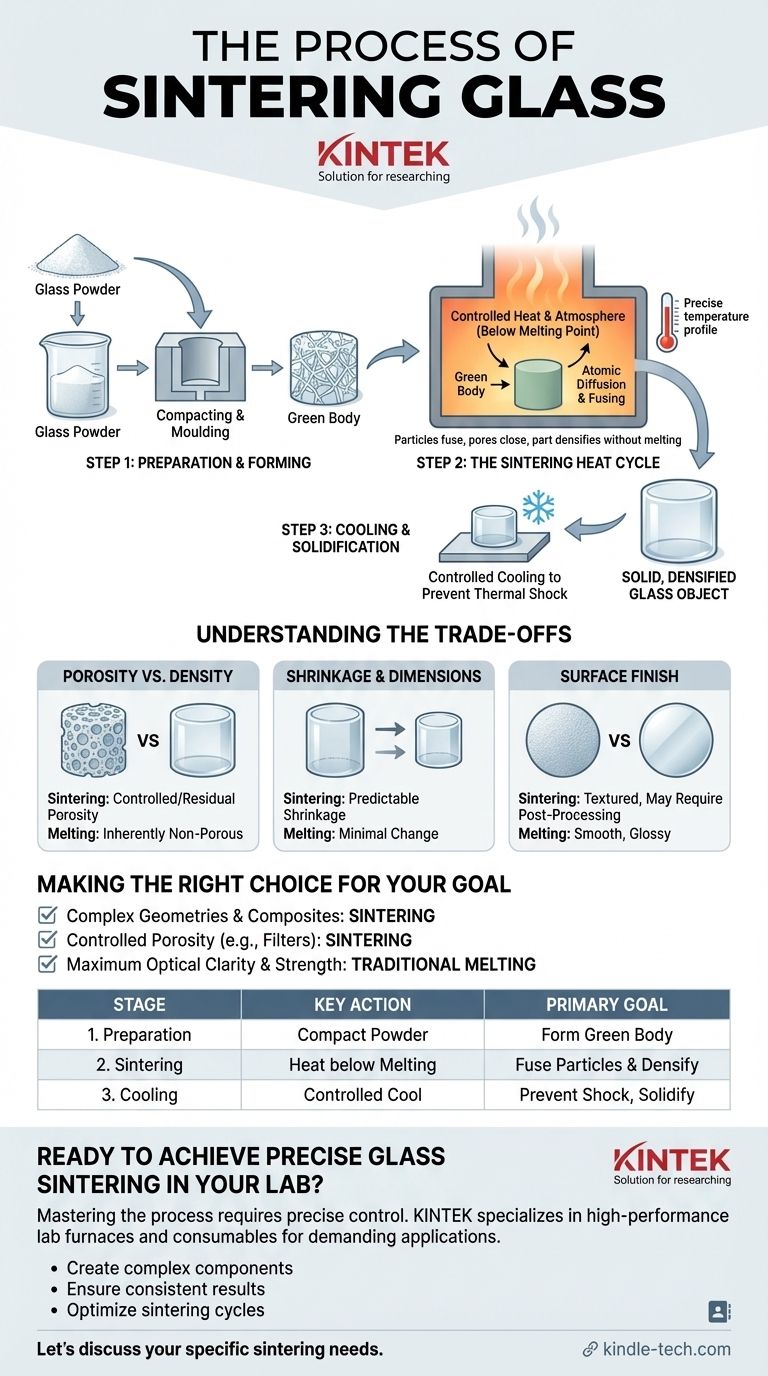
In essence, sintering glass is a manufacturing process that transforms fine glass powder into a solid, dense object. This is achieved by applying heat and pressure to fuse the powder particles together, critically, without melting the glass into a liquid state. The process allows for the creation of complex shapes and composite materials that would be difficult or impossible with traditional glass melting techniques.
The core principle of sintering is not to melt, but to fuse. By heating glass powder to a temperature below its melting point, individual particles bond at their contact points through atomic diffusion, gradually eliminating the spaces between them to form a unified, solid mass.

The Fundamental Goal: Fusing Without Melting
Sintering is a process of solid-state diffusion. It relies on precise control over temperature and pressure to achieve results that are fundamentally different from simple casting or blowing.
What Sintering Achieves
Instead of turning the material into a liquid, sintering provides just enough thermal energy for atoms to migrate across the boundaries of individual glass particles.
This migration causes the particles to stick and merge, reducing the overall surface area and eliminating the pores, or empty spaces, between them. The result is a densified, strengthened final part.
The Starting Material: Glass Powder
The process begins with finely powdered glass. The small particle size is crucial, as it creates a vast amount of surface area, which provides more contact points for the particles to bond during the heating phase.
Sometimes, coupling agents or binders are mixed with the powder to help the initial shape hold together before it is heated.
The Role of Temperature and Atmosphere
The temperature is carefully raised to a point where the glass becomes soft enough for atoms to move, but not so hot that it flows like a liquid.
This heating is often done in a controlled atmosphere, such as a nitrogen-hydrogen mix, to prevent unwanted chemical reactions and ensure the integrity of the final product.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
While specifics can vary, the sintering process for glass generally follows three primary stages, from a loose powder to a finished component.
Step 1: Preparation and Forming
First, the glass powder is compacted into the desired shape. This can be done by pressing it into a rigid mold, often made of a material like graphite that can withstand high temperatures.
This initial, fragile form is often called a "green body." It has the geometry of the final part but lacks the strength and density, which it will gain during the heating stage.
Step 2: The Sintering Heat Cycle
The green body is placed in a furnace and heated according to a precise temperature profile. As the temperature rises, any volatile binders are burned off.
The part is then held at the peak sintering temperature for a set duration. During this time, the particles fuse, pores are closed off, and the part shrinks and densifies into a solid whole.
Step 3: Cooling and Solidification
After the sintering is complete, the part is carefully cooled. This controlled cooling is critical to prevent thermal shock, which could cause cracks or internal stresses in the newly formed glass object.
The result is a single, solid piece with a microstructure and properties directly determined by the sintering cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful technique, but it involves trade-offs that are critical to understand when compared to traditional glass melting.
Porosity vs. Density
A primary challenge in sintering is achieving full densification. It is difficult to eliminate every single pore, and any residual porosity can impact the optical clarity and mechanical strength of the glass.
Melted glass, by contrast, is inherently non-porous.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Control
The process of eliminating pores inherently causes the entire part to shrink. This shrinkage must be accurately predicted and accounted for in the initial mold design to achieve precise final dimensions.
Uncontrolled or uneven shrinkage can lead to warped or unusable parts.
Surface Finish and Post-Processing
A sintered part may not have the perfectly smooth, glossy surface characteristic of molten glass.
Depending on the application, a sintered glass component may require subsequent machining or polishing with specialized diamond tools to meet final specifications for surface finish or dimensional accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding between sintering and traditional melting depends entirely on the specific properties and geometry you need to achieve in your final component.
- If your primary focus is creating complex geometries or embedding other materials: Sintering is the superior choice, as it allows you to form intricate shapes or fuse glass around metal parts in a mold.
- If your primary focus is achieving controlled porosity: Sintering is the only method that can produce a glass object with a specific, engineered level of porosity for applications like scientific filters.
- If your primary focus is maximum optical clarity and mechanical strength: Traditional melting and forming processes are generally better, as they produce a fully dense, non-porous material without the risk of residual voids.
Ultimately, sintering offers a powerful engineering tool to construct glass components with tailored microstructures and properties that are simply unattainable through conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Compacting glass powder into a mold | Form a 'green body' with the desired shape |
| 2. Sintering | Heating below melting point in a controlled furnace | Fuse particles via atomic diffusion to densify the part |
| 3. Cooling | Controlled cooling of the sintered part | Prevent thermal shock and solidify the final object |
| Trade-off | Sintering | Traditional Melting |
| Porosity | Can be controlled/engineered | Inherently non-porous |
| Geometry | Ideal for complex shapes & composites | Limited by flow and moldability |
| Shrinkage | Predictable shrinkage occurs | Minimal dimensional change |
Ready to Achieve Precise Glass Sintering in Your Lab?
Mastering the sintering process requires precise temperature control and reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for demanding applications like glass sintering.
We provide the tools and expertise to help you:
- Create complex glass components with tailored microstructures.
- Ensure consistent results with precise, uniform heating.
- Optimize your sintering cycles for maximum density and strength.
Let's discuss your specific sintering needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What temperature does molten steel melt? Understand the Melting Range, Not a Single Point
- What is the temperature of furnace exhaust? A Key Indicator of Efficiency and Safety
- What is the primary use of furnace in the chemical industry? Master Thermal Treatment for Material Transformation
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- What is the cooling rate of a muffle furnace? Understanding Its Slow, Passive Nature



















