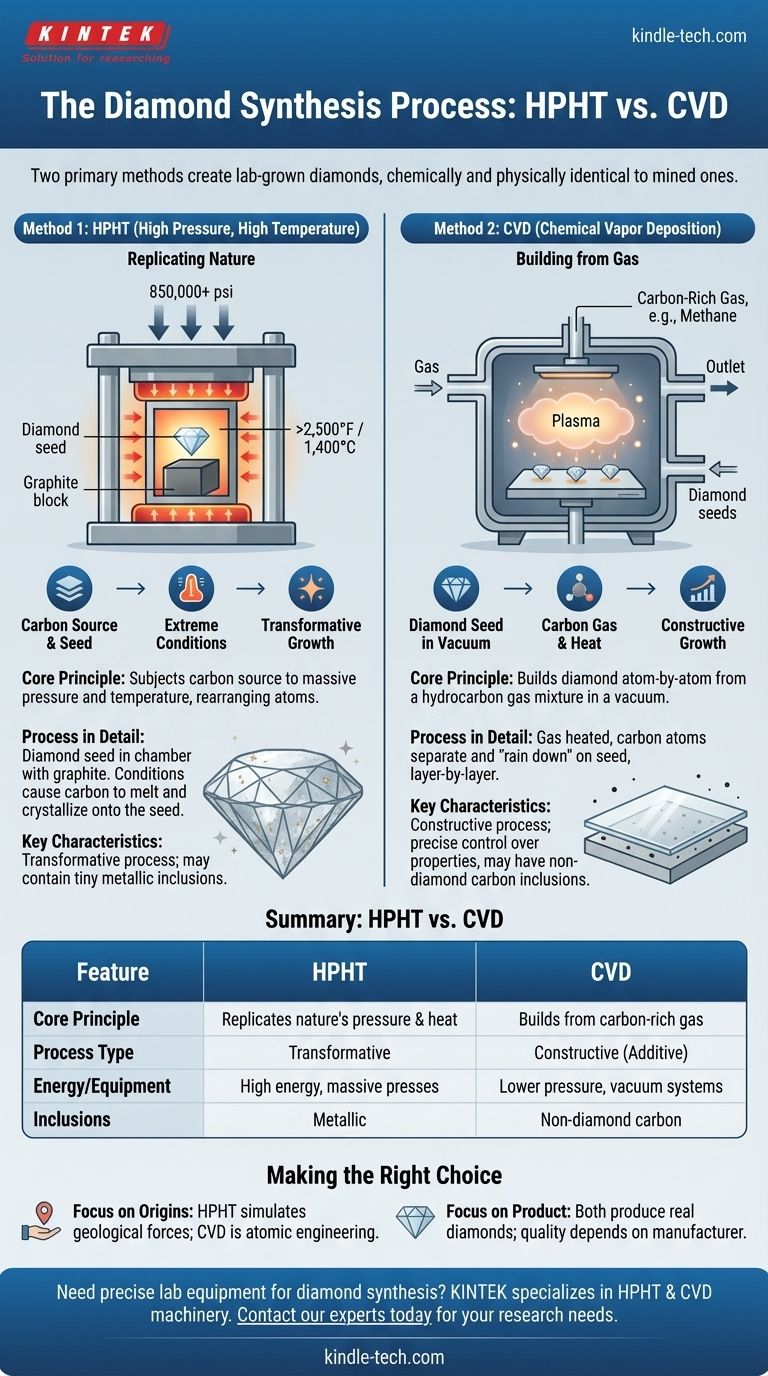
There is no single process for making diamonds. Instead, two primary industrial methods are used to create lab-grown diamonds: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Both processes result in diamonds that are chemically and physically identical to those mined from the earth.
The core distinction lies in their approach: HPHT mimics the intense, crushing force of nature that forms diamonds deep within the Earth, while CVD systematically builds a diamond layer by layer from a carbon-rich gas.

Method 1: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) – Replicating Nature
The HPHT method is the original process for creating diamonds and is engineered to replicate the natural conditions found in the Earth's mantle.
The Core Principle
This process subjects a carbon source to enormous pressure and extremely high temperatures, forcing the carbon atoms to rearrange into the crystal lattice structure of a diamond.
The Process in Detail
A small, natural diamond fragment, known as a diamond seed, is placed in a chamber with a pure carbon source, like graphite.
The chamber is then subjected to pressures exceeding 850,000 pounds per square inch and temperatures over 2,500° F (1,400° C).
Under these extreme conditions, the carbon source melts and dissolves, then crystallizes onto the diamond seed, growing into a larger, rough diamond.
Method 2: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) – Building from Gas
The CVD method is a more recent innovation that grows diamonds in a completely different environment, moving away from brute force and toward atomic precision.
The Core Principle
CVD involves growing a diamond from a hydrocarbon gas mixture. It is fundamentally an additive process, building the diamond one atomic layer at a time.
The Process in Detail
A diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is then filled with a mixture of carbon-rich gases, such as methane.
This gas is heated to a high temperature, causing the carbon atoms to separate from their molecules. These free carbon atoms then "rain down" and bond to the diamond seed, slowly building up the crystal structure.
Key Advantages of CVD
The CVD process is noted for its flexibility. It allows for precise control over the chemical impurities and ultimate properties of the diamond, and it can be used to grow diamond films over large surface areas for industrial applications.
Understanding the Key Differences and Trade-offs
While both HPHT and CVD produce real diamonds, the processes themselves have distinct characteristics and implications for the final product.
Mimicking Nature vs. Atomic Construction
HPHT is a transformative process; it transforms one form of carbon (graphite) into another (diamond). CVD is a constructive process; it builds a diamond from individual atoms supplied by a gas.
Energy and Equipment
The HPHT method requires massive, complex presses capable of generating immense force, making it a highly energy-intensive process. CVD operates at much lower pressures, though it requires sophisticated vacuum and gas control systems.
Growth Patterns and Inclusions
Due to the different growth environments, HPHT and CVD diamonds can sometimes be distinguished by their growth patterns when examined by gemologists. HPHT diamonds may contain tiny metallic inclusions from the machinery, while CVD diamonds are more likely to have non-diamond carbon inclusions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these methods is less about choosing one over the other and more about appreciating the technology behind modern diamonds.
- If your primary focus is on the origins: Recognize that HPHT most closely simulates the geological forces of nature, while CVD represents a triumph of atomic-scale engineering.
- If your primary focus is on the final product: Know that both methods produce physically and chemically real diamonds, with the final quality depending entirely on the skill and precision of the manufacturer.
Ultimately, both HPHT and CVD are sophisticated engineering achievements that produce diamonds identical to their natural counterparts.
Summary Table:
| Process | Core Principle | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT | Replicates natural conditions with extreme heat and pressure. | Transformative process; may contain metallic inclusions. |
| CVD | Builds diamond layer-by-layer from a carbon-rich gas. | Constructive process; offers precise control over properties. |
Need precise, high-quality lab equipment for your diamond synthesis or material science research? KINTEK specializes in the advanced machinery and consumables required for both HPHT and CVD processes. Our expertise ensures you have the reliable tools needed for successful outcomes. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD better than CVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between thermal CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- How is PECVD different from CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















